脊髓损伤
-
Figure 4|DPSC-CM inhibits microglial pyroptosis after SCI.
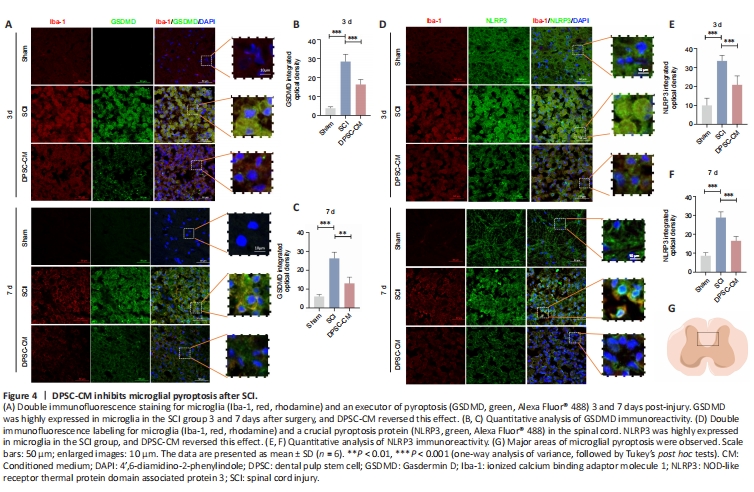
Co-immuno?uorescence staining for ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba-1) and GSDMD was used to examine whether DPSC-CM affects microglial pyroptosis in vitro. The fluorescence intensity of GSDMD in Iba1+ cells in the DPSC-CM group was signi?cantly lower than that in the SCI group 3 and 7days after SCI (Figure 4A–C). To further determine the effect of DPSC-CM on microglial pyroptosis, we NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β expression in microglia 3 and 7 days post-SCI using co-immunofluorescence staining. The fluorescence intensity of NLRP3 in Iba1+ cells in the Con-CM SCI group was signi?cantly higher than that in the DPSC-CM SCI group 3 and 7 days after SCI (Figure 4D–F). Caspase-1 and IL-1β exhibited similar changes to NLRP3 at 3 (Additional Figure 2A–D) and 7 days after SCI (Figure 4G and Additional Figure 3A–D).
Figure 5|DPSC-CM enhances neural repair and reduces GFAP expression in the spinal cord after SCI.
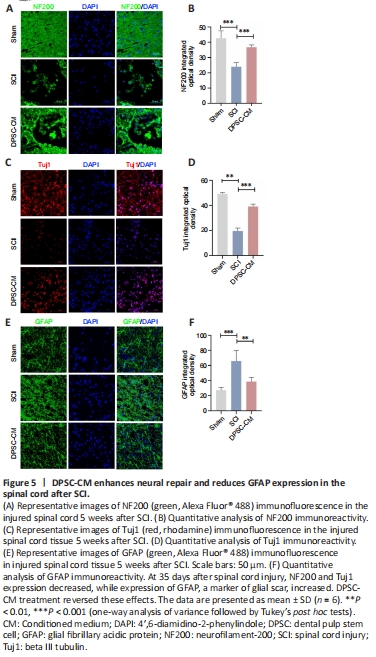
Immuno?uorescence staining showed higher integrated optical densities of neurofilament-200 (NF200), beta III tubulin (Tuj1), and myelin basic protein (MBP) in the spinal cord of DPSC-CM–treated rats compared with rats in the SCI group (Figure 5A–D and Additional Figure 4A and B). The fluorescence intensity of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), a marker of activated astrocytes and glial scar (Jiang and Zhang, 2018), was increased in Con-CM SCI rats at 35 days post-SCI compared with the control group. Importantly, DPSC-CM treatment inhibited GFAP upregulation after SCI (Figure 5E and F). These findings suggest that DPSC-CM attenuated SCI-induced downregulation of neuro?lament protein and myelin, and reduced glial scar formation.