视神经损伤
-
Figure 1|Characterization of CTH-mNFG.
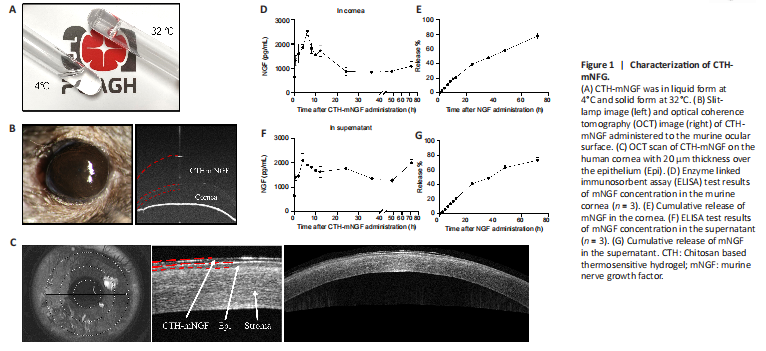
结果:As shown in Figure 1A, CTH-mNGF was in liquid form at 4°C and solid form at 32°C. Transparence of CTH-mNGF on the murine ocular surface was shown by a low OCT reflection signal (Figure 1B). CTH-mNGF on the human cornea was observed by OCT scan, with 20 μm thickness over the epithelium (Figure 1C). The kinetics of mNGF release were calculated from the concentration of mNGF in the murine cornea after CTH-mNGF administration, along with the concentration of mNGF in the supernatant of solidified CTH-mNGF within 72 hours. As shown in Figure 1D, mNGF was maintained over 1300 pg/mL for more than 20 hours in vivo. Accumulative release of NGF was 39.1% at 24 hours and 77.8% at 72 hours in vivo (Figure 1E). mNGF was maintained at about 1500 pg/mL for more than 36 hours in the supernatant (Figure 1F), with the accumulative NGF release rate being 41.2% at 24 hours and 73.9% at 72 hours (Figure 1G). The sustained-release system was used to reduce the dosing frequency, and may also help maintain NGF concentration on the ocular surface during sleep. CTH-mNGF was applied twice a day for 10 days in the subsequent animal study, and twice a day for 8 weeks in the clinical study.
Figure 2|Corneal denervation model.
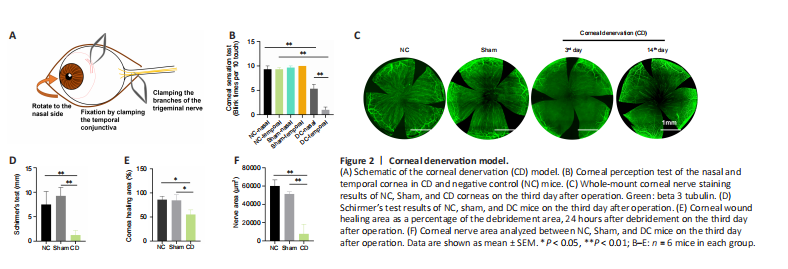
结果:To determine the effect of CTH-mNGF on corneal reinnervation, we used a murine model of NK. To induce CD, the mice underwent clamping of the ciliary nerve of the trigeminal nerve. The experimental procedures are summarized in Figure 2A and were confirmed by whole-mount corneal nerve staining and the corneal perception test. Sham mice underwent the same ciliary nerve exposure process but without clamping, with unoperated mice as negative controls (NC). Whole-mount corneal nerve staining showed that most of the corneal nerves had disappeared by 3 days after clamping, except for the nasal quarter in CD mice (Figure 2C and F). Two weeks after operation, the corneal nerves of mice had regenerated, but at a lower density than in the control group. The corneal perception test showed a loss of temporal perception in the cornea of CD mice on the third day after operation (Figure 2B). Schirmer’s test results showed decreased tear secretion in the CD group, while the epithelial debridement wound area showed less corneal healing area in the CD group on the third day after operation (Figure 2D and E). The intervention started on the fourth day in the follow-up study.
Figure 3|Corneal perception, corneal nerve attribution, Schirmer’s test, and corneal epithelial wound healing of CD mice 10 days after CTH-mNGF treatment.
