NRR:中南大学万莉莉和严小新团队综述报道代谢型谷氨酸受体(mGluRs)在癫痫发生中的作用
撰文:肖文杰 万莉莉
癫痫是一种常见的神经系统性疾病,目前全球有7000多万人患有癫痫,约占总人口的近1%。该疾病以脑内异常同步化放电引起短暂且反复反作为主要特征,若不及时进行诊断及治疗,极易导致患者身体损害甚至死亡。研究表明,癫痫可能是由体内兴奋性和抑制性神经递质的相对不平衡引起[1]。其中,谷氨酸作为哺乳动物中枢神经系统中的重要兴奋性神经递质[2-3],通过激活离子型谷氨酸受体和代谢型谷氨酸受体 (mGluRs) 两种受体,参与调节各种神经元和突触活动。这两种受体对整体脑功能、突触传递和神经元发育的调节至关重要[4],关系着认知、记忆形成、疼痛管理、成瘾和焦虑等各个方面[5-6]。代谢型谷氨酸受体家族是一类在细胞表面广泛分布于大脑主要区域的上游蛋白质,表达于神经元和非神经元细胞中,它们主要通过激活G蛋白调节的信号转导机制调节神经元兴奋性和突触传递[7-9]。因此,明晰mGluRs在癫痫、脑卒中、精神分裂症和神经退行性病变等疾病中的作用意义重大。虽然目前为止有关mGluRs参与癫痫发生的研究众多,但仍缺乏深入而全面的总结。
近期,中南大学万莉莉及严小新团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) in epileptogenesis: an update on abnormal mGluRs signaling and its therapeutic implications”的综述。通过深入总结与分析,作者介绍了三组mGluRs及其相关信号通路(图1),并详细介绍这些受体如何影响癫痫,进而阐述mGluRs的靶点作用以及受体介导的神经保护在癫痫发生机制中的作用。此外,该综述还总结了在癫痫动物和临床研究中这些受体的药理学干预,旨在总结mGluRs在癫痫发生中的不同机制及意义,为未来研究mGluR靶向抗癫痫药物的发展奠定基础。中南大学湘雅医学院临床医学八年制博士生黄乐仪和肖文杰为论文共同第一作者,万莉莉为论文通讯作者。
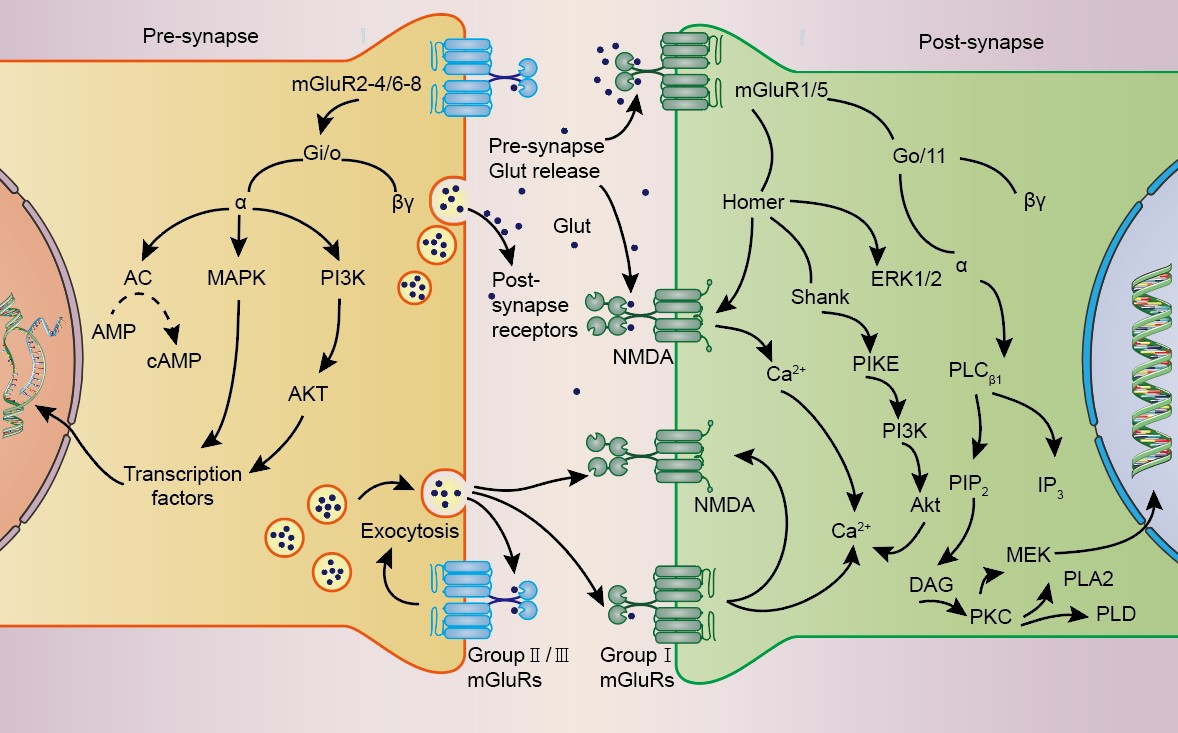 #br#
#br#
图1 Group I, II and III mGluRs及其相关信号通路。(图源:Leyi Huang, et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
Group I mGluRs与癫痫发生
突触后表达的Group I mGluRs 亚型(mGluR1和mGluR5)很少在GABA和谷氨酸神经元突触前终端定位,其表达通常局限于大脑发育早期并影响癫痫发作。对Group I mGluRs介导的癫痫发作研究已有数十年历史,最初主要强调Group I mGluRs和癫痫发作的相关信号通路及机制。尽管Group I mGluRs的高表达与癫痫发作的关系已被充分证实,但其中的因果关系仍尚未明确。Notenboom等证明,mGluR5在存活的神经元中上调可能是癫痫发作的一个原因,并可能进一步导致耐药性颞叶癫痫(TLE)患者海马过度兴奋。这表明mGluR5信号是新型抗癫痫药物的潜在靶标[10]。此外,Sanon等发现,位于口-脑层的癫痫样突发放电部分离不开mGluR5的作用,并且突触后电流包含不同成分,mGluR5对其中的慢速和快速成分均有贡献,而mGluR1α仅对慢速有贡献[11]。