周围神经损伤
-
Figure 1 | FK506 improves motor function in rats with sciatic nerve injury.
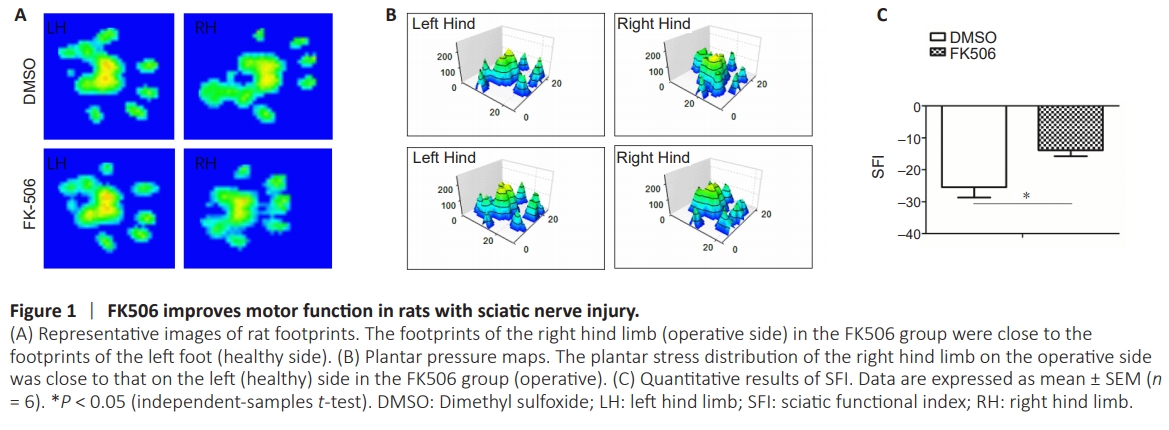
The SFI of the FK506 group was significantly higher than that of the DMSO group at 6 weeks after surgery (P < 0.001; Figure 1)
Figure 3 | FK506 improves sciatic nerve morphology in rats with sciatic nerve injury.
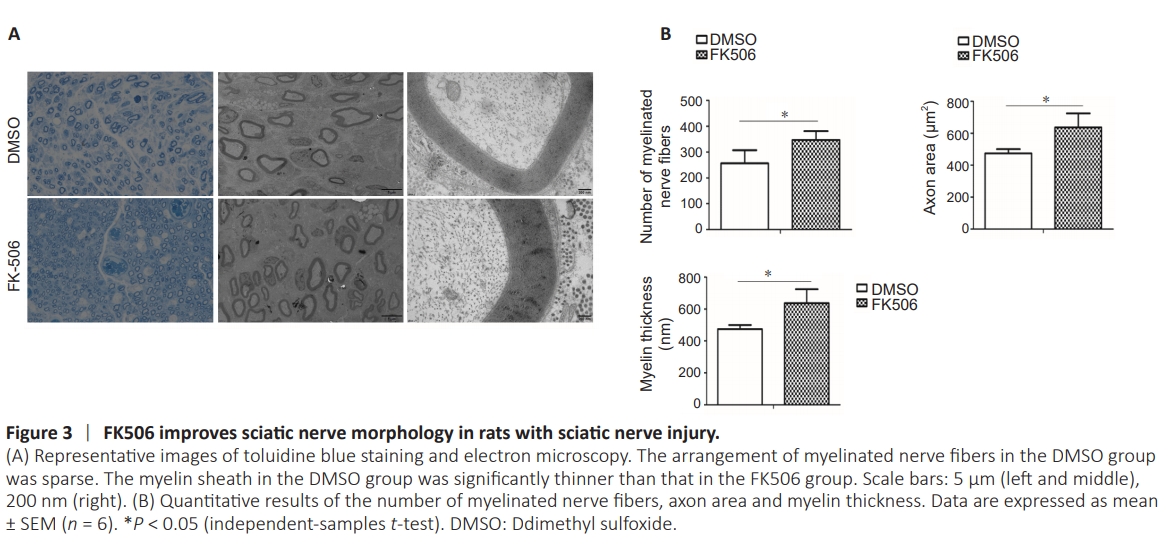
Toluidine blue staining showed that myelin sheaths in the FK506 group were substantial and evenly distributed, with a regular and even appearance. In the DMSO group, myelin regeneration was poor and unevenly distributed (Figure 3). The number of myelinated nerve fibers, axon area, and myelin thickness in the FK506 group were higher than those in the DMSO group.
Figure 4 | FK506 promotes the recovery of sensory neural circuits in rats with sciatic nerve injury.
