神经退行性病
-
Figure 1|Nurr1 knockdown reduces TH expression.
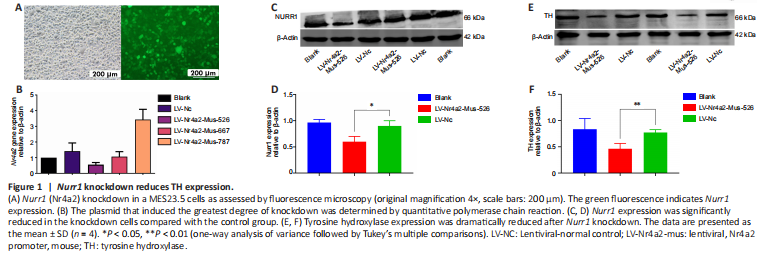
TH is a well-known dopaminergic neuron marker (Mendez et al., 2005; Tian et al., 2008). To determine whether Nurr1 is necessary for dopaminergic neuron survival, TH expression was analyzed after Nurr1 knockdown. First, we sought to identify the plasmid that conferred the greatest level of knockdown. MES23.5 cells were transiently transfected with the three plasmids using LipofectamineTM 2000. Fluorescence was evident after 72 hours, indicating that the transfection was successful. Additional file 1 explains how the transfection was conducted. For the sake of simplicity, only the most effective knockdown plasmid is shown. The knockdown efficiency of the plasmids was also determined by qPCR, which showed that LV-Nr4a2-mus-526 conferred the greatest level of knockdown (Figure 1A and B). The western blot results indicated that Nurr1 expression was significantly lower in cells transfected with LV-Nr4a2-mus-526 compared with the control (P = 0.0487, t = 4.366, df = 2; Figure 1C and D). TH expression was markedly lower in Nurr1 knockdown cells compared with control cells (P = 0.0021, t = 21.95, df = 2; Figure 1E and F).
Figure 4|Nurr1 (A) and tyrosine hydroxylase (B) immunoreactivity.
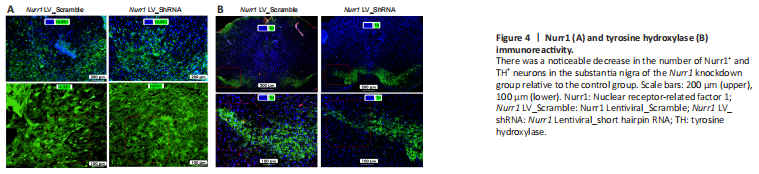
The methods used to assess TH and Nurr1 immunoreactivity in the striatum and perform double labeling of TH and Nurr1 in the substantia nigra are described in Additional file 1. The immunofluorescence staining results showed a noticeable decrease in Nurr1+ and TH+ neurons in the substantia nigra, as indicated in Figure 4A and B, respectively, suggesting that Nurr1 knockdown leads to dopaminergic neurons degeneration.
Figure 8|Dual immunofluorescence analysis of CD74 expression in the substantia nigra of a Nurr1 knockdown mouse model (n = 5).

To ascertain whether CD74 expression is altered in Nurr1 knockdown mouse cells, we performed double immunofluorescence staining. This experiment was performed as part of the second phase of the study in which Nurr1 LV_shRNA was injected into the left striatum of the mouse brain, while the right striatum was injected with Nurr1 LV_Scramble as a control (n = 10). Dual immunofluorescence analysis indicated that the elevated CD74 expression observed in the Nurr1 knockdown group relative to the control group corresponds to dopaminergic neuron degeneration, as indicated by a decrease in TH and Nurr1 immunoreactive neurons (Figure 8).