脑损伤
-
Figure 3| 5-aza inhibits the hippocampal synaptic damage induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.
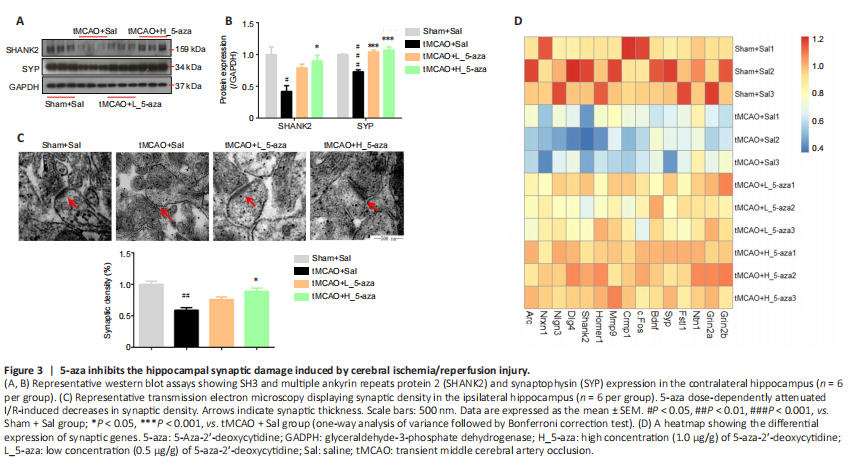
To assess whether synaptic function was involved in learning and memory deficits, the expression of synaptic proteins, mRNA, and synaptic density were observed at 1 hour after the behavioral tests. The expression of SHANK2 and SYP was significantly downregulated (SHANK2: P < 0.05, SYP: P < 0.001; Figure 3A and B), and synaptic density was reduced remarkably (P < 0.001; Figure 3C) in the Sham + Sal group compared with the tMCAO + Sal group. A heatmap analysis also showed that cerebral I/R injury markedly reduced the expression of 15 synapse-associated genes (Figure 3D). In general, 5-aza dose-dependently inhibited cerebral I/R injury-induced decreases in synaptic density in the ipsilateral hippocampus (P < 0.01), and the expression of synaptic proteins (SHANK2: P < 0.05, SYP: P < 0.001) and mRNA in the contralateral hippocampus (Figure 3).