神经退行性病
-
Figure 1|2N4R-TAU is necessary and sufficient for AβO-induced spine loss in primary neurons.
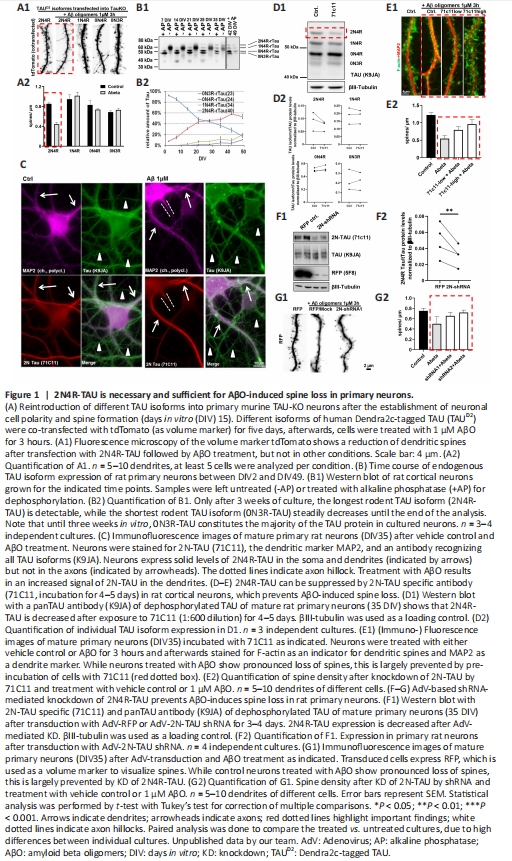
Preliminary results: 2N4R-TAU resensitizes TAU KO neurons to AβO-induced spine loss: TAU is essential for Aβ-induced neurotoxicity: Previous reports have already shown that TAU KO rodent neurons are resistant to Aβ-mediated toxicity (Roberson et al., 2007; Zempel et al., 2013). However, little is known about the contribution of the different TAU isoforms to synapse loss after Aβ insult. To study the influence of the different TAU isoforms on Aβ-mediated spine loss, human Dendra2c (D2)-tagged TAU isoforms were re-expressed in mature primary neuronal cultures (DIV16, prepared E16.5) from Mapt knockout mice, as described previously (Zempel et al., 2017). To assess spine density, tdTomato was co-expressed as a volume marker. Afterwards, neurons were exposed to 1 μM Aβ7:3 oligomers (as prepared before (Zempel et al., 2013, 2017)) for 3 hours. Interestingly, significant (~50%) AβO-mediated spine loss was only observed in neurons expressing human 2N4R-TAU, but not the other three TAU isoforms typically present in rodent neurons, namely 1N4R, 0N4R and 0N3R (Figure 1A).
Since TAU isoform expression in rodents differs strongly from human TAU expression (Goedert et al., 1989; Bullmann et al., 2009), we next monitored TAU isoform expression in primary neurons from wild type rats by western blot analysis of neuronal cell lysates for 49 days (Figure 1B). In line with previous reports from mice (Bullmann et al., 2009), only 0N isoforms were detectable in young neurons (DIV2), with 0N3R as the major isoform expressed (> 90%; Figure 1B). Upon neuronal maturation, 0N3R expression decreased at a constant rate until it reached a proportion of ~20% of all isoforms in old neurons (DIV49). In contrast, 0N4R expression constantly increased until it reached an expression level of ~50% at DIV49. In addition, expression of both 2N4R and 1N4R isoforms increased from DIV7, finally reaching 15% and 20% of all isoforms at DIV49, respectively. Especially the expression levels of 2N4R, 1N4R, and 0N3R, ranging between 15–20%, resemble the isoform expression reported by Trabzuni et al. (2012) for the human brain. All in all, these results suggest that rat primary neurons are rather suitable for the analysis of TAU isoforms if to be compared to the human brain, and considering that in the murine brain – in contrast to humans – up to 45% of 2N4R-TAU is expressed (Bullmann et al., 2009).
Recent studies suggest a sub-cellular difference in the human TAU isoform localization, and especially human 2N-TAU isoforms are retained in the somatodendritic compartment of wild type primary neurons (Zempel et al., 2017; Bachmann et al., 2021). Endogenous 2N-TAU localization was assessed in rat primary neurons by immunofluorescence staining with a 2N-TAU specific antibody (71C11; Figure 1C). Note that, as 2N3R-TAU is not expressed in our primary neurons (Figure 1B) and other rodents (Bullmann et al., 2009), this antibody here exclusively marks 2N4R-TAU. Total TAU was stained by a polyclonal TAU antibody (K9JA), recognizing all isoforms of TAU, while MAP2 was used as a dendritic marker as described before (Zempel et al., 2017). We found that primary rat neurons showed solid staining for 2N-TAU only present in the soma and dendrites of the cells, in line with our previous findings (Zempel et al., 2017; Bachmann et al., 2021). All in all, 2N4R-TAU is retained from axonal sorting, and as dendritic TAU has been shown to drive spine loss and neuronal dysfunction (Zempel and Mandelkow, 2014), 2N4R-TAU could be a driver of Aβ-induced spine loss observed in rodent neurons.
Downregulation of endogenous 2N4R-TAU prevents AβO-induced spine loss: Next, we aimed to suppress endogenous TAU in our primary neuron cultures. In a first attempt, primary rat neurons were incubated with a 2N-TAU specific antibody (71C11) for 4–5 days. TAU isoform levels were assessed by western blot assay under dephosphorylating conditions. 2N4R-TAU levels, but none of the other isoforms of TAU, were suppressed after incubation with 71C11 antibody compared to untreated controls (Figure 1D) in all three cultures. This hints towards antibody-mediated suppression of TAU isoforms (here, due to the absence of 2N3R TAU, specifically 2N4R TAU) in neurons being possible. In the next step, to test whether 2N4R suppression may be beneficial in a disease context, the spine density of neurons after treatment with AβOs was analyzed in dependence on antibody-mediated 2N-TAU suppression. 2N4R-TAU was suppressed by two different concentrations of 71C11 (hereafter referred to as 71C11-low (1:600) and 71C11-high (1:300)), resulting in lower or stronger 2N4R repression, respectively (Figure 1E). In line with previous reports (Zempel et al., 2013) and with our results above, AβO-treatment resulted in dendritic spine loss that was prevented by the suppression of 2N4R-TAU in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 1E). To further validate a potential beneficial effect of 2N4R-TAU, we next downregulated 2N4R-TAU by RNAi. For this, an adenovirus (AdV)-delivered shRNA construct was generated that specifically targets rat 2N-TAU isoforms (Figure 1F and G). AdV-mediated delivery resulted in significant knockdown of 2N4R-TAU (but not the other three detectable TAU isoforms) in our rat primary neurons, as analyzed by western blot assay (Figure 1F). These results indicate that RNAi-based knockdown of 2N-TAU isoforms is suitable to suppress 2N4R-TAU in rat primary neurons selectively, due to the absence of 2N3R-TAU. Analysis of spine density after knockdown of endogenous rat 2N4R-TAU and subsequent AβO treatment again showed a noticeably increased spine density compared to AβO treated and mock-transduced neurons (Figure 1G), which confirmed that, indeed, 2N4R-TAU may mediate AβO-induced spine loss. Our results indicate that the 2N4R-TAU isoform may specifically mediate acute AβO-induced spine loss.