视神经损伤
-
Figure 1|Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction determination of MIAT mRNA expression in the retinas of mice at 1 day after transfection.

Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction results showed that the expression level of MIAT in the retinas of the hyperoxia MIAT siRNA group was reduced to 67.52% of that in hyperoxia control siRNA group at 1 day after transfection (P < 0.05; Figure 1).
Figure 2|Effect of long non-coding RNA on the retina morphology of oxygen-induced retinopathy mice detected by fluorescein isothiocyanate staining.
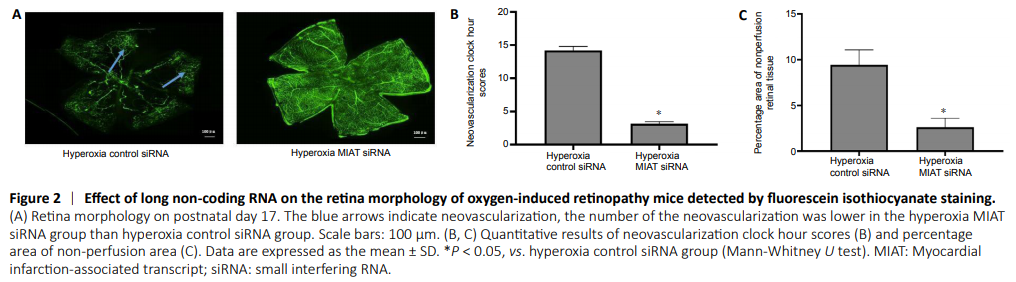
Results of fluorescein isothiocyanate staining showed that in the hyperoxia control siRNA group, the retina showed obvious vascular leakage and a large area of no perfusion area (Figure 2A). The pathological changes were alleviated in hyperoxia MIAT siRNA group compared with the hyperoxia control siRNA group (P < 0.05; Figure 2B and C).
Figure 3|Effect of long non-coding RNA on the preretinal neovascular cells of oxygen-induced retinopathy mice detected by hematoxylin-eosin staining.

Hematoxylin-eosin staining showed that the number of neovascular nuclei breaking through the inner limiting membrane was calculated to quantify the RNV (Figure 3). The number of preretinal neovascular cells in the hyperoxia MIAT siRNA group was lower than that in hyperoxia control siRNA group (Z = –4.427, P < 0.05). This result suggested that MIAT siRNA exhibited anti-neovascularizative effects in the retina.
Figure 4|Effect of long non-coding RNA on the immunopositivities of p-PI3K, p-AKT, and VEGF in the oxygen-induced retinopathy model mice as determined by immunohistochemistry.
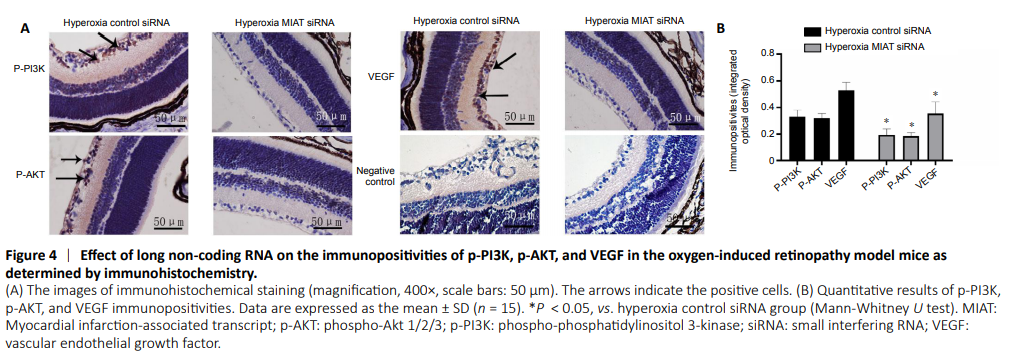
Immunohistochemical staining of retinal sections revealed that p-PI3K, p-AKT, and VEGF were highly expressed in the ganglion cell layer, inner plexiform layer, inner nuclear layer, and outer plexiform layer (Figure 4). However, their immunopositivities were lower in the hyperoxia MIAT siRNA group than those in hyperoxia control siRNA group (P < 0.05).
Figure 5|Effect of long non-coding RNA on the protein and mRNA expression in the PI3K/AKT/VEGF signaling pathway in the oxygen-induced retinopathy mouse model.
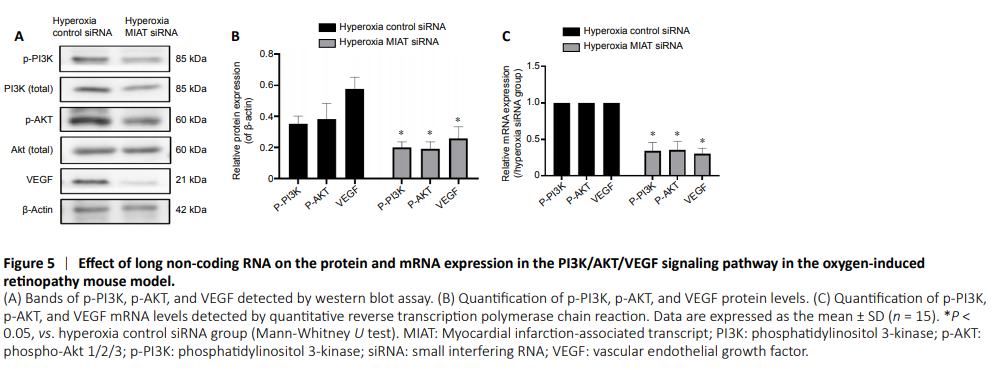
Western blot analysis and quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction were performed to detect the expression levels of PI3K, AKT, and VEGF. Western blot results showed that the p-PI3K, p-AKT, and VEGF protein levels in the hyperoxia MIAT siRNA group were decreased by 40.94 ± 3.94%, 49.28 ± 4.16%, and 40.63 ± 4.03%, respectively (P < 0.05, vs. hyperoxia control siRNA group; Figure 5A and B). Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction revealed that the p-PI3K, p-AKT, and VEGF mRNA levels in the hyperoxia MIAT siRNA group were decreased by 48.73 ± 3.98%, 46.79 ± 3.87%, and 55.09 ± 4.26%, respectively (P < 0.05, vs. hyperoxia control siRNA group; Figure 5C). These results demonstrated that MIAT is involved in the process of RNV in ROP, and inhibition of MIAT may effectively inhibit RNV through the PI3K/AKT/VEGF signaling pathway.