周围神经损伤
-
Figure 1|Differentially expressed mRNA-associated upstream miRNAs after peripheral nerve injury
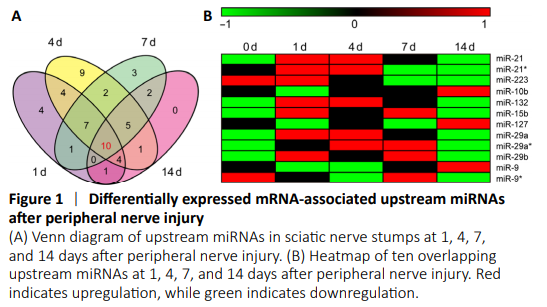
To investigate miRNAs associated with differentially expressed mRNAs after PNI, previously obtained sequencing data of rat sciatic nerve stumps at 0, 1, 4, 7, and 14 days after crush injury (Yi et al., 2015) were subjected to IPA core analysis. Bioinformatic analyses using IPA upstream regulator function identified 31 upstream miRNAs for the cellular growth and proliferation-associated acute phase (1 day post nerve injury), 72 upstream miRNAs for the cellular function and maintenance-associated sub-acute phase (42 upstream miRNAs at 4 days post nerve injury and 30 upstream miRNAs at 7 days post nerve injury), and 23 upstream miRNAs at the tissue formation-associated post-acute stage (14 days post nerve injury). Upstream miRNAs were ranked by their P-values. Upstream miRNAs with P-values less than 0.05 are listed in Additional Table 1. To explore temporal characteristics, upstream miRNAs identified during the time course were displayed as a Venn diagram (Figure 1A). Ten miRNAs, including miR-21, miR-223, miR-10, miR-155, miR-132, miR-15, miR-127, miR-29, miR-135, and miR-9, were enriched in differentially expressed mRNAs at all time points. In addition, many other upstream miRNAs were involved at multiple time points. Seven miRNAs were enriched at 1, 4, and 7 days after PNI, including let-7, miR-208, miR-25, miR-34, miR-192, miR-17, and miR-19. Four miRNAs were enriched at 1, 4, and 14 days after PNI, including miR-146, miR-23, miR-27, and miR-218. Five miRNAs were enriched at 4, 7, and 14 days after PNI, including miR-8, miR-185, miR-133, miR-130, and miR-145.
Expression patterns of overlapping upstream miRNAs were revealed at all time points based on previously obtained miRNA sequencing data of rats with sciatic nerve transection injury (Yu et al., 2011). According to miRNA sequencing data reported by Yu et al. (2011) 225 miRNAs were differentially expressed after PNI. Among the ten overlapping upstream miRNAs, only miR-155 and miR-135 were not found to be differentially expressed, while the other eight displayed altered expression levels after nerve injury. Two family members of miR-29 (miR-29a and miR-29b) were both differentially expressed after nerve injury. In addition, different isoforms of miR-21, miR-29a, and miR-9 were differentially expressed. miRNAs labeled with an asterisk indicate isoforms with relatively low expression levels. Temporal expression patterns of these miRNAs are displayed as a heatmap (Figure 1B). miR-21, miR-21*, miR-132, miR-15b, miR-29a, miR-29a*, and miR-29b were upregulated after nerve injury. miR-223 was downregulated after nerve injury; whereas miR-10b, miR-127, miR-9, and miR-9* were first downregulated and then upregulated.
Figure 2|miRNA-mRNA-GO term network of miR-21, miR-132, miR-223, and miR-9
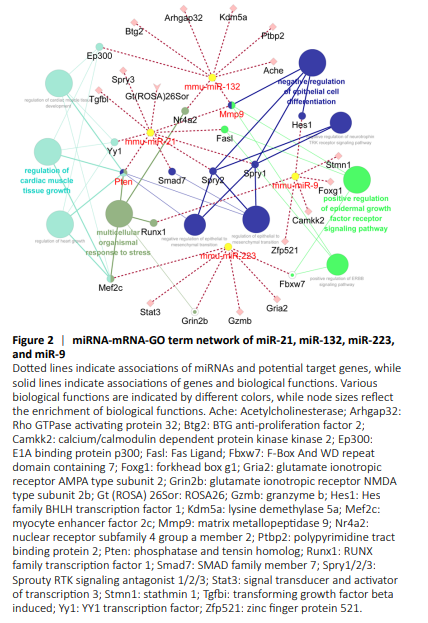
Target genes of these miRNAs were determined using the built-in miTarBase database in Cytoscape software and connected by importing networks. miR-21 targeted Mmp9 (matrix metallopeptidase 9), Smad7 (SMAD family member 7), Yy1 (YY1 transcription factor), Spry1/2/3 (Sprouty RTK signaling antagonist 1/2/3), Gt(ROSA)26Sor (ROSA26), Fasl (Fas Ligand), Pten (phosphatase and tensin homolog), and Tgfbi (transforming growth factor beta induced). miR-132 also targeted Mmp9, as well as Btg2 (BTG anti-proliferation factor 2), Nr4a2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group a member 2), Ptbp2 (polypyrimidine tract binding protein 2), Ache (acetylcholinesterase), Arhgap32 (Rho GTPase activating protein 32), Ep300 (E1A binding protein p300), and Kdm5a (lysine demethylase 5a). miR-223 targeted Stat3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3), Mef2c (myocyte enhancer factor 2c), Gria2 (glutamate ionotropic receptor AMPA type subunit 2), Gzmb (granzyme b), Grin2b (glutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA type subunit 2b), and Fbxw7 (F-Box and WD repeat domain containing 7). miR-9 targeted Zfp521 (zinc finger protein 521), Camkk2 (calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase kinase 2), Stmn1 (stathmin 1), Runx1 (RUNX family transcription factor 1), Foxg1 (forkhead box g1), and Hes1 (Hes family BHLH transcription factor 1). miR-127 targeted Fcgr1 (Fc fragment of IgG receptor 1) (Figure 2).
