神经退行性病
-
Figure 1|FGF13 expression level is downregulated in Aβ-induced rats.
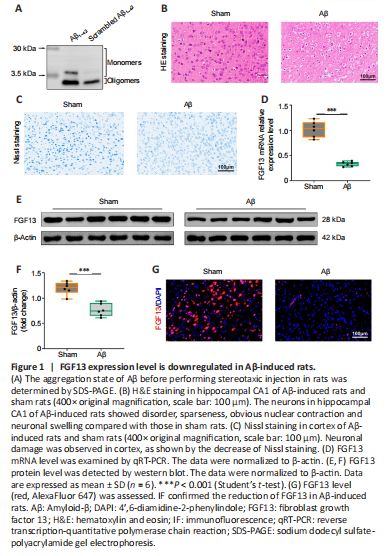
Because the biological effects of Aβ significantly differ according to its conformational state (Nortley et al., 2019), it is important to verify the aggregation state before performing stereotaxic injection. A characteristic appearance for Aβ1–42 is a mixture of oligomers and monomers that form at 3.5–30 kDa, whereas scrambled Aβ1–42 mainly formed monomers (Figure 1A). The AD rat model was then constructed through the stereotaxic injection of Aβ1–42 into bilateral hippocampus of rats. Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed that the neurons in hippocampal CA1 showed disorder, sparseness, obvious nuclear contraction and neuronal swelling compared with those in sham rats (Figure 1B), which suggested the successful establishment of the AD rat model. Additionally, Nissl staining also showed neuronal damage in cortex, as observed by the decrease of Nissl staining (Figure 1C). Subsequently, the level of FGF13 was detected in Aβ-induced rats. Both the transcriptional and translational levels of FGF13 were significantly decreased in Aβ-induced rats compared with these in sham rats (P < 0.001; Figure 1D–F). Moreover, immunofluorescence further confirmed the reduction of FGF13 in Aβ-induced rats (Figure 1G). Thus, FGF13 was downregulated in Aβ-induced rats.
Figure 3|FGF13 overexpression represses neuronal apoptosis in the brain of Aβ-induced rats.
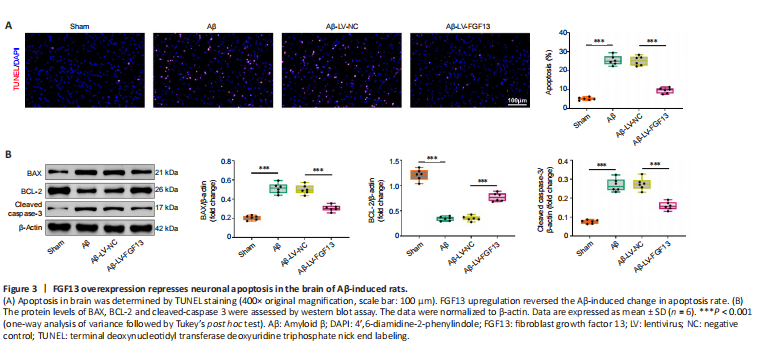
Apoptosis in brain of Aβ-induced rats with or without overexpression of FGF13 was detected by TUNEL assay. The apoptosis rate of Aβ-induced rats was dramatically elevated compared with that of sham rats, and the rate was significantly reduced with upregulation of FGF13 (P < 0.001; Figure 3A). Furthermore, FGF13 overexpression significantly attenuated the Aβ-induced increases in the protein levels of BAX and cleaved-caspase 3, and significantly reversed the Aβ-induced decrease in the relative protein level of BCL-2 (P < 0.001; Figure 3B). Therefore, these results suggest that FGF13 overexpression suppressed apoptosis in the Aβ-induced rat brain.
Figure 5|FGF13 overexpression ameliorates AD pathological characteristics.
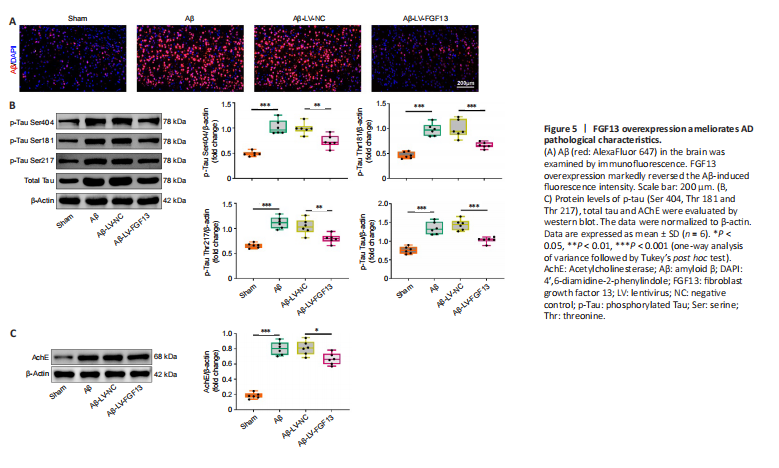
The fluorescence intensity of Aβ in the Aβ-induced rat brain was significantly enhanced compared with that in sham rats (Figure 5A), which was markedly reversed by overexpression of FGF13. In addition, FGF13 upregulation decreased the Aβ-induced protein levels of p-tau (Ser 404, Thr 181 and Thr 217) and total tau (P < 0.01; Figure 5B). Similarly, FGF13 upregulation notably diminished the relative protein expression of AChE compared with these in Aβ-induced rats (P < 0.05; Figure 5C). Thus, these results suggested that FGF13 overexpression ameliorated pathological AD features.