这些发现说明不同mGluR1α和mGluR5将通过不同机制导致特异性癫痫活动。基于Group I mGluRs的抑制剂开发药物是有效的。近年随着科学研究的快速发展,早在1995年,McBain等发现mGluR拮抗剂(+)-2-甲基-4-羧基苯甘氨酸(MCPG)可逆地废除周期性内向电流,从而抑制癫痫活动。 随后,Micheli团队开发了甲基苯乙炔吡啶,这是一种选择性和全身活性的非竞争性mGluR5拮抗剂,可有效抑制磷酸肌苷水解,被证明具有治疗癫痫的潜力。Borowicz等重点研究了SIB 1893,这是一种非竞争性的Group I mGluRs拮抗剂,与传统的抗癫痫药物组合,成为一种新的癫痫治疗方法[12]。
近年来人们对mGluRs参与癫痫发生的机制开展了广泛研究。如D'Amore等证明,mGluR5的变化可能是WAG/Rij大鼠失神癫痫发作表型的核心[13],且药物性mGluR5活性增强会导致WAG/Rij大鼠的大剂量依赖性棘波放电发生率和平均持续时间减少,由此提出mGluR5增强剂是治疗失神癫痫的潜在候选药物。同样,Kandratavicius等支持mGluR5在TLE中的保护作用,mGluR5上调可能有助于突触后过度兴奋的适应和谷氨酸过度释放的控制[14]。矛盾的是,Paquet等的研究表明,mGluR5上调可以激活磷脂酶C,并选择性地促进星形细胞从细胞内钙释放库中凋亡,从而引起包括癫痫在内的众多神经系统疾病[15]。此外,Potter等研究了mGluR5在结节性硬化综合症中的作用,验证了mGluR5的增加有助于TSC的癫痫发作活动,并导致成年小鼠海马CA1区突触效能的长时程抑制(LTD)[16]。
异体mGluRs调节剂的研究是未来药物开发的关键。D'Amore等比较了mGluR1的和mGluR5的治疗激活剂在无癫痫发作的WAG/Rij大鼠中的变异性[17]。他们证实,mGluR5(VU0360172)的正向异生调节剂致痫作用是长期存在的,且只伴有轻微耐受性现象。相反,mGluR1受体PAM RO0711401的耐受性在相对较短时间内开始,他们的结果证实了mGluR5 PAM具有治疗长期失神性癫痫的潜能。另研究者将mGlu1和mGlu5受体阳性可变调节剂局部注射到丘脑和皮层,发现两者都能削弱失神性癫痫发作。此外,皮层中的Group I mGluRs刺激会增强GABA能抑制,而丘脑中的刺激会减少GABA能的强直抑制。基于前期研究,D'Amore等得出结论,VU0360172在长期治疗后保持其抗失神癫痫作用,VU0360172可以与乙琥胺联合作用于失神癫痫治疗。还有许多研究基于类似机制测试抗癫痫药物。Kelly等提出用mGluR5 PAM RO6807794治疗Tsc2突变体小鼠模型会加剧癫痫发作和多动性[18]。这一发现证实了mGluR5的抑制可以通过纠正疾病的核心表型,包括癫痫发作、多动性和突触蛋白合成的升高以潜在地治疗癫痫。Hanak等使用塞勒氏小鼠脑脊髓炎病毒诱导的TLE小鼠模型,证明VU0360172,一种选择性的阳性变态mGluR5调节剂,在感染后三天可减少癫痫的急性发作和肿瘤坏死因子-α产生的小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞百分比。此外,VU0360172治疗并没有改变病毒抗原水平,表明它并不影响病毒清除[19]。
