NRR:天津大学杨佳佳教授团队总结超声调控治疗阿尔茨海默病的作用及机制
阿尔茨海默病是一种常见的神经退行性疾病。阿尔茨海默病的典型特征是推理能力下降、记忆力损伤和认知能力下降。阿尔茨海默病发病机制主要有以下4个因素:淀粉样β蛋白的沉积、tau蛋白的过度磷酸化、神经元和突触损伤以及神经炎症[1-3]。当前,针对阿尔茨海默病的治疗主要包括药物治疗[4-6]和物理治疗[7-9]。近年来,超声作为一种新兴的物理疗法受到了广泛关注,其具有非侵入性、穿透力强和空间分辨率高等优势[10]。目前,超声[11],超声联合微泡[12],超声联合药物[13]等方式治疗阿尔茨海默病已开展了部分研究。但以上多种超声方法作用机制的差异性及其适用情形尚未明确。尤其是2018年以来,上述疗法逐步由啮齿类动物转向人体研究[14],系统性的归纳总结对阿尔茨海默病的临床应用具有重要意义。研究团队认为超声是治疗阿尔茨海默病的有效方法。
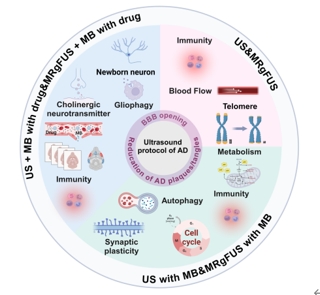
天津大学杨佳佳团队在发表于《中国神经再生研究(英文)》杂志(Neural Regeneration Research)2025年10期的综述中,详细论述了超声,超声联合微泡,超声联合药物三种超声疗法,调控阿尔茨海默病的作用机制。这些超声疗法都可以通过打开血脑屏障,减少阿尔茨海默病斑块/缠结等机制缓解阿尔茨海默病。此外,单独使用超声治疗可能会通过增加脑血流量、免疫反应和减缓端粒缩短等机制缓解阿尔茨海默病。超声联合微泡治疗可能通过增强免疫反应、恢复突触可塑性、增强自噬、调节葡萄糖代谢和细胞周期等机制治疗阿尔茨海默病。超声联合药物治疗可能通过增强神经元再生、免疫反应、神经胶质细胞吞噬和激活胆碱能系统等机制治疗阿尔茨海默病。最后,研究团队总结了各种超声方法在不同情境下的优势及局限性,归纳了超声在阿尔茨海默病治疗中的里程碑事件,并展望了未来超声技术在阿尔茨海默病治疗中的发展方向和应用前景,为超声技术治疗阿尔茨海默病的临床应用提供了理论基础。天津大学硕士生蔡秋全,博士生孟靓辉为该综述的共同第一作者。杨佳佳副教授,明东教授为通讯作者。
#br#
参考文献
[1]
Long JM, Holtzman DM. Alzheimer disease: an update on pathobiology and
treatment strategies. Cell 2019;179:312-339.
[2]
Cosacak MI, Bhattarai P, Kizil C. Alzheimer’s disease, neural stem cells and
neurogenesis: cellular phase at single-cell level. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15:824-827.
[3]
Zhang FQ, Jiang JL, Zhang JT, et al. Current status and future prospects of
stem cell therapy in Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15:242-250.
[4]
Gracon SI, Knapp MJ, Berghoff WG, et al. Safety of tacrine: clinical trials,
treatment IND, and postmarketing experience. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1998;12:93-101.
[5]
Tayeb HO, Yang HD, Price BH, et al. Pharmacotherapies for Alzheimer's disease:
beyond cholinesterase inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther. 2012;134:8-25.
[6]
van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, et al. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer's
Disease. N Engl J Med. 2023;388:9-21.
[7]
Huang C, Chu H, Ma Y, et al. The neuroprotective effect of deep brain
stimulation at nucleus basalis of Meynert in transgenic mice with Alzheimer's
disease. Brain Stimul. 2019;12:161-174.
[8]
Brem AK, Di Iorio R, Fried PJ, et al. Corticomotor plasticity predicts clinical
efficacy of combined neuromodulation and cognitive training in Alzheimer's
disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020;12:200.
[9]
Guo Y, Dang G, Hordacre B, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex modulates electroencephalographic
functional connectivity in Alzheimer's disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:679585.
[10]
Polania R, Nitsche MA, Ruff CC. Studying and modifying brain function with
non-invasive brain stimulation. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21:174-187.
[11]
Eguchi K, Shindo T, Ito K, et al. Whole-brain low-intensity pulsed ultrasound
therapy markedly improves cognitive dysfunctions in mouse models of dementia -
Crucial roles of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Brain Stimul. 2018;11:959-973.
[12]
Leinenga G, Gotz J. Safety and Efficacy of Scanning Ultrasound Treatment of
Aged APP23 Mice. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:55.
[13]
Liu M, Jevtic S, Markham-Coultes K, et al. Investigating the efficacy of a
combination Abeta-targeted treatment in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Brain Res. 2018;1678:138-145.
[14]
Lipsman N, Meng Y, Bethune AJ, et al. Blood-brain barrier opening in
Alzheimer's disease using MR-guided focused ultrasound. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2336.
#br#
