NRR:上海交通大学医学院陈生弟团队揭示生酮饮食改善阿尔茨海默病的新作用机制
撰文:江静雯,潘泓,沈帆霞,谭玉燕,陈生弟
阿尔茨海默病 (AD) 是一种慢性进展性神经退行性疾病,以认知功能下降以及伴随精神和行为障碍为特征。目前很少有药物被证明可有效降低AD的患病风险或减缓疾病的进展,因此,营养和代谢治疗可能成为解决这些问题的策略之一。生酮饮食(Ketogenic diet,KD)是一种低碳水化合物、高脂肪和适量蛋白质的营养饮食模式。已有小样本人群的临床研究中显示生酮饮食能改善患者的语言记忆。这些发现令人鼓舞,尤其KD的益处如果在长期研究中得以证实,将为AD的防治带来希望,然而KD神经保护机制尚未得到充分研究。Aβ级联反应假说和 tau 蛋白假说已逐渐成为AD相关研究的主导理论,发现代谢降低、线粒体功能障碍、炎症和氧化应激都与AD的发病机制有关。一些研究表明,生酮饮食的积极作用与减轻炎症反应和氧化损伤密切相关。核因子E2相关因子2(nuclear factor E2-related factor 2,Nrf2) 作为内源性氧化应激的重要调节器,已被证明可以减少炎症反应。因此,上海交通大学医学院的陈生弟团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》 (Neural Regeneration Research)上发表的最新研究探究了KD通过调节APP/PS1小鼠模型中的Nrf2信号通路产生抗炎作用的具体机制。
阿尔茨海默病(AD)是一种导致认知功能下降的神经退行性疾病,与大脑慢性炎症有关。生酮饮食(KD)是一种广泛应用于顽固性癫痫的辅助疗法,最近的研究表明,它可能对包括AD在内的某些神经疾病具有治疗作用。该研究旨在探索KD在AD小鼠模型中对认知功能的治疗作用以及相关机制。采用雄性APP/PS1小鼠随机分配到KD或对照饮食组,接受3个月的饮食治疗。结果表明,KD改善了AD小鼠的认知功能,并减少了淀粉样斑块的沉积、胶质细胞增生和促炎细胞因子的水平;并且KD这种抗炎效应是通过增强Nrf2/HO-1信号通路抑制了NF-κB通路活性所产生。因此,以上结果表明,由于KD能够减轻Aβ诱导的炎症所引起的神经毒性,它可能具有防治AD发生发展的潜力。
生酮饮食可改善 APP/PS1 小鼠的认知功能
在该研究中,在给予APP/PS1小鼠三个月的KD治疗后,使用新物体识别实验和Y迷宫自发交替实验评估小鼠的认知功能。结果显示 KD 干预可使APP/PS1小鼠的识别指数显着增加(F [2,33] = 24.32,P < 0.001,图1B),表明KD干预后的APP/PS1小鼠对新物体有更大的探索兴趣。另一方面,CD治疗组显示出较低的比率,表明接受CD的APP/PS1小鼠未能分辨出新事物表现出相应的探索兴趣。为了评估小鼠的空间工作记忆,应用Y 迷宫自发交替实验进行评估。 根据图1D所示,三组之间的小鼠进入Y迷宫各臂条目总数没有显着差异 (p > 0.05)。 表明KD饮食干预对APP/PS1小鼠的运动功能没有影响。该研究结果还显示喂食CD的野生型小鼠的自发交替率显著高于APP/PS1+CD 组 (P < 0.0001) 和 APP/PS1+KD 组 (P<0.05) . (图1E)。与 APP/PS1+CD 组相比,KD 治疗组的自发交替率明显更高(F [2,33] =18.19,P < 0.001)。因此,该研究结果表明 KD 能够减轻APP/PS1小鼠的认知功能缺损。