关于mGluR5拮抗剂是否能预防癫痫,目前仍有相互矛盾的结论。Dyomina等使用选择性mGluR5拮抗剂MTEP来预防癫痫脑中伴随的星形胶质增生[20]。MTEP引起了短期的胶质激活,并阻止了胺基酸转运体2蛋白的减少。然而,潜伏期加入MTEP并没有改善或缓解癫痫发展。因此,尽管MTEP具有诱导性的神经保护作用,但其对癫痫的预防并无明显效果。
mGluR5也可以与其他分子协同作用影响癫痫。例如,Wang等发现在脑损伤后癫痫发生早期应用CB1受体拮抗剂可以防止mGluR5诱导的海马癫痫发生并延长高兴奋性出现[21]。Xu等证明norbin是一个有力的内源性mGluR5信号调节器,因为norbin和mGluR5在TLE和氯锂-匹罗卡品诱导的癫痫大鼠神经元中共同表达,进一步推测norbin表达减少与癫痫发作有关[22]。此外,mGluR1和mGluR5影响其他途径和蛋白质,如Celli等阐明了mGluR5受体调节GABA传递的过程,其中涉及mGluR5的激活可刺激癫痫WAG/Rij大鼠丘脑中GABA摄取[23]。在各种临床失神癫痫模型中,GABA摄取缺陷与SWD病理生理学有时联系密切。另Crans等利用海人酸(KA)模型,证明了海马CA1区mGluR5受体蛋白在潜伏期晚期(T10)和指数生长早期及晚期(分别为T80和T120)下调[24]。此外,数据表明,在KA模型中癫痫发作率和Homer-1b/c下调有关,认为可能存在一个内源性的神经保护机制。Di Cicco等确定在有症状的WAG/Rij大鼠中,mGluR5受体和Homer蛋白表达的变化会导致LTD缺乏,在Schaffer collateral-CA1突触中mGluR1和mGluR5介导的LTD明显减少,而海马mGluR5依赖的突触可塑性与大鼠的病态WAG/Rij表型有关[25],这些发现证实了长期抑制和冲击吸收是体外低频电刺激抗癫痫活动的体外效应,但是仍需要进一步研究以充分阐明低频电刺激参与抗癫痫效应的细胞及分子机制。
Group II and III mGluRs与癫痫发生
研究表明Group II and III mGluRs 位于谷氨酸神经元的突触前末端,可以减少谷氨酸的释放,进而用于抗癫痫药物的开发。然而,与Group I mGluRs相比,近年来对Group II and III mGluRs 的研究并不多。Das等TLE患者海马组织中检测到明显的mGluR2和mGluR3的升高和星形胶质细胞的激活,提出mGluR2的失调可能在TLE发展中发挥重要作用[26],但他们的研究未能证实这是否是减少神经元活动的一种补偿机制。为了更好地解释其相关机制,Howlett等证明了mGluR II基因突变通过破坏自分泌谷氨酸介导的负反馈和阻止PI3K的激活来提高运动神经元的兴奋性[27]。这些结果表明神经元兴奋性的破坏可能会诱发多种神经疾病,这其中就包括癫痫。
