脑损伤
-
Figure 3|In situ hybridization autoradiographic images of coronal sections of the adult rat superior colliculus (SC).

A comprehensive in situ hybridization study using oligonucleotide probes labeled at the 3 prime ends with [35S]dATP revealed the distribution of cells in the adult rat SC expressing mRNAs for seven neurotransmitters/neuromodulators (Harvey et al., 2001). A novel finding was the existence of a sub-laminar distribution of neuropeptides within the superficial SC layers. While cells expressing glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA (GAD, marker for gamma aminobutyric acid) were the most abundant and distributed throughout the depth of the rat SGS, in the superficial SC the expression of mRNA for preprotachykinin (PPT - substance P), cholecystokinin (CCK) and somatostatin (SOM) was largely restricted to sub-laminae: PPT cells most superficial, CCK cells in an intermediate zone, and SOM cells located deeper in SGS, adjacent to stratum opticum (Harvey et al., 2001). Figure 3 (right-hand panel) presents data obtained using these radioactive probes showing the characteristic distribution of GAD, PPT, CCK, and SOM-expressing cells in rat SGS. In these animals, under anesthesia, one eye had been removed at birth (Harvey et al., 1995); the panel on the left (Figure 3) is contralateral to the enucleated side and shows a smaller SC and noticeably reduced levels of expression of GAD, PPT and CCK mRNAs in the SGS, but with only minor if any impact on SOM expression. Quantitative analysis of total cell counts in tissue sections and density of silver grains in autoradiogram films confirmed these qualitative findings. Overall these data show that retinal input enhances the expression of GAD and some neuropeptide genes in the superficial SC, but that there is ongoing basal expression of these genes in the absence of visual drive from the contralateral eye. This is an important observation of relevance to the graft work discussed below.
Figure 4|In situ hybridization autoradiographic images of coronal sections of transplanted fetal tectal tissue.
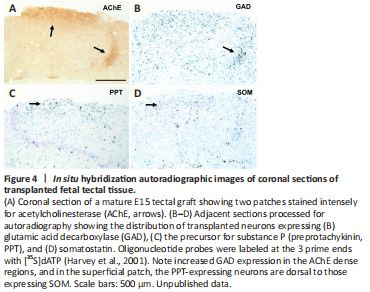
Gene expression was analyzed in E15 tectal tissue transplanted onto the midbrain of neonate rat hosts (Harvey et al., 1994). An example is shown in Figure 4. Two AChE dense patches are labeled (arrows, Figure 4A), one at the graft surface and one deeper within the mature graft neuropil. Adjacent sections were probed for expression of GAD, PPT, or SOM mRNA. In strong support of the homology between AChE patches in grafts and normal rat SGS (Figure 3), these localized regions contained many GAD-expressing cells (arrow in Figure 4B). It is noteworthy that there was a differential distribution of PPT- (Figure 4C) and SOM- (Figure 4D) expressing cells in the superficial AChE patch. The CCK cells are located towards the graft surface and the SOM-expressing cells are situated more deeply, typical of their sub-laminar distribution in normal SGS.
Figure 5|Expression of different neuropeptide mRNAs in a fetal tectal transplant.

One further example of mRNA expression in a tectal graft is shown in Figure 5; here the AChE patch is deep within the graft (Figure 5A). Again, note the concentration of GAD mRNA-expressing cells in this patch (Figure 5B). The patterns of expression of GAD, SOM, PPT and CCK mRNA expression in and around the AChE dense region are shown at higher power in Figure 5C–F respectively, and are digitally mapped in Figure 5G. Note that cells expressing low levels of PPT mRNA are located towards the center of this deep patch, CCK-expressing cells have a more intermediate location, and cells expressing relatively high levels of SOM mRNA form a peripheral ring around the patch border (Figure 5D and G). These features again reflect the differential distribution of these peptide-expressing cells in tectal grafts, in a manner markedly similar to that seen in normal superficial SC. The difference here is that the circular distribution of SOM-expressing cells around the edge of this deep AChE dense patch suggests that the normal horizontal lamination pattern had been lost and the presumptive SGS had curled into a discrete ball. As described earlier, deeply located fiber-free/AChE dense patches in grafts do not receive host retinal input; the sustained expression of these various mRNAs in fetal tectal transplants is consistent with the basal level of expression seen in normal rat superficial SC deprived of retinal input from birth (Figure 3).
Figure 6|E15 tectum grafted onto the superior colliculus (SC) of older hosts.

When transplanted onto the intact SC of rats aged between 3 and 21 days (Figure 6), ingrowth of 3H proline labeled retinal axons was consistently seen in fiber-free patches in fetal tectum grafted in day 3 hosts and also occasionally in tissue grafted into 7-day-old hosts (Figure 6A and B). A retinal projection into fetal tectal tissue transplanted onto the unlesioned SC in 14-day hosts was rarely seen (Figure 6E), and even when there was clear host-graft continuity (Figure 6D) input was sparse and restricted to the host-graft interface. This decrease in innervation plasticity parallels the maturation of retinal input into normal SC, which in the rat continues until about postnatal day 5 or 6 and originates primarily from late-born retinal ganglion cells (Dallimore et al., 2002). In contrast, after lesions of the host occipital cortex, large numbers of degenerating profiles (Fink-Heimer stain) were evident in tectal tissue grafted into 7 (Figure 6C) and 14-day hosts (Figure 6F), although the density was reduced and ingrowth more limited in older hosts. In tissue transplanted to 14-day-old host rats, occasional retrogradely labeled pyramidal neurons in the host visual cortex were seen after injections of HRP into grafts. The extended period of host-graft plasticity shown by the cortex compared to the retina presumably reflects the relative immaturity of corticotectal projections in the postnatal rat (de Carlos and O’Leary, 1992).