脑损伤
-
Figure 4|Effect of BDMC on brain edema in rats with RBI.

To investigate the effects of BDMC on brain edema in rats with radiation-induced brain injury, the brain water content was evaluated, and hematoxylin and eosin staining were performed. Compared with the control group, the BDMC group exhibited no change in brain water content, and the RBI group exhibited higher brain water content. Compared with the RBI group, the BDMC + RBI group exhibited significantly decreased brain water content (P < 0.05; Figure 4A).
Hematoxylin and eosin staining showed that the neural cells and vascular endothelial cells in the control and BDMC groups had complete structures, normal morphology, and no interstitial edema, and were neatly arranged. In contrast, tissue samples from the RBI group exhibited swelling of nerve cells in the hippocampus, swelling of the cytoplasm of vascular endothelial cells, congestion and expansion of capillaries, and obvious interstitial edema. Compared with the RBI group, the swelling of nerve cells and vascular endothelial cells in the hippocampus of rats from the RBI + BDMC group was significantly improved, and the capillary congestion and dilatation and interstitial edema were improved (Figure 4B).
Figure 5|Effect of BDMC on astrocyte activation in the hippocampi of rats with RBI.

To investigate the effects of BDMC on astrocyte activation in the hippocampi of rats with radiation-induced brain injury, western blot and inmmunofluorescence staining were performed to evaluate changes in GFAP expression. Compared with the control group, the BDMC group exhibited similar GFAP levels, and the RBI group exhibited higher GFAP levels. Compared with the RBI group, the BDMC + RBI group exhibited significantly decreased GFAP levels (P < 0.001; Figure 5A and B). A similar pattern was observed for GFAP-positive cells in the four groups (Figure 5C).
Figure 7|Effect of BDMC on Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in the hippocampi of rats with RBI.
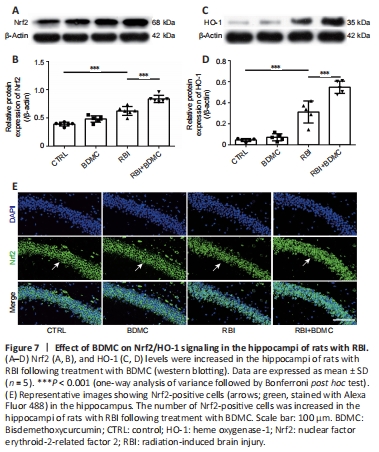
To investigate the effects of BDMC on Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in the hippocampi of rats with radiation-induced brain injury, western blotting and inmmunofluorescence staining were performed to evaluate changes in Nrf2 and HO-1 levels. Compared with the control group, the BDMC group exhibited similar Nrf2 levels, and the RBI group exhibited higher Nrf2 levels. Compared with the RBI group, the BDMC + RBI group exhibited significantly increased Nrf2 levels (P < 0.001; Figure 7A and B). A similar pattern was observed for HO-1 levels by both western blotting and immunofluorescence staining (P < 0.001; Figure 7C and D). The western blotting results for Nrf2 levels were confirmed by inmmunofluorescence staining (Figure 7E).