脊髓损伤
-
Figure 9|Immunofluorescence micrographs of myelinated axons in the gracile fasciculus (A) and dorsal corticospinal tract (B) (CST).
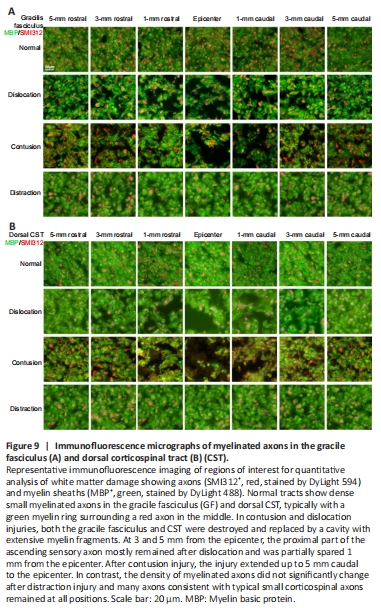
SMI312/myelin basic protein immunofluorescence staining showed that density of myelinated axons qualitatively differed among the three injury types and varied according to location. At the epicenter of injury in the gracile fasciculus of the contusion injury group, myelinated axon density was low and a cavity filled with myelin debris was observed; damage extended 5 mm caudally (Figure 9A). In the dislocation injury group, the degree of damage and cavitation was slightly lower. Although most axons at the epicenter were variably destroyed, most ascending sensory axons were preserved 3 and 5 mm rostral and caudal to the epicenter; partial sparing was observed as close as 1 mm from the epicenter (Figure 9A). The extent and distribution of damage differed in the distraction injury group, which showed a relative reduction in packing density of myelinated axons because of an increase in extracellular spaces (Figure 9A).
Similar patterns of myelinated axon injury were observed in the dorsal corticospinal tract. In the contusion and dislocation injury groups, approximately 10% to 50% of myelinated corticospinal axons were spared 3 mm proximal to the injury; few were spared at the epicenter, where myelin debris, tract interruption and cavitation were observed (Figure 9B).
Figure 10| Immunofluorescence micrographs of myelinated axons in the lateral white matter (A) and ventral white matter (B).
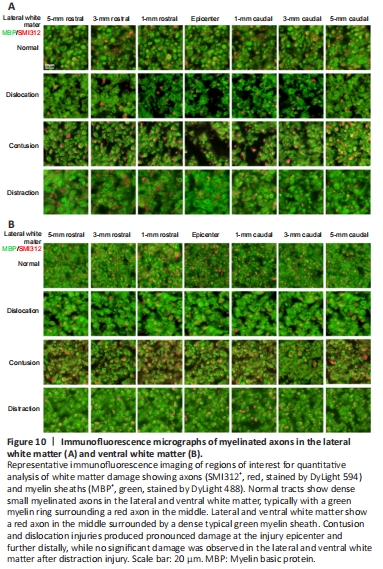
Many corticospinal axons were preserved at all locations in the distraction injury group. Both groups showed extensive degeneration of lateral white matter axons, a large amount of myelin debris, and many demyelinated axons (Figure 10A). Axon damage in the lateral white matter was limited to within 1 mm from the epicenter in the contusion and dislocation injury groups. Interestingly, ventral white matter damage was not observed in any of the three injury types (Figure 10B).