周围神经损伤
-
Figure 5| Identification of Schwann cells and luciferase reporter assay.
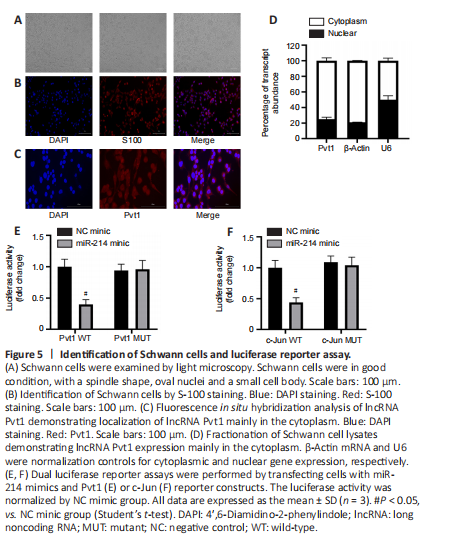
Cultured Schwann cells (Figure 5A) were identified by S-100 staining (Figure 5B). In fluorescence in situ hybridization using a probe for Pvt1 showed fluorescence mostly in the cytoplasm (Figure 5C). Examination of nuclear and cytoplasmic RNAs of Schwann cells by qPCR further confirmed that Pvt1 was primarily present in the cytoplasm. These results indicate that Pvt1 may regulate its target gene at the post-transcriptional level (n = 3, P < 0.05; Figure 5D).
Figure 7| lncRNA Pvt1 can promote the proliferation and migration of Schwann cells in vitro.
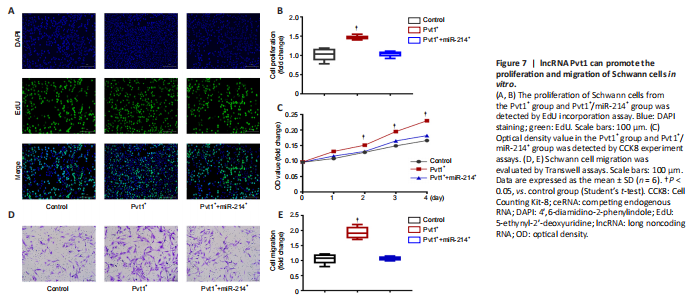
To examine the role of lncRNA Pvt1 on Schwann cell proliferation, we performed EdU incorporation and CCK8 assays. EdU assays showed that the proliferative ability of Schwann cells in the Pvt1+ group was clearly higher compared with that of controls (n = 6; Figure 7A and B). However, co-transfection with miR-214 reduced proliferation to levels similar to those of controls (P > 0.05). Similarly, CCK8 assays showed increased proliferation of the Pvt1+ group; there was no significant difference in proliferation between the Pvt1+/miR-214+ and control groups at any time point (n = 6, P > 0.05; Figure 7C). These results show that lncRNA Pvt1 can promote the proliferation of Schwann cells in vitro, but miR-214 overexpressing eliminates the effect of Pvt1 on Schwann cell proliferation.
Figure 8|Pvt1 promotes Schwann cell migration and peripheral nerve repair in the in vivo environment.
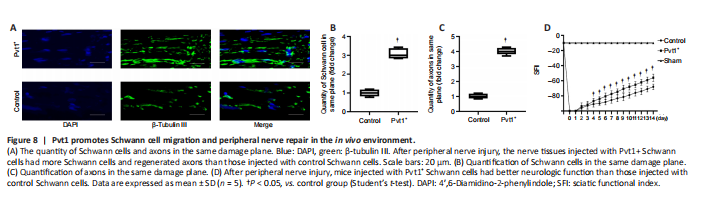
To elucidate the effect of Pvt1 on Schwann cell activation and nerve regeneration in vivo, we generated a PNI model and Schwann cells expressing pcDNA3.1-Pvt1 or vector controls were injected into injured sites of mice. Two weeks later, the nerve tissues in the damaged area were collected and analyzed. The proliferative ability of Schwann cells in the injured nerve segment in the Pvt1+ group was significantly higher than that in the control group (n = 5, P < 0.05; Figure 8A and B). In addition, the number of axons across the injured sites was greater in the Pvt1+ group than that in the control group (n = 5, P < 0.05; Figure 8A and C). These results demonstrated that Pvt1 overexpressing Schwann cells enhanced the regenerative ability of injured nerves following PNI.