周围神经损伤
-
Figure 4|Whole-mount immunofluorescence imaging of the sciatic nerve for neurofilaments, blood vessels, and myelin proteins.
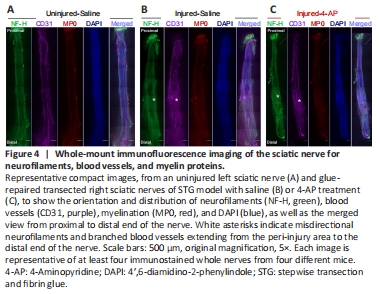
To examine the histology of the regenerating nerve after 12 weeks of surgery, we performed immunofluorescence staining of the whole nerve stained with NF-H to label neurofilament, CD31 to label blood vessels, MP0 to label myelin, and DAPI to label nuclei. We first compared the STG model treated with saline and 4-AP (Figure 4). Figure 4 shows representative whole-mount immunofluorescence images of left (uninjured; A) and right (injured) sciatic nerves in saline (injured-saline; B) and 4-AP (injured-4-AP; C) groups of the STG model stained with NF-H, CD31, MP0, and DAPI. Uninjured nerve displays normal nerve architecture with uniform neurofilaments (NF-H), blood vessels (CD31), myelination (MP0), DAPI, and merged staining over the entire length. In contrast, peri-injury and distal ends of the injured nerve in both saline and 4-AP groups are markedly different with misdirected neurofilaments and branched blood vessels. We did not observe any noticeable effect of 4-AP on the regenerating nerve after STG surgery.
Figure 5|Whole-mount immunofluorescence imaging of the sciatic nerve for neurofilaments, blood vessels, and myelin proteins.
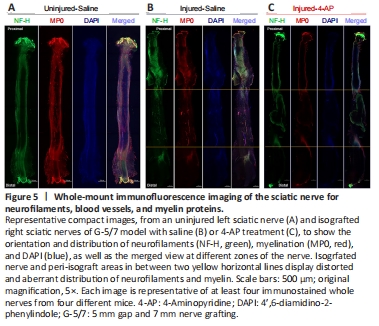
We next examined the G-5/7 model treated with saline and 4-AP for nerve histology (Figure 5). Figure 5 shows representative whole-mount immunofluorescence images of left (uninjured; A) and right (injured) sciatic nerves in saline (injured-saline; B) and 4-AP (injured-4-AP; C) groups of the G-5/7 model stained with NF-H, CD31, MP0, and DAPI. While the uninjured nerve demonstrates normal nerve architecture with uniform NF-H, MP0, and DAPI and merged staining over the entire length, the isografted nerve (G-5/7) in both saline and 4-AP groups was strikingly different from the uninjured nerve with bulging at the peri-isograft areas, aberrant distribution of neurofilaments, and disruption of myelination.
Figure 6|Whole-mount immunofluorescence imaging of the sciatic nerve for neurofilaments, blood vessels, and myelin proteins.
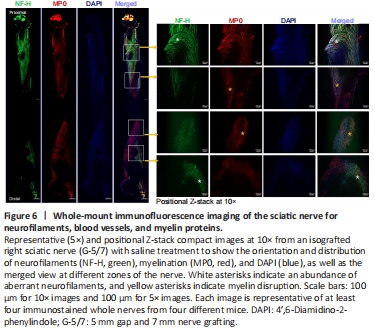
The magnified images of an isografted nerve (G-5/7 saline) in Figure 6 shows markedly distorted and haphazardly arranged neurofilament-stained regenerating axons with myelin breakdown. Similar to the STG model we did not observe any noticeable effect of 4-AP on the regenerating nerve in the G-5/7 model. In the G-7/0 model, there was no nerve to examine because it was dissected out for isografting and the proximal end was buried inside the adjacent muscle.