许多研究已经证明,在部分人类癫痫综合征中,由于潜在的癫痫发作机制,谷氨酸摄取不足可诱导啮齿动物癫痫发作。然而,将氨基酸转运体功能障碍与病理性皮质活动联系起来的细胞机制仍然难以捉摸。因此,Molinari等在海马切片的CA1区使用了氨基酸转运体抑制剂TBOA[28],结果显示,细胞外谷氨酸缓冲不足,会导致Group II mGluRs和NMDAR相互转换。这种相互作用启动了海马网络的高兴奋性,促进了谷氨酸释放期间癫痫样活动的产生,并减少了后电流超极化。这项研究加深了我们对潜在的氨基酸转运体异常和癫痫机制的理解。体内实验表明,Group III mGluRs 的表达可能有助于通过内源性谷氨酸激活、兴奋性毒性对抗和癫痫发作抑制来预防和治疗癫痫。此外,Group III mGluRs可能在癫痫发作时神经递质之间的平衡中转向产生更多兴奋性氨基酸。根据Kovalenko等[29]的研究,在锂-匹罗卡品癫痫模型的潜伏期和慢性期,Group III mGluRs基因在海马和颞叶皮层的表达减少,此外,他们得出结论,mGluR8 mRNA的产生在慢性阶段持续减少,而在潜伏阶段几乎没有其他表达变化,因此认为Group III mGluRs 是最有可能预防癫痫的靶点。
近期研究者观察到细胞外富含亮氨酸重复的纤维蛋白域家族蛋白(Elfn1和Elfn2)和Group III mGluRs之间的蛋白质相互作用,Elfn2-KO(LacZ-neo-knockin突变体)小鼠表现出各种行为异常,包括癫痫易感性、多动性和焦虑的增加。最终,使用mGluR4选择性正变体调节剂VU0155041缓解了这些行为异常。由于自身低谷氨酸亲和力,mGluR7被推测为防止谷氨酸水平过高的一种制动器,从而解释了mGluR7缺陷的动物中癫痫发作的难控性。Dunn等猜想,Elfn1对mGluR7激活参与了这一过程,这可以解释当Elfn1被敲除并导致mGluR7功能障碍时由外部刺激引发的癫痫发作[32]。由此可以看出mGluRs的有关蛋白质组和基因组研究对揭开癫痫的神秘面纱具有重要意义,将大大促进有关癫痫治疗的发展。
总结与展望
总之,mGluRs 家族在癫痫的发生和发展中至关重要。研究者总结了这三组mGluRs与癫痫的关系,由此进一步促进癫痫分子标记和药物靶点的开发。他们提出mGluR激动剂和拮抗剂在癫痫治疗中的作用,这为癫痫的药物联合治疗和针对不同发病机制的个体化治疗提供了参考。当然该综述也存在一定性局限性。首先,癫痫一直以来吸引着大量神经科学领域专家们的关注,这些年来有着大量研究产出,在文献检索和筛选中,研究者们难以避免疏漏一些非常好或者新颖的研究。此外,在有关mGluRs参与的信号通路总结中,由于其中复杂的分子机制和涉及的各种理化因素,很难进行深入而详尽的描述。mGluRs与其相互作用的蛋白质、mGluR激动剂或拮抗剂的剂量与癫痫发作不同阶段的复杂交互作用可能会显著影响mGluR激动剂和拮抗剂的治疗效果,而对于不同病理机制进行特定的治疗也值得进一步研究。多种分子可能是癫痫治疗的药物靶点,例如AMPA受体、蛋白激酶和mGluRs。然而,这些目标大多仅经过动物测试,其在人类癫痫中的潜在作用和安全性尚未在临床试验中得到证明。对mGluRs的研究可以用于预防癫痫的发生,而癫痫的预防将会是未来研究的重点。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.379018
参考文献
[1]Akyuz E, Polat AK, Eroglu E, et al. Revisiting the role of neurotransmitters in epilepsy: An updated review. Life Sci. 2021;265:118826.