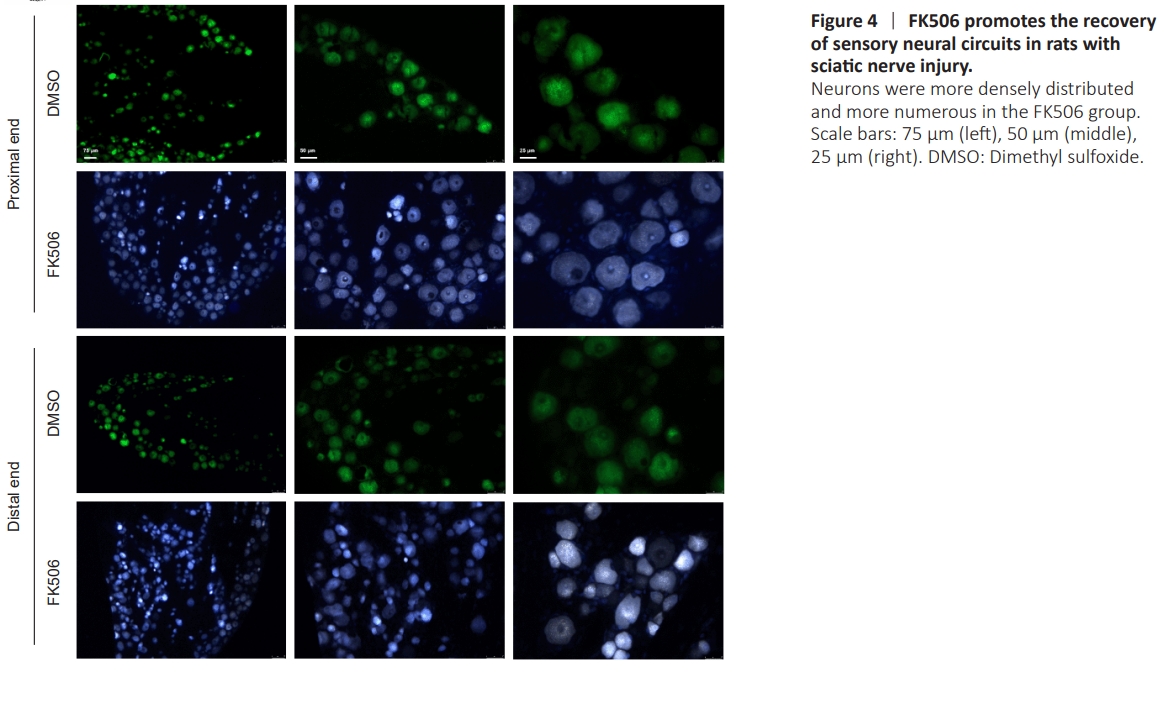
Figure 5 | FK506 promotes the recovery of motor neural circuits in rats with sciatic nerve injury.
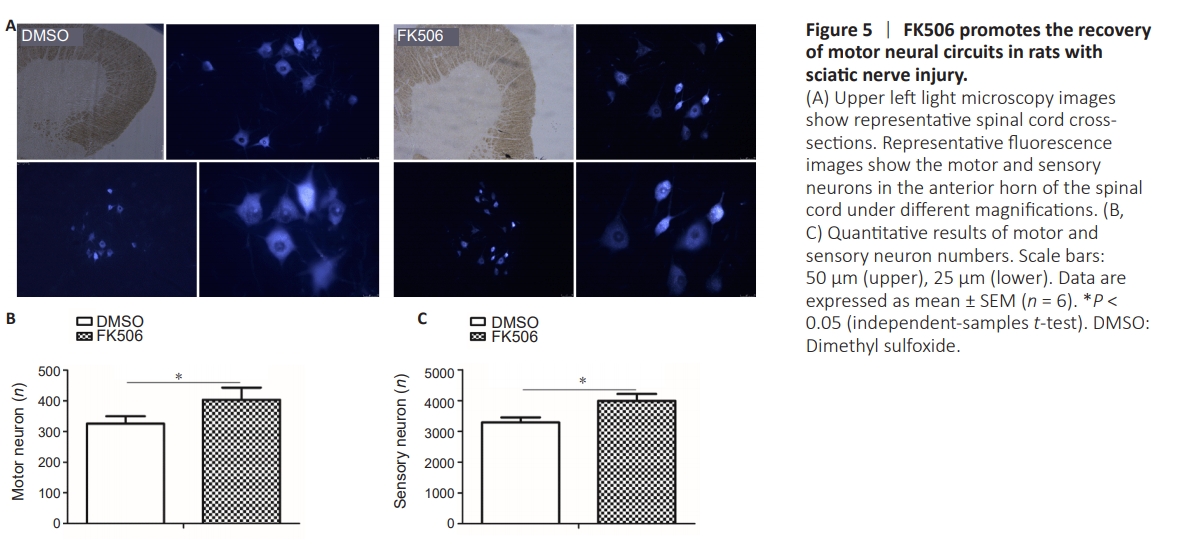
The numbers of sensory neurons and anterior horn motor neurons in the L4 dorsal root ganglion of the FK506 group were significantly higher than those in the DMSO group (Figures 4 and 5).
Figure 6 | FK506 suppresses inflammation in the dorsal root ganglion of rats with sciatic nerve injury.

The expressions of inflammatory factors NF-κB, TLR-4, MMP13, AKT, m-TOR, p70S6K, and IL-1β) were significantly reduced in the FK506 group compared with the DMSO group (Figure 6). The expression of SIRT1 was not different between the two groups (P = 0.177).