脑损伤
-
Figure 3|Effects of CXCR7 antibody on CST fiber sprouting in the spinal cord of stroke model rats.
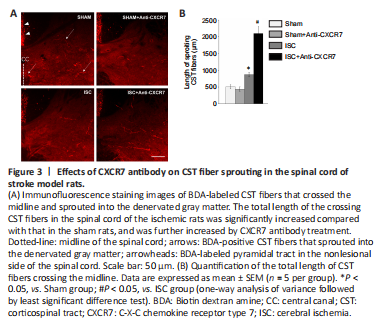
After cerebral ischemia, CST fibers generate collateral branches from the intact spinal cord that sprout across the midline into the denervated side, which represents axonal regeneration (Benowitz and Carmichael, 2010). Immunofluorescence of BDA-labeled axons showed that the total length of the crossing CST fibers in the ISC group was significantly longer than that in the Sham group (P < 0.05). CXCR7 antibody treatment further increased the total length of CST fibers after cerebral ischemia (P < 0.05), and did not alter the length in Sham rats (P < 0.05; Figure 3). The crossing fiber number showed similar trends to that of the total length. The number of CST axons in the ISC + anti-CXCR7 group was significantly increased compared with that in the ISC group, both in regions M (P < 0.05) and D1 (P < 0.01). In region D2, the number of CST axons in the ISC group was significantly increased compared with that in the Sham group (P < 0.05), and treatment with CXCR7 antibody further strengthened this trend (P < 0.01; Figure 2).
Figure 4|Effects of CXCR7 antibody on the levels of synaptic markers in the spinal cord of stroke model rats.
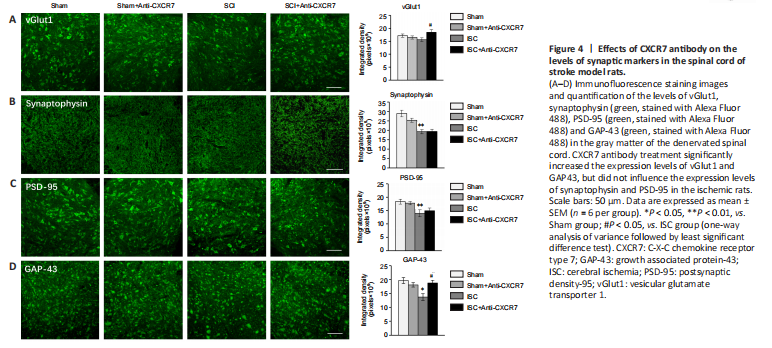
The effect of CXCR7 antibody on synaptogenesis was determined by examining the expression of synaptic markers, including vGlut1, synaptophysin, PSD-95, and GAP43, in the denervated gray matter of the spinal cord. Immunofluorescence staining showed that synaptophysin (P < 0.01), PSD-95 (P < 0.01), and GAP43 (P < 0.05) expression levels in the ischemic rats were all significantly lower, and vGlut1 expression was decreased but not significantly (P > 0.05) compared with those in the sham-operated rats. CXCR7 antibody treatment significantly increased vGlut1 and GAP43 expression levels in the ischemic rats (both P < 0.05; Figure 4), but did not influence synaptophysin and PSD-95 expression levels. None of the synaptic markers in Sham rats were influenced by the CXCR7 antibody.
Figure 5|Effects of CXCR7 antibody on OPC proliferation in the SVZ and OPC differentiation and maturation in the perilesional striatum of stroke model rats.
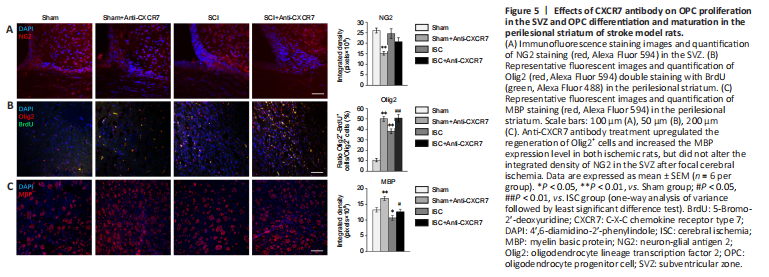
During the process of remyelination after brain injury, OPCs residing in the SVZ proliferate, migrate to the demyelinated area, and differentiate into mature oligodendrocytes to repair the impaired myelin sheaths (Franklin and Ffrench-Constant, 2008; Merino et al., 2015). NG2-positive glia are often equated to OPCs (Song et al., 2017), and are absent during the differentiation and maturation of oligodendrocytes (Goldman and Kuypers, 2015). Olig2, a marker for immature oligodendrocytes, is an essential activator in OPC differentiation and is critical for myelin sheath formation (Ligon et al., 2006). MBP is the marker of mature myelinating oligodendrocytes and a multifunctional protein that maintains the stability and integrity of the myelin sheath (Sarg et al., 2017; Brosolo et al., 2022). Immunofluorescence staining showed no significant differences in the integrated density of NG2 in the SVZ between the four groups (Figure 5A). After focal cerebral ischemia, the proportion of Olig2+BrdU+ cells among BrdU+ cells within the perilesional striatum was significantly higher (P < 0.01), whereas MBP expression was significantly lower (P < 0.05) compared with that in Sham rats. Anti-CXCR7 antibody treatment not only significantly upregulated the proportion of Olig2+BrdU+ cells (both P < 0.01; Figure 5B) but also greatly increased the MBP expression level in both ischemic rats and sham-operated rats (P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively; Figure 5C).