周围神经损伤
-
Figure 7|Adenosine Adora2b (A2B) receptors are involved in the modulation of itch.
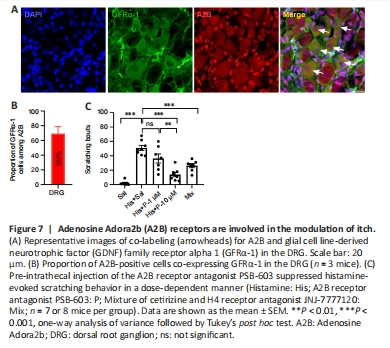
The expression of Mrgpra3 in neuron_10 suggests that it might mediate itch sensation (Usoskin et al., 2015; Li et al., 2016; Peirs and Seal, 2016). Notably, this type of neuron also highly expressed Gfra1 and Adora2b (Figures 2C, D and 6F). We next carried out immunohistochemical co-labeling for the A2B receptor and GFRα-1 (Sakai et al., 2017) in DRG neurons (Figure 7A). Approximately 69% of A2B-positive neurons were also positive for GFRα-1 (Figure 7B). Next, we used the scratching behaviour assay (Jang et al., 2015) to determine whether A2B receptors in the DRG are involved in itching behaviour. We employed a pharmacological approach to block the activities of A2B receptors by intrathecal injection of PSB-603, a selective A2B receptor antagonist (Schiedel et al., 2011). Interestingly, pre-administration of PSB-603 effectively prevented histamine-induced scratching behaviour in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 7C). The histamine-induced scratching bouts were reduced by PSB-603 at a dose of 10 μM, but not 1 μM (Figure 7C). To examine the involvement of histamine receptors in the scratching behaviour, we pre-administered a cocktail of the H1 receptor antagonist cetirizine and the H4 receptor antagonist JNJ 7777120 (Rossbach et al., 2011). The scratching behaviour was suppressed by this combination of histamine receptor antagonists (Figure 7C). These results indicate that A2B receptors are involved in histamine-induced itch sensation.