神经损伤与修复
-
Figure 1|Mechanisms of action and molecular targets of naturally sourced bioactive polysaccharides.
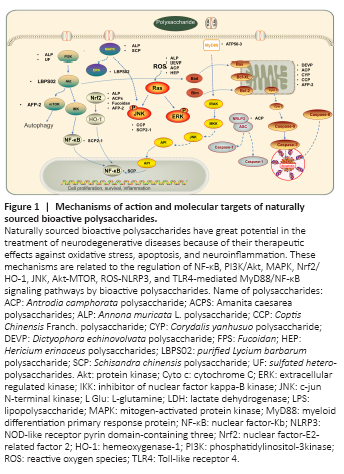
Figure 2|Neuroprotective effects of bioactive polysaccharides in animal models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
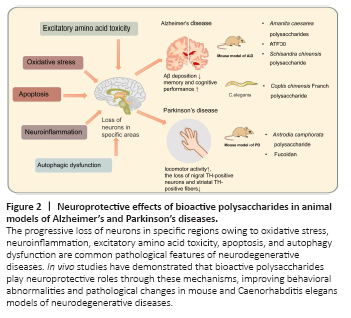
At present, the rising prevalence of NDDs places a heavy burden on society and families. Owing to the complexity of the NDD pathologies and the limitations of current therapeutics, the development of innovative treatment methods has received increasing attention. After the integration and analysis of related studies published in the past 5 years, this review introduced 15 bioactive polysaccharides with neuroprotective effects, including their possible action mechanisms and application prospects in the prevention and treatment of NDDs. These studies indicate that bioactive polysaccharides have potential medicinal values in the treatment of NDDs through various mechanisms, including the inhibition of oxidant stress, neuroinflammation, cell apoptosis, and excitotoxicity (Table 1 and Figure 1). In addition, the neuroprotective effects of naturally sourced bioactive polysaccharides have many advantages, such as multi-targeting, lower toxicity levels, and potential synergistic effects (Xie et al., 2016). Therefore, bioactive polysaccharides are promising neuroprotective agents. Unfortunately, most of these studies focused on in vitro studies and only a few have been validated in animal models (Figure 2). Consequently, information on the pharmacokinetics of these biologically active polysaccharides and the differences in their mechanisms of action in vivo and in vitro are lacking. In addition, although the neuroprotective mechanisms of these agents are diverse, there may be more mechanisms waiting to be determined. Recent studies have reported a bidirectional relationship between gut microbiota and the brain, and polysaccharides regulate the composition of gut microbiota and play positive roles in the prevention and treatment of NDDs through the microbiota-gut-brain axis (Sun et al., 2020).