脑损伤
-
Figure 1|Characterization of MSC-Exo.
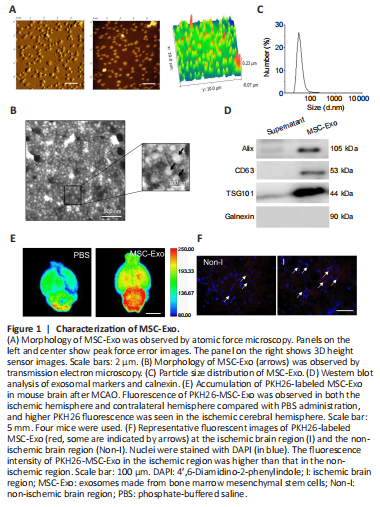
MSC-Exo were collected and purified from BM-MSCs. The morphology of MSC-Exo was verified using atomic force microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. As shown in Figure 1A and B, MSC-Exo were characterized by nanometric spheres with a smooth surface and a nanometric diameter. The average size of MSC-Exo was 70 ± 5 nm (Figure 1C). Western blot assay showed that Alix, CD63 and TSG101 (exosomal markers) were expressed in the MSC-Exo (pellet) fraction, but not in the cell culture supernatant, suggesting that MSC-Exo have been isolated and collected by centrifuging culture medium (Figure 1D). Calnexin, which is expressed in endoplasmic reticulum, was not expressed in the MSC-Exo fraction.
We next labeled MSC-Exo with fluorescence labeling (PKH26) to examine the ability of PKH26-labeled MSC-Exo to penetrate the blood-brain barrier in ischemic injury model animals. PKH26-MSC-Exo fluorescence was observed in both the ischemic hemisphere and contralateral hemisphere, and higher PKH26 fluorescence was seen in the ischemic cerebral hemisphere compared with the contralateral hemisphere (Figure 1E and F). This result indicated that MSC-Exo efficiently crossed the blood-brain barrier.
Figure 3| IL-33 expression level in the peri-infarct penumbra of mice with ischemic stroke.
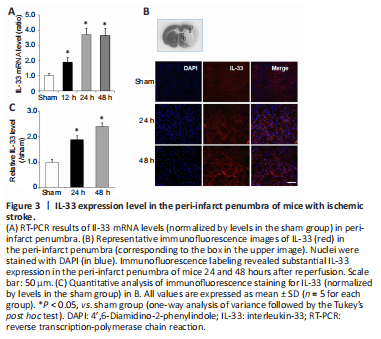
We next investigated Il-33 mRNA and protein expression in the peri-infarct penumbra of mice using RT-PCR and immunofluorescence labeling. At 12, 24, and 48 hours after reperfusion, Il-33 expression was elevated in the peri-infarct penumbra relative to the sham group for 25 hours (Figure 3A). Immunofluorescence labeling also revealed substantial IL-33 expression in the peri-infarct penumbra at 24 and 48 hours after reperfusion (Figure 3B and C). These findings imply that IL-33 may play a crucial role in the response to cerebral ischemic damage.
Figure 5|MSC-Exo regulates the IL-33/ST2 pathway in the peri-infarct penumbra of mice.
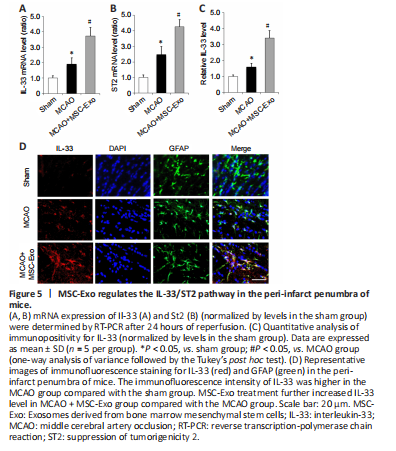
We next investigated the effects of MSC-Exo administration on the IL-33 signaling pathway after ischemic injury. At 24 hours following MCAO, Il-33 and St2 mRNA expression levels were elevated in the peri-infarct penumbra of mice; both Il-33 and St2 expression levels were enhanced by MSC-Exo treatment (Figure 5A and B). We then co-stained brain slices for IL-33 and the astrocyte marker GFAP (Xu et al., 2020). As shown in Figure 5C and D, the immunofluorescence intensity of IL-33 was higher in the MCAO group compared with the sham group, and MSC-Exo treatment further increased IL-33 level compared with levels in the MCAO group. Immunofluorescence staining showed that IL-33 was mainly co-localized with astrocytes (indicated by GFAP staining) (Figure 5D). These data suggest that MSC-Exo modulates the IL-33/ST2 pathway in astrocytes after cerebral ischemic injury.