脊髓损伤
-
Figure 11|Histopathological changes in the spinal cord of a patient who underwent surgical detethering 9 months after injury.
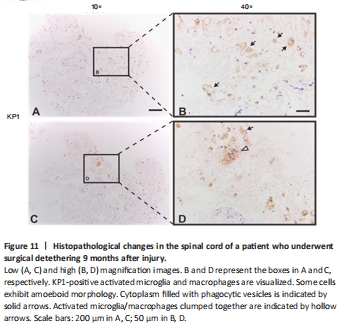
To evaluate whether inflammatory responses were still present over time, we examined histopathological spinal cord changes in an SCI patient who underwent surgical detethering 9 months after injury. This patient was from a different patient cohort not reported in this study. Paraformaldehye-fixed paraffin-embedded spinal cord tissue samples were shipped to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, where sections (4 μm) were stained with mouse anti-human CD68 (KP1, Dako, Glostrup, Denmark). Results indicated that the tissue contained KP1-positive (a marker for macrophages) activated microglia and macrophages (Figure 11). Currently, there is no effective medication to ensure the efficient and proper synchronization of the microglia-to-macrophage transition that occurs in the injured spinal cord. to a more favorable phenotype, inflammatory material was occasionally observed and, when examined microscopically contained debris-laden macrophages.