周围神经损伤
-
Figure 1|RAW 264.7 cell proliferation situation.
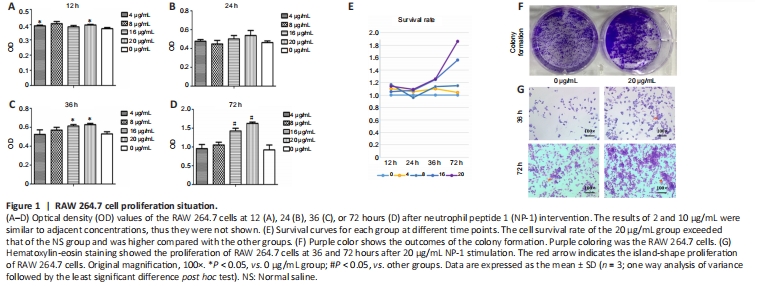
Cells cultured in 20 μg/mL NP-1 had a higher OD value at each time point than the blank-control group and the lower NP-1 concentrations groups (P < 0.05; Figure 1A–D), and had a higher cell survival rate than the other groups, especially after stimulation for 72 hours. The cell survival rate of the 20 μg/ml group was 186.17%, which was significantly higher than that in the other groups (Figure 1).
Hematoxylin-eosin staining and colony formation showed more cell proliferation in the NP-1 group, which was similar to the trend of Cell Counting Kit-8 results. The island-shaped proliferation of cells occurred earlier in the NP-1 group than in the control group (Figure 1).
Figure 4|Transwell cell migration assays in RAW 264.7 cells.
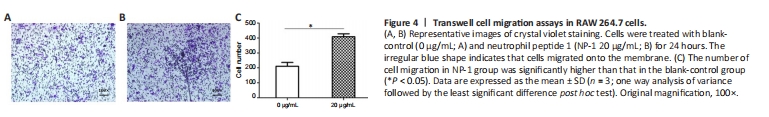
After 24 hours of culture, macrophages migrated from Transwell chambers to 24-well plates, and the number of cells in the 24-well plates was counted after crystal violet staining. The number of cells in the NP-1 group was significantly higher than that in the blank-control group (P < 0.05; Figure 4).
Figure 5|Phagocytosis of fluorescent microspheres in RAW 264.7 cells.
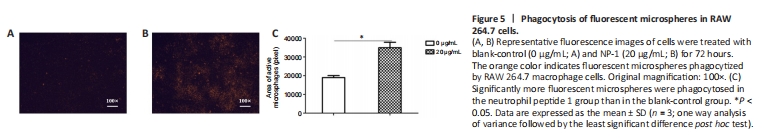
To observe the phagocytic ability of macrophages treated with NP-1 in vitro, fluorescent microspheres and RAW 264.7 cells were coincubated. The fluorescence-positive area of the NP-1 group was significantly larger than that of the blank-control group (P < 0.05; Figure 5).
Figure 7| Polarization of macrophages and secretion of inflammatory cytokines.
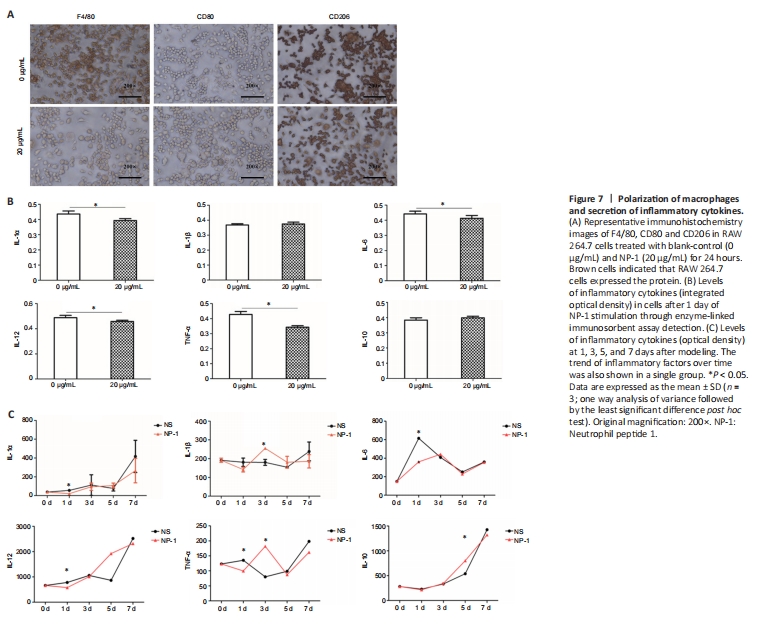
Macrophages are divided into two phenotypes: proinflammatory macrophages (M1) and anti-inflammatory macrophages (M2). M1 macrophages express the CD80 protein marker and M2 macrophages express the CD206 marker. The F4/80 protein is a marker of mature macrophages. Immunochemistry showed that the RAW 264.7 cells expressed F4/80?CD80?CD206+ after stimulation with NP-1 for 24 hours and F4/80+CD80?CD206+ in the blank group (0 μg/mL NP-1; Figure 7A).
M1 macrophages secrete IL-1α, -1β, -6, -12 and TNF-α, and M2 macrophages secrete IL-10. IL-1α, -6, -12 and TNF-α in the NP-1 group were significantly lower than those in the blank-group (0 μg/mL NP-1; P < 0.05). There were no differences in levels of IL-1β and -10 between the NP-1 group and the blank-control group (P > 0.05; Figure 7B).
There were significant differences in the expression of IL-1α, -6, -12 and TNF-α on the protein chip at many time points (P < 0.05). IL-1α, -10 and -12 showed an increasing trend in the first week after crush injury in the injured nerve in the NP-1 group and the blank-control group. IL-1β, -6 and TNF-α fluctuated over time. IL-10 expression on the fifth day was significantly higher in the NP-1 group than in the NS group (P < 0.05; Figure 7C).