[2]Servaes S, Kara F, Glorie D, et al. In Vivo Preclinical Molecular Imaging of Repeated Exposure to an N-methyl-d-aspartate Antagonist and a Glutaminase Inhibitor as Potential Glutamatergic Modulators. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019;368:382-390.
[3]Meldrum BS, Akbar MT, Chapman AG. Glutamate receptors and transporters in genetic and acquired models of epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 1999;36:189-204.
[4]Luessen DJ, Conn PJ. Allosteric Modulators of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors as Novel Therapeutics for Neuropsychiatric Disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2022;74:630-661.
[5]Abd-Elrahman KS, Ferguson SSG. Noncanonical metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 signaling in Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022;62:235-254.
[6]Cleva RM, Olive MF. mGlu receptors and drug addiction. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Membr Transp Signal. 2012;1:281-295.
[7]Guo B, Wang J, Yao H, et al. Chronic inflammatory pain impairs mGluR5-mediated depolarization-induced suppression of excitation in the anterior cingulate cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2018;28:2118-2130.
[8]Seven AB, Barros-Alvarez X, de Lapeyriere M, et al. G-protein activation by a metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature. 2021;595:450-454.
[9]Liang X, Mao A, Zhang W, et al. Effect of family integrated care on physical growth and language development of premature infants: a retrospective study. Transl Pediatr. 2022;11:965-977.
[10]Notenboom RG, Hampson DR, Jansen GH, et al. Up-regulation of hippocampal metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in temporal lobe epilepsy patients. Brain. 2006;129:96-107.
[11]Sanon NT, Pelletier JG, Carmant L, et al. Interneuron subtype specific activation of mGluR1/5 during epileptiform activity in hippocampus. Epilepsia. 2010;51:1607-1618.
[12]Borowicz KK, Łuszczki JJ, Czuczwar SJ. SIB 1893, a selective mGluR5 receptor antagonist, potentiates the anticonvulsant activity of oxcarbazepine against amygdala-kindled convulsions in rats. Pol J Pharmacol. 2004;56:459-464.
[13]D'Amore V, Santolini I, van Rijn CM, et al. Potentiation of mGlu5 receptors with the novel enhancer, VU0360172, reduces spontaneous absence seizures in WAG/Rij rats. Neuropharmacology. 2013;66:330-338.
[14]Kandratavicius L, Rosa-Neto P, Monteiro MR, et al. Distinct increased metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5 (mGluR5) in temporal lobe epilepsy with and without hippocampal sclerosis. Hippocampus. 2013;23:1212-1230.
[15]Paquet M, Ribeiro FM, Guadagno J, et al. Role of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 signaling and homer in oxygen glucose deprivation-mediated astrocyte apoptosis. Mol Brain. 2013;6:9.
[16]Potter WB, Basu T, O'Riordan KJ, et al. Reduced juvenile long-term depression in tuberous sclerosis complex is mitigated in adults by compensatory recruitment of mGluR5 and Erk signaling. PLoS Biol. 2013;11:e1001627.