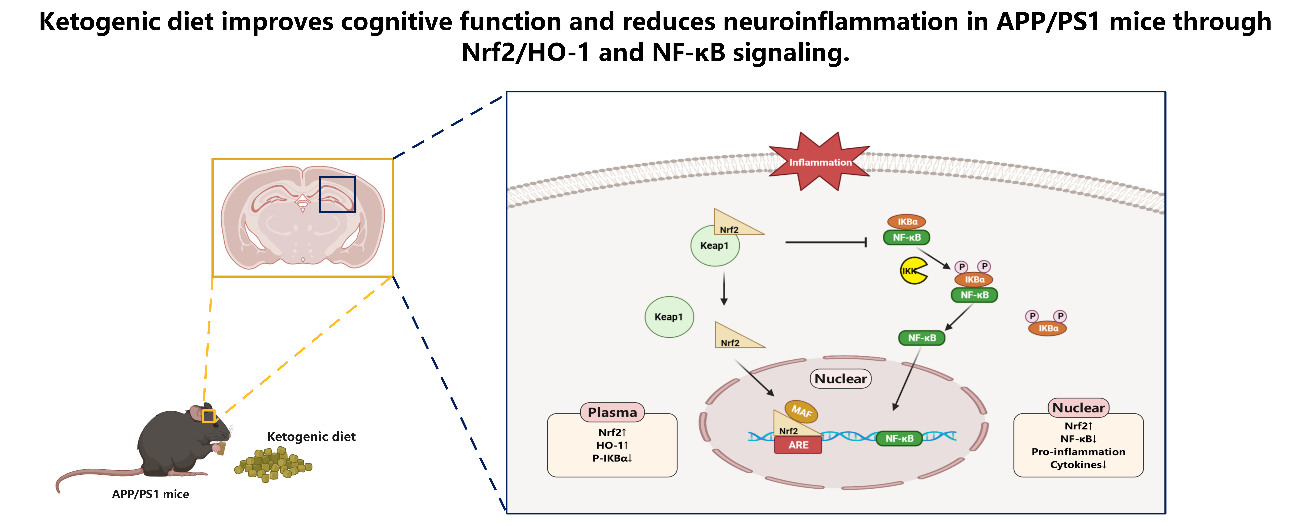
图1 新物体识别和Y迷宫自发交替实验流程示意图和结果
生酮饮食可减少 APP/PS1 小鼠脑内淀粉样斑块沉积
淀粉样蛋白被广泛认为是阿尔茨海默病发病机制的关键因素。 其中Aβ1-42 亚型更易聚集形成Aβ斑块沉淀,是与AD进展密切相关的主要致病因子。实验的免疫荧光结果表明,APP/PS1小鼠海马部位Aβ1-42免疫荧光强度远高于WT小鼠。与采用CD治疗的 APP/PS1 小鼠相比,给予KD的 APP/PS1 小鼠海马部位的 Aβ 斑块阳性区域在统计学上显著减少 (P < 0.0001) (图2A,B)。
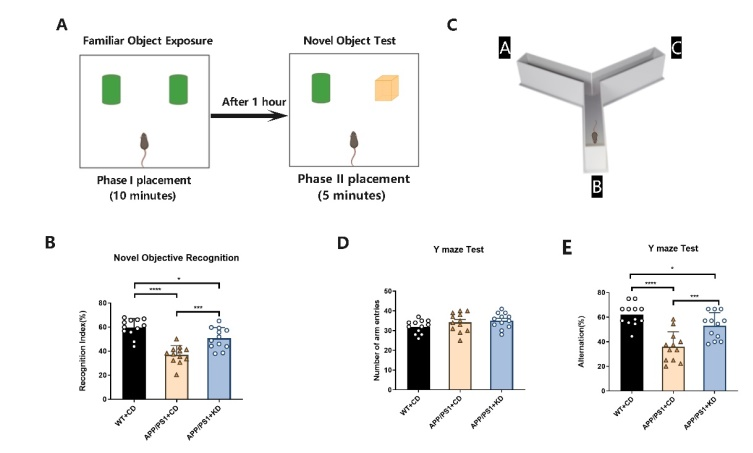
图2 海马部位Aβ1-42免疫荧光染色
生酮饮食可抑制 APP/PS1 小鼠脑内反应性胶质细胞增生
多项研究表明,Aβ异常沉积引起的神经炎症与阿尔茨海默病的进展恶化密切相关,并且星形胶质细胞和小胶质细胞的激活对促进AD的发生发展具有重要作用。为了评估神经炎症,观察小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞的活化情况是被广泛接受的指标。在实验中,免疫荧光染色分析显示 APP/PS1小鼠脑内Iba1 阳性小胶质细胞比例增多,表明 APP/PS1 小鼠脑内小胶质细胞激活显著增高。而KD干预组的小鼠,脑内Iba1 阳性小胶质细胞的比例在皮质和海马部位都显著减少,导致神经炎症反应减少。此外,GFAP表达在APP/PS1模型小鼠的皮质和海马部位显著上调; 然而,KD 干预明显降低了APP/PS1脑内GFAP阳性的星形胶质细胞活化。根据这些结果可以得出:KD 处理可以有效抑制 APP/PS1小鼠脑内小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞的活化(图 3A-D)。
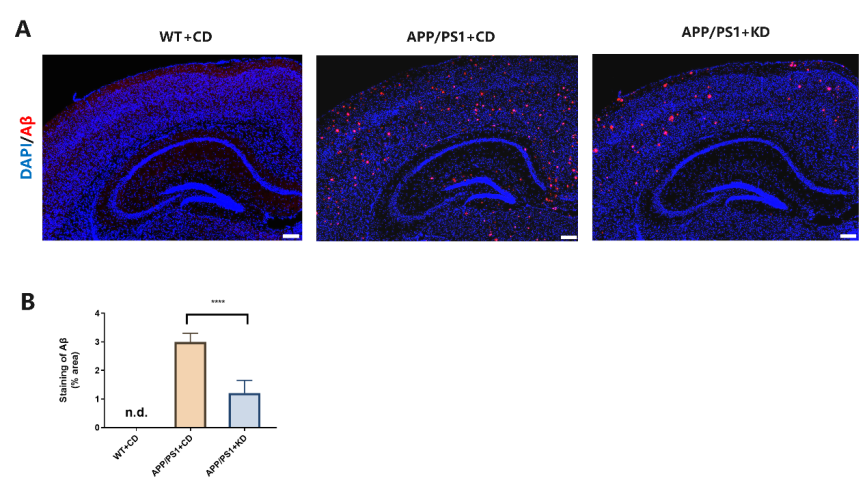
图3 海马皮质部位Iba-1+和GFAP+胶质细胞免疫荧光染色
生酮饮食可降低 APP/PS1 小鼠脑内促炎细胞因子水平
许多细胞因子的释放在神经炎症的致病过程中起着重要的作用。因此,该研究继续观察与 Aβ 沉积引起相关细胞因子的释放水平,包括促炎因子IL-1β、IL-6 和 TNF-α,以及抗炎细胞因子 (IL-10) 。与 WT+CD 组相比,研究结果表明接受CD 干预的 APP/PS1小鼠脑内皮质和海马部位 IL-1β (P < 0.001)、IL-6 (P < 0.01) 和 TNF-α (P < 0.05) 的水平明显增高。 然而,KD 治疗组在皮质和海马部位脑组织中的促炎因子 IL-1β、IL-6 和 TNF-α 水平均显着降低(每个变量 P < 0.05)。通过luminex实验显示,KD干预组APP/PS1小鼠皮质部位IL-10的水平显著增加(P <0.05)。此外,单核细胞趋化蛋白-1 (MCP-1/CCL2)是控制单核细胞和小胶质细胞募集和激活的主要趋化因子之一。检测结果显示KD 治疗干预导致皮质中 MCP-1 水平显著下降 (P < 0.05)。这一发现表明 KD 能够减少 APP/PS1 小鼠的皮层和海马部位的促炎因子的水平(图 4A 和 B)。
