脑损伤
-
Figure 1|NBP improves cell viability and inhibits apoptosis in H2O2-treated cells.
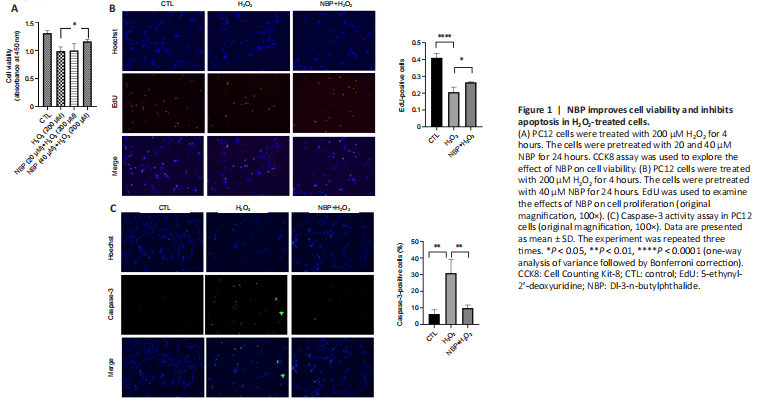
PC12 cells are commonly used as an in vitro model to study central nervous system neurons (Wu et al., 2020). We first examined the effects of NBP on the viability of PC12 cells treated with H2O2, as a model of oxidative stress, using CCK8. While H2O2 reduced the viability of cells compared with controls, NBP pretreatment significantly prevented the decrease in viability of H2O2-treated cells (P = 0.0344; Figure 1A). EdU assay showed that NBP pretreatment reversed the inhibition of cell proliferation after H2O2 treatment (Figure 1B). Caspase-3 plays a key role in regulating apoptosis (Porter and J?nicke, 1999). Caspase-3 activity assays showed that pretreatment with NBP significantly reduced the induction of caspase-3 activity caused by H2O2 treatment (Figure 1C).
Figure 2|NBP protects mitochondrial function and inhibits ROS production in PC12 cells exposed to H2O2.
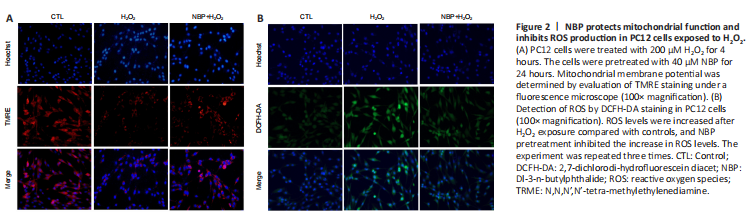
To assess whether NBP protected PC12 cells against H2O2 treatment by mitigating mitochondrial dysfunction associated with apoptosis, we measured the mitochondrial membrane potential by TRME staining assay. TRME intensity decreased following H2O2 exposure; however, NBP cotreatment prevented H2O2-induced changes in the mitochondrial membrane potential (Figure 2A). These results demonstrated that NBP mitigated H2O2 exposure-induced mitochondrial dysfunction.
We next investigated the effects of NBP on intracellular ROS levels in PC12 cells after H2O2 treatment using DCFH-DA. The results showed that ROS levels increased after H2O2 exposure compared with controls, and NBP pretreatment inhibited the increase in ROS levels (Figure 2B).
Figure 6|NBP inhibits H2O2-induced ECM degradation.
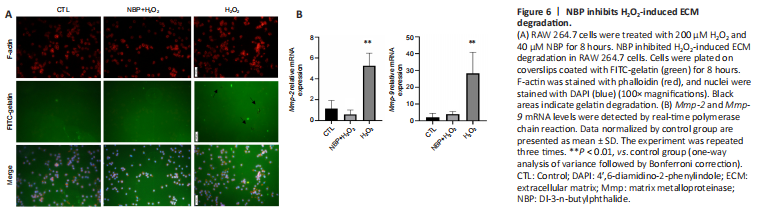
BBB damage is a critical pathological process that contributes to poor prognosis in cerebral ischemia (Li et al., 2019b), inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases protects the BBB (Li et al., 2019b; Candelario-Jalil et al., 2022). Given the reported protective effects of NBP on the BBB (Li et al., 2019a; Wu et al., 2020), we determined the effect of NBP on extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation in H2O2-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages, which have been reported as a potential source of MMPs that can degrade the BBB (Jiang et al., 2018). Matrix degradation assays showed that H2O2 treatment caused ECM degradation around the periphery of macrophages, and this was attenuated by NBP (Figure 6A). We next sought to investigate the mechanisms by which NBP treatment blocked H2O2-induced BBB degradation. Real-time PCR of RAW 264.7 macrophages demonstrated that H2O2 increased Mmp-2 and Mmp-9 mRNA expressions compared with controls, while NBP blocked the increase of Mmp-2 and Mmp-9 mRNA expression (Figure 6B). Previous studies showed that HIF-1α transcriptionally upregulates the expression of MMPs, and in the absence of HIF-1α, the level of MMPs decreased (Du et al., 2008; Palazon et al., 2014). Our findings suggest that NBP promotion of the degradation of HIF-1α may be responsible for the decrease in Mmp-9 levels in RAW 264.7 macrophages.