中国神经再生研究(英文版) ›› 2023, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (9): 1976-1982.doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.363835
CXC趋化因子受体7增强缺血性脑卒中后的神经可塑性
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 7 antibody enhances neural plasticity after ischemic stroke
Xiao-Qian Zhang1, Xiao-Yin Wang1, Bing-Chao Dong1, Mei-Xuan Li1, Yu Wang1, Ting Xiao2, Shan-Shan Zhao1, *
- 1Department of Neurology, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Immunodermatology, Ministry of Health, Ministry of Education, Shenyang, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
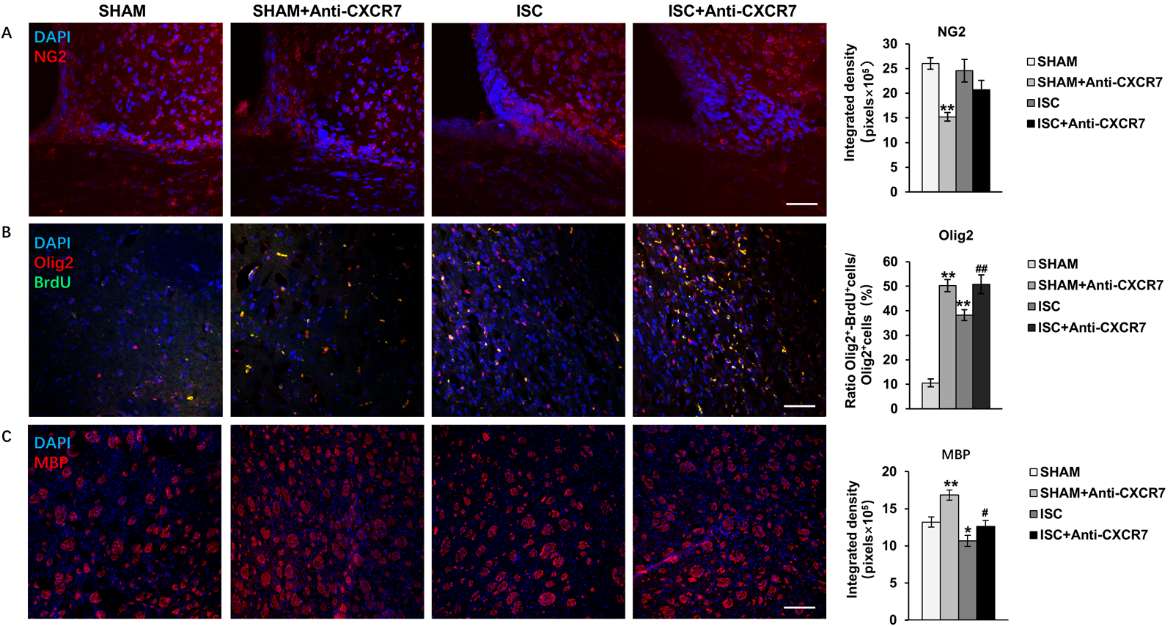
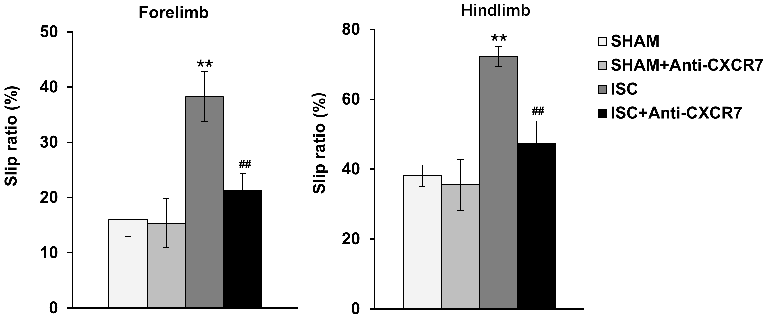
基质细胞衍生因子1及其受体CXC趋化因子受体4可调节脑卒中后的神经再生,但其另一种广泛分布于发育和成年的中枢神经系统的受体CXC趋化因子受体7是否也参与神经再生,目前尚不可知。实验通过大脑皮质和纹状体注射内皮素1制作局灶性脑缺血大鼠模型,从损伤后第7天开始,连续6d通过微量给药系统向侧脑室内注射CXC趋化因子受体7中和抗体。结果显示,CXC趋化因子受体7抗体能增加脑缺血大鼠发芽皮质脊髓束纤维的总长度和数量,促进去神经支配脊髓突触标志物囊泡谷氨酸转运体和生长相关蛋白43的表达,促进纹状体中少突胶质细胞祖细胞的分化和成熟。此外,CXC趋化因子受体7抗体还能增加纹状体中CXC趋化因子受体4的表达,激活 RAS/ERK 信号通路相关蛋白RAS和ERK1/2的表达,并改善大鼠运动功能。提示CXC趋化因子受体7可通过促进轴突再生、突触发生以及髓鞘再生,改善缺血性脑卒中后神经功能的恢复,且这一作用可能通过激活CXC趋化因子受体4以及激活RAS/ERK1/2信号通路实现的。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9785-2861 (Shan-Shan Zhao)