[17]D'Amore V, Raaijmakers RH, Santolini I, et al. The anti-absence effect of mGlu5 receptor amplification with VU0360172 is maintained during and after antiepileptogenesis. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2016;146-147:50-59.
[18]Kelly E, Schaeffer SM, Dhamne SC, et al. mGluR5 Modulation of Behavioral and Epileptic Phenotypes in a Mouse Model of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018;43:1457-1465.
[19]Hanak TJ, Libbey JE, Doty DJ, et al. Positive modulation of mGluR5 attenuates seizures and reduces Tumor necrosis factor-alpha(+) macrophages and microglia in the brain in a murine model of virus-induced temporal lobe epilepsy. Exp Neurol. 2019;311:194-204.
[20]Dyomina AV, Kovalenko AA, Zakharova MV, et al. MTEP, a selective mGluR5 antagonist, had a neuroprotective effect but did not prevent the development of spontaneous recurrent seizures and behavioral comorbidities in the rat lithium-pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:497
[21]Wang X, Wang Y, Zhang C, et al. CB1 receptor antagonism prevents long-term hyperexcitability after head injury by regulation of dynorphin-KOR system and mGluR5 in rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 2016;1646:174-181.
[22]Xu Y, Li Z, Yao L, et al. Altered norbin expression in patients with epilepsy and a rat model. Sci Rep. 2017;7:13970.
[23]Celli R, Wall MJ, Santolini I, et al. Pharmacological activation of mGlu5 receptors with the positive allosteric modulator VU0360172, modulates thalamic GABAergic transmission. Neuropharmacology. 2020;178:108240.
[24]Crans RAJ, Daelemans S, Raedt R, et al. Kainic acid-induced status epilepticus decreases mGlu(5) receptor and phase-specifically downregulates Homer1b/c expression. Brain Res. 2020;1730:146640.
[25]Di Cicco G, Marzano E, Iacovelli L, et al. Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated long term depression is disrupted in the hippocampus of WAG/Rij rats modelling absence epilepsy. Neuropharmacology. 2021;196:108686.
[26]Das A, Wallace GC 4th, Holmes C, et al. Hippocampal tissue of patients with refractory temporal lobe epilepsy is associated with astrocyte activation, inflammation, and altered expression of channels and receptors. Neuroscience. 2012;220:237-246.
[27]Howlett E, Lin CC, Lavery W, et al. A PI3-kinase-mediated negative feedback regulates neuronal excitability. PLoS Genet. 2008;4:e1000277.
[28]Molinari F, Cattani AA, Mdzomba JB, et al. Glutamate transporters control metabotropic glutamate receptors activation to prevent the genesis of paroxysmal burst in the developing hippocampus. Neuroscience. 2012;207:25-36.
[29]Kovalenko AA, Zakharova MV, Schwarz AP, et al. Changes in metabotropic glutamate receptor gene expression in rat brain in a lithium-pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci 23:2752.
[30]Dunn HA, Zucca S, Dao M, et al. ELFN2 is a postsynaptic cell adhesion molecule with essential roles in controlling group III mGluRs in the brain and neuropsychiatric behavior. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24:1902-1919.
主要贡献者介绍及基金支持:
第一作者:黄乐仪、肖文杰,中南大学湘雅医学院八年制临床医学专业博士生;
通讯作者:万莉莉,博士,博士后,中南大学基础医学院人体解剖学与神经生物学系讲师。
该论文获得以下基金项目资助:
1.湖南省重点领域研发计划:基于多模态磁共振的机器学习对颞叶癫痫记忆障碍类型识别 及预测的研究(龙莉莉,No. 2022SK2042)。
2.湖南省自然科学基金面上项目:基于全外显显子测序的早发性癫痫性脑病影像遗传学研究(龚姣娥,No.20200475)。
3.湖南省重点领域研发计划:人类独特性海马苔藓纤维α-SMA表达在颞叶癫痫诊断和治 (涂鄂文,No. 2020SK2122)。
 #br#
#br#
通讯作者万莉莉
 #br#
#br#
 #br#
#br#