神经退行性病
-
Figure 2|LTG alleviated synapse and nerve cell damage in the brains of APP/PS1 mice.
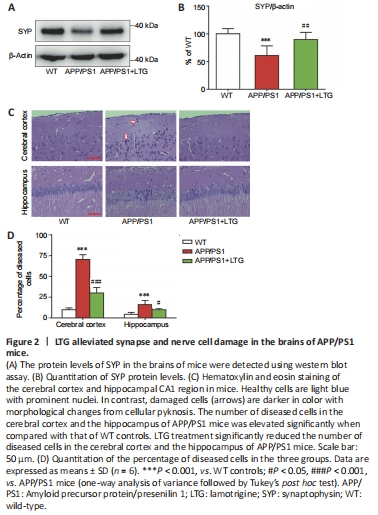
Western blots demonstrated that the levels of synaptophysin in the brains of APP/PS1 mice were lower than those in WT controls (P < 0.001), indicating obvious synaptic injury in the brains of APP/PS1 mice at 8 months of age (Figure 2A and B). LTG treatment reversed the decrease of synaptophysin in APP/PS1 mouse brains (P < 0.01), indicating that LTG treatment attenuated synaptic injury in the APP/PS1 mice.
H&E staining was performed to determine the protective effect of LTG on nerve cells in the brains of APP/PS1 mice. The percentage of diseased cells in the cerebral cortex and the hippocampal CA1 region of APP/PS1 mice was elevated significantly when compared with that of WT controls (P < 0.001), indicating marked damage of nerve cells in the brains of APP/PS1 mice at 8 months of age. LTG treatment significantly reduced the percentage of diseased cells in the cerebral cortex (P < 0.001) and the hippocampus (P < 0.05) of APP/PS1 mice (Figure 2C and D), indicating a protective effect of LTG against nerve cell damage.