Figure 3|Mechanistic network of let-7-associated genes at 1 day after PNI
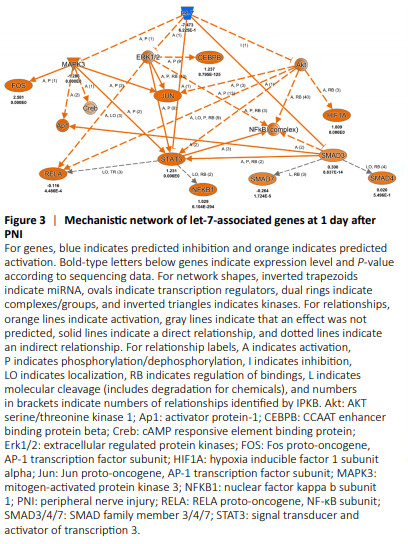
Let-7 was most significantly enriched during the acute phase after nerve injury (1 day after PNI). Let-7 was predicted to decrease the activities of Stat3, Mapk3 (mitogen-activated protein kinase 3), Erk1/2 (extracellular regulated protein kinases), Smad3 (SMAD family member 3), and Akt (AKT serine/threonine kinase 1). Many downstream cascades of Mapk3, Stat3, Erk1/2, Smad3, and Akt, such as NF-κB (nuclear factor κB) and AP-1 (activator protein-1) would be affected by let-7 (Figure 3).
Figure 4|Mechanistic network of miR-21-associated genes at (A) 4 days and (B) 7 days after PNI
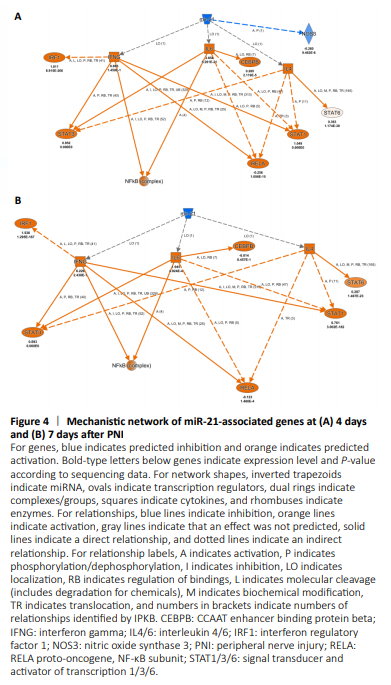
miR-21 was most significantly enriched at both 4 and 7 days after PNI, indicating that miR-21 was critical for the sub-acute phase after nerve injury. IPA analyses showed that miR-21 targeted ACTA2 (actin alpha 2, smooth muscle), AIF1 (allograft inflammatory factor 1), ALOX15 (arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase), AOAH (acyloxyacyl hydrolase), ARF6 (ADP ribosylation factor 6), ARNTL (aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator like), ASPM (abnormal spindle microtubule assembly), ATAD2 (ATPase family AAA domain containing 2), CASP4 (caspase 4), and CCL17 (C-C motif chemokine ligand 17) at 4 days post nerve injury. At 7 days post nerve injury, ALOX15, ARF6, and ATAD2 were not predicted to be target molecules in the dataset; whereas, CCL19 (C-C motif chemokine ligand 19), CCL2 (C-C motif chemokine ligand 2), and CCL3L3 (C-C motif chemokine ligand 3 like 3) were included in the dataset. Constructed mechanistic networks of miR-21 at 4 and 7 days after PNI were also slightly different. miR-21 was predicted to affect IFNG (interferon gamma), IL4 (interleukin 4), IL6 (interleukin 6), and their downstream molecules at both time points (Figure 4). In addition to activation of these essential molecules, miR-21 might also inhibit NOS3 (nitric oxide synthase 3) (Figure 4A) at 4 days after PNI.
Figure 5|Mechanistic network of miR-223-associated genes at 14 days after PNI
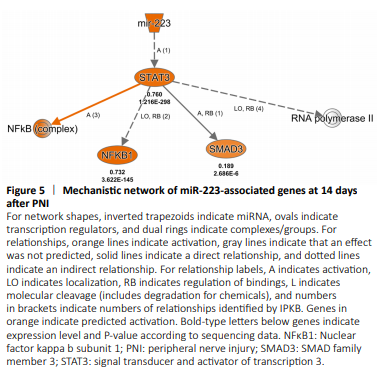
The most significantly enriched miRNA at the post-acute stage (14 days after PNI) was miR-223. The mechanistic network of miR-223 was also created (Figure 5). The built-in Ingenuity ExpertAssist Finding in IPA software indicated that downregulation of miR-223 was involved in activation of Stat3 (Chen et al., 2012). Therefore, the Stat3 signaling pathway might be involved in miR-223-mediated biological functions after PNI.