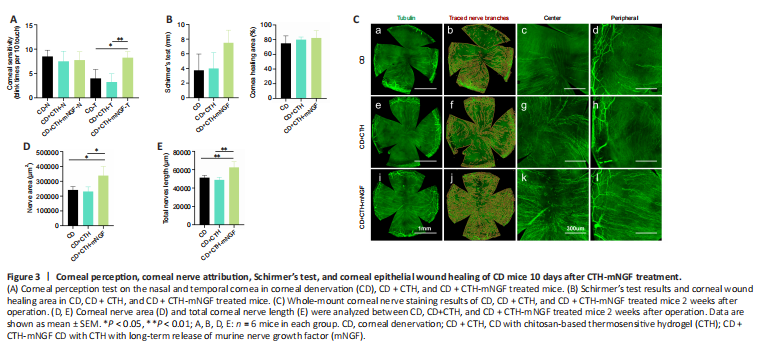
结果:On the fourth day of the CD model, the postoperative mice were randomly divided into three groups, in which the CD group received no eye drops and the other two groups received 10 μL of CTH or CTH-mNGF eye drops twice a day for 10 days. The mice were observed after 2 weeks. As shown in Figure 3A, the nasal corneal perception was 8–10 blinks per 10 stimuli across the three groups. Temporal corneal perception was significantly higher in the CTH-mNGF treated group compared with the CD and CTH treated groups (P < 0.05). Schirmer’s test and epithelial debridement wound healing area showed a trend of improvement in the CTH-mNGF treated group, albeit without statistical significance (Figure 3B). Whole-mount corneal nerve staining showed a higher nerve density in the central and peripheral cornea in the CTH-mNGF treated group (Figure 3C). Quantitative statistical results showed that the corneal nerve area and total nerve length were significantly higher in the CTH-mNGF treated mice compared with the other two groups (P < 0.05; Figure 3D and E).
Figure 4|Clinical results following 8 weeks of CTH-mNGF treatment in seven eyes (from six patients) with neurotrophic keratopathy.
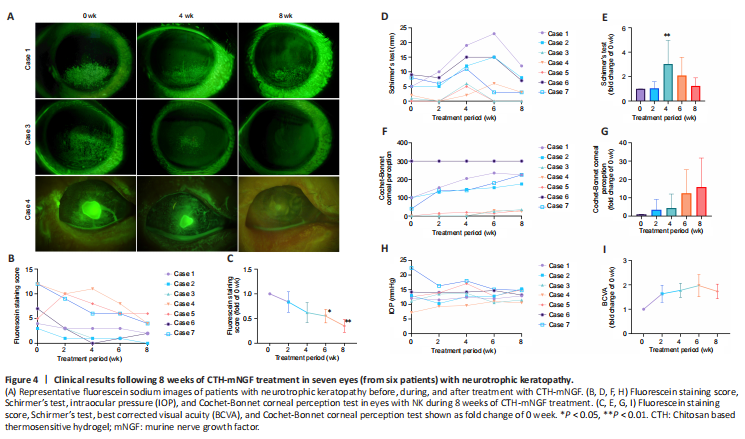
结果:The patients received one drop (approximately 50 μL) of CTH-mNGF on the ocular surface of the affected eye twice a day for 8 weeks. After 8 weeks of treatment with CTH-mNGF, all participants showed a decreased corneal epithelial defect area, as stained by fluorescence (Figure 4A–C). Cases 2 and 3 reached full recovery, while six out of seven eyes had a fluorescence staining score < 5. Schirmer’s test results showed improved tear secretion at 4 weeks but this effect was not prominent at 8 weeks (Figure 4D and E). The corneal perception test (Figure 4F and G) and BCVA results (Figure 4I) showed a trend of improvement but without statistical significance. Intraocular pressure showed no obvious alterations (Figure 4H).
Figure 5|IVCM results of Case 1.
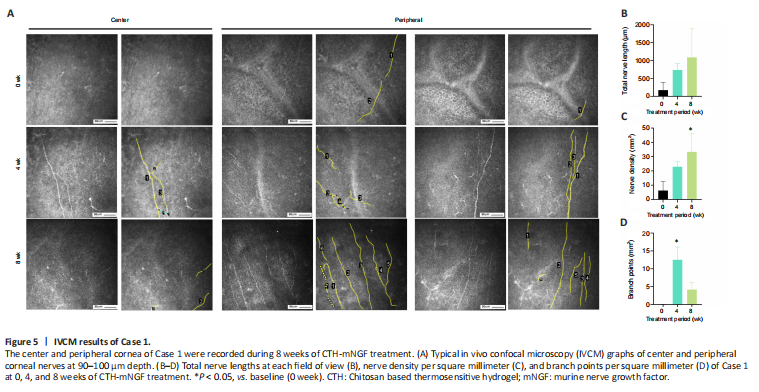
结果:An increase in corneal nerve density after 8 weeks of CTH-mNGF treatment was observed in three out of seven eyes (in cases 1, 2, and 6). The IVCM results of Case 1 showed a significant increase in nerve density compared with baseline at week 8 (P < 0.05; Figure 5A and C), and a significant increase in the number of branches of corneal nerves compared with baseline at week 4 (P < 0.05; Figure 5D). There was no statistical difference in the length of the nerve among the three time points (Figure 5B).
点击此处查看全文