 #br#
#br#
图4 海马皮质部位细胞因子水平
生酮饮食可能通过调节Nrf2/HO-1通路影响神经炎症
转录因子 Nrf2 在调节初始免疫反应中起着关键作用。 Nrf2 从细胞质转移到细胞核并与核内DNA中的抗氧化反应区域结合,激活细胞保护基因的转录以响应氧化应激产生一系列调控反应。帕金森病、阿尔茨海默病和肌萎缩侧索硬化被证明是与 Nrf2 活性降低相关的少数几种退行性疾病。根据最近的研究显示,激活的 Nrf2 通路可以抑制 NF-κB 信号通路。在这里,使用蛋白质印迹法观察小鼠皮层和海马部位的脑组织细胞核及细胞浆 Nrf2 水平以及NF-κB 信号通路相关蛋白的表达。 在 APP/PS1 小鼠的皮层和海马部位的脑组织中,KD干预显著提高了组织蛋白细胞浆 Nrf2 和 HO-1 的表达,同时细胞浆中 P-IKBα 的表达显著降低(图 5A 和 B);并且核内 NF-κB 水平降低,核内 Nrf2 内移增加(图 5C 和 D)。这些结果表明,生酮饮食可能通过 Nrf2/HO-1 通路直接在 APP/PS1 模型小鼠中引发保护性反应,并且这些反应的效应可能是通过抑制NF-κB 信号通路所产生。

图5 海马皮质部位组织液细胞核及细胞浆各蛋白的表达
结论
该研究证实了生酮饮食可通过激活Nrf2/HO-1途径抑制NF-κB信号通路减轻神经炎症,进而缓解APP/PS1转基因小鼠认知功能的减退。因此,生酮饮食具有缓解Aβ斑块聚集诱导产生神经炎症和认知障碍的能力,证明生酮饮食可能成为防治阿尔茨海默病和其他具有类似病理的神经疾病的治疗策略之一。
讨论与展望
该研究表明,生酮饮食可以减少APP/PS1小鼠脑内Aβ沉积,减轻神经炎症 ,提供神经保护作用,并且这种效应是通过增加AD小鼠脑内Nrf2表达激活Nrf2信号途径抑制NF-κB信号通路所产生,因此可考虑生酮饮食作为Nrf2的天然激动剂成为防治AD有前途的治疗策略之一。尽管需要进一步研究以充分了解其基础机制,但目前的研究结果是乐观的,支持将生酮饮食作为防治阿尔茨海默病的潜在疗法进一步进行探索。
未来,将生酮饮食在阿尔茨海默病和其他神经退行性疾病中的益处继续探究将是有重要临床指导意义的。随着更多研究的进行,将更好地了解饮食的保护作用的潜在机制,并能够设计更有效的治疗阿尔茨海默病和其他相关疾病的防治策略。随着生酮饮食在预防和治疗阿尔茨海默病方面的应用越来越多,以及进一步的基础机制研究。未来,生酮饮食将成为一种更健康、更有效的饮食方式,为人们提供更好的健康保障。
资金支持:研究得到了陈生弟教授主持的国家自然科学基金(82171401,81971187)、上海市科技重大专项(2018SHZDZX05)和上海市教育委员会(2017-01-07-00-01-E00046)的资助,此外,该研究还得到了谭玉燕教授主持的国家自然科学基金(81971183)的资助。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.373715



 #br#
#br#
