周围神经损伤
-
Figure 4|Representative histological sections of peripheral nerves with viable axons showing five axonal/myelin categories.
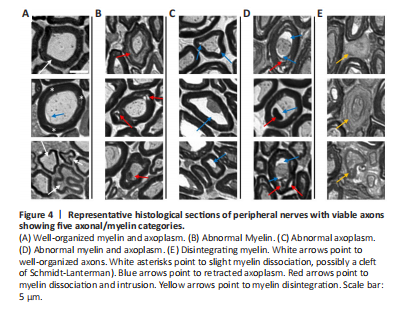
To characterize some of the unique features that represent less severe WD in PNVAs following multiple days of storage, we have developed a five-category classification system to describe axonal morphologies. Those five categories are (1) well-organized myelin and axoplasm, (2) abnormal myelin, (3) abnormal axoplasm, (4) abnormal myelin and axoplasm, and (5) disintegrating myelin. Figure 4 shows examples of this five-category classification system illustrated in individual panels as follows.
Figure 5|Morphological analyses of axons in stored peripheral nerves with viable axons.
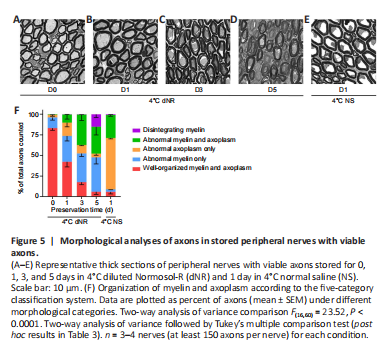
To assess the morphological correlates of PNVAs in 4°C dNR, we sampled PNVAs on storage days 0, 1, 3, and 5 (Figure 5A–E). We compared morphological data for 4°C dNR (the solution with the best CAP survival curve in Figure 3) with those for PNVAs stored 4°C NS (one of the storage solutions with the worst CAP survival curve) on day 1, since that is the last day when CAPs in most PNVAs remained viable in NS. Table 3 shows percentages of axons for each morphological category within each group; Table 4 shows statistical comparisons for each morphological category between groups.