神经损伤与修复
-
Figure 1|Alterations in m5C and m6A RNA modification systems contribute to neurocognitive disorders.
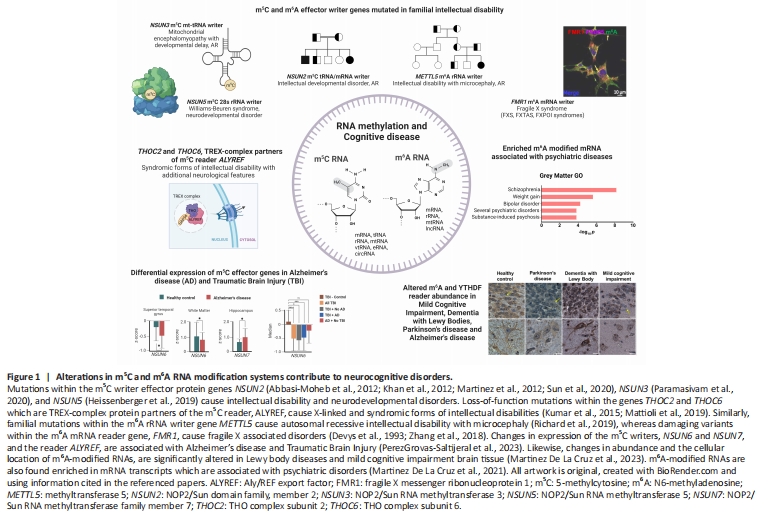
m5C RNA methylation, although less prevalent than m6A RNA modification, has been characterized across multiple tissues and is found highest in abundance within mRNAs in the brain (Huang et al., 2019). Evidence initially from pedigree studies in which causative mutations were identified, led to the discovery that several NSUN writers cause neurodevelopmental conditions (Figure 1). For example, NSUN2 is known to cause forms of autosomal recessive intellectual disability (Abbasi-Moheb et al., 2012; Khan et al., 2012; Martinez et al., 2012; Sun et al., 2020), as well as Dubowitz syndrome, a rare multiple congenital syndrome characterized by growth retardation, microcephaly, distinctive facial dysmorphism, and intellectual deficits (Martinez et al., 2012). NSUN3, a mitochondrial tRNA writer, causes autosomal recessive mitochondrial encephalomyopathy characterized by global developmental delay (Van Haute et al., 2016; Paramasivam et al., 2020). Likewise, the rRNA writer, NSUN5, is located within the critical region for Williams Beuren syndrome, a rare neurodevelopmental condition; and haploinsufficiency of NSUN5 in fibroblasts from Williams Beuren syndrome patients causes a partial loss of 28S rRNA m5C methylation (Heissenberger et al., 2019). Furthermore, in a very recently published report, biallelic mutations within a fourth NSUN writer, NSUN6, were described to cause autosomal recessive neurodevelopmental disorders (Mattioli et al., 2023). The different mutations identified, i.e., two homozygous frame shift mutations and a homozygous missense mutation, were suggested, by the authors, to lead to a loss of functional NSUN6 protein abundance and hence to a loss of m5C modification of tRNAs. Finally, the m5C reader, ALYREF, is part of the TRanscription-EXport (TREX) protein complex that regulates mRNA transcription and processing and shuttles mRNA out of the nucleus (Dufu et al., 2010). Mutations within THOC2 and THOC6 that are protein binding partners of the TREX mRNA-export complex are reported to cause X-Linked intellectual disability and rare autosomal recessive syndromic intellectual disability (Najmabadi et al., 2011; Kumar et al., 2015).