脑损伤
-
Figure 4|Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), and protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis of cortical DEPs between the TBI and control mice.
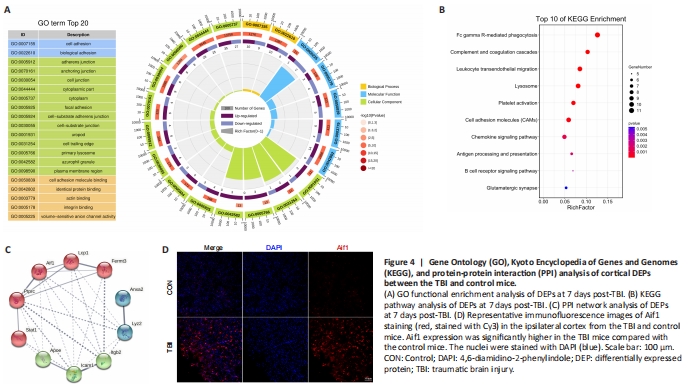
The enrichment analysis was performed to determine the function of the DEPs according to the three aspects mentioned above. The 20 most significantly enriched GO terms, consisting of two biological processes, five molecular functions, and thirteen cellular components, are shown in Figure 4A. Cell adhesion and biological adhesion were the most overrepresented biological processes. The significantly enriched molecular functions comprised cell adhesion molecule binding, identical protein binding, actin-binding, integrin binding, and volume-sensitive anion channel activity. As for the cellular component annotation, the significantly enriched terms included adherens junction, anchoring junction, cell junction, focal adhesion, cell-substrate adherens junction, cell-substrate junction, and more. GO enrichment analysis of the DEPs illustrated that these proteins are related to the immune system and inflammation-related processes.
A pathway represents the sequence of chemical reactions in the cell that causes a particular biological effect (Schmidt et al., 2014). KEGG pathway analysis demonstrated that the significantly enriched pathways in the CCI group were mainly involved in inflammation (Figure 4B). Among the identified KEGG pathways, Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis exhibited the highest statistical significance and the largest number of genes, including ASAP2, FCGR2, FCGR1, RAC2, and LYN. Additionally, inflammation-related pathways such as complement and coagulation cascades, leukocyte transendothelial migration, antigen processing and presentation, and the B cell receptor signaling pathway were significantly enriched and share proteins with altered expression levels such as RAC2, FCGR2, and LYN. Other noticeably enriched pathways included lysosome, platelet activation, cell adhesion molecules, chemokine signaling pathway, and glutamatergic synapse. Taken together, KEGG pathway analysis of the DEPs revealed that these proteins are mainly involved in inflammatory signaling pathways, which was consistent with the GO annotation results.
PPI networks are interaction networks that represent the high connectivity and complexity of hub proteins. PPI network analysis of the DEPs showed direct and indirect interconnections among 302 DEPs. Based on the generated PPI network, the ten most highly connected hub genes, which are the significant nodes in PPI networks and represent DEGs with a large number of associations with other DEGs (Chen et al., 2020a), were identified (Figure 4C). Among these hub genes, Lyz2 exhibited the most significant difference between the CCI and control groups. GO and KEGG analyses demonstrated that the hub genes, such as Itgb2, Icam1, Fermt3, Lcp1, Aif1, and Ptprc, were primarily associated with inflammatory processes and complement systems. Immunofluorescence analysis further confirmed the significant upregulation of Aif1 in the CCI group compared with the control group (Figure 4D).
Figure 6|Validation of the differential expression of the identified hub protein C3 in the cortex between TBI and control mice by immunofluorescence staining.
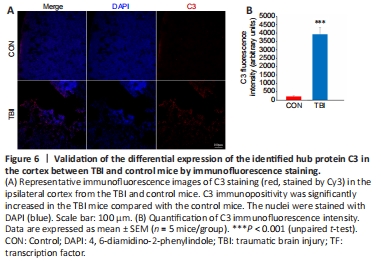
The functional analyses described above suggested that the complement cascade may exert a detrimental effect in the context of TBI. To confirm this finding, the expression of the hub protein complement C3, which is a central molecule in the complement cascade and the inflammatory response (Ricklin et al., 2016), was investigated by immunofluorescence. There was a highly statistically significant increase in total C3 protein immunopositivity in cortices from mice 7 days post-TBI compared with control mice (P < 0.001; Figure 6), which verified the bioinformatics-based functional analysis.
点击此处查看全文