NRR:国家重点实验室、广东省中医院程骁团队揭示星形胶质细胞内皮素1过表达对脑卒中后认知功能的影响及机制
撰文:蒋雯
脑卒中后,35%-47%的患者会发生认知功能障碍[1]。脑卒中患者的脑脊液及血液中内皮素1(Endothelin-1,ET-1)的水平升高[2]。缺血性脑卒中后,脑内的ET-1主要由星形胶质细胞和血管内皮细胞释放 [3]。课题组前期研究发现,短暂性缺血和长期再灌注模型中,血管内皮细胞ET-1过度表达会加重认知障碍[4]。星形胶质细胞ET-1过表达(astrocytic ET-1 overexpression,GET-1)加剧脑缺血性损伤引发的空间学习和记忆障碍,但其机制目前仍不清楚[5]。认知功能与成年小鼠的海马神经发生密切相关[6]。哺乳动物大脑中有两个区域可以产生新的神经元,即侧脑室的脑室下区和海马齿状回的颗粒下区。课题组前期研究发现GET-1小鼠通过Jak2/Stat3途径增强了脑室下区的神经发生,导致脑缺血再灌注损伤后梗塞面积增大,神经系统损伤加重[7]。深入探讨GET-1小鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后颗粒下区的神经发生是否受累,以及GET-1小鼠脑卒中后认知功能障碍发生可能的机制,可以为脑卒中后认知功能障碍提供新的治疗靶点。
最近,来自中医湿证国家重点实验室、广东省中医院程骁团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“Astrocytic endothelin-1 overexpression impairs learning and memory ability in ischemic stroke: impairment of hippocampal neurogenesis and lipid metabolism”的文章,发现星形胶质细胞过表达ET-1损伤了海马区神经发生,加剧脑卒中后认知功能障碍。进一步蛋白组学和代谢组学的结果证实,星形胶质细胞过表达ET-1后产生的这些作用可能是通过负向调控神经发生以及脂质代谢来实现。ET-1作为脑卒中后星形胶质细胞释放的重要物质,其可能在未来脑卒中后认知功能障碍的治疗靶点起关键作用。李杰、蒋雯和蔡粤芳为论文共同第一作者,程骁为论文通讯作者。
ET-1是一种含有21个残基的多肽,具有强大的缩血管功能,在血管重塑、细胞生长和增殖等血管损伤反应机制中起着非常重要的作用。星形胶质细胞中过表达内皮素使缺血性脑损伤更加严重,同时加剧了缺血性损伤引起的空间学习和记忆障碍[5],但具体机制仍不清楚。而认知功能障碍与成人神经发生有着密不可分的联系。成人神经发生是指神经干/祖细胞分化成新的成熟神经元的过程,包括4个阶段:细胞增殖、细胞分化、神经元的成熟和神经元功能整合到神经回路。因此研究者猜测星形胶质细胞过表达ET-1可能通过改变海马区的神经发生,从而影响了缺血性脑卒中后小鼠的空间学习与记忆能力,加剧了脑卒中后认知功能障碍。
该研究通过对GET-1小鼠和野生型(wild type, WT)小鼠的大脑中动脉进行1小时的梗塞,然后再进行长时间的再灌注(7天、28天和3个月)来建立脑缺血再灌注损伤模型,利用水迷宫评估缺血性脑卒中后空间学习与记忆能力,随后采用荧光共染色检测齿状回区神经发生情况。然后利用脑组织的蛋白质组学和代谢组学分析来比较GET-1和WT小鼠在MCAO损伤后7和28天的差异表达的蛋白质与代谢物,并进一步采用京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,KEGG)分析这些差异表达的物质主要与哪些生物学过程相关。
水迷宫结果首先表明,对比WT小鼠,GET-1小鼠经历脑缺血再灌注损伤后表现出更严重的空间学习与记忆障碍。

图1.小鼠脑内星形胶质细胞过表达ET-1对脑缺血后空间学习与记忆的作用。
(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
然后在脑缺血后第1-5天尾静脉给予5-溴脱氧尿苷(Bromodeoxyuridine,BrdU)标记标记增殖的细胞,荧光显象表明星形胶质细胞过表达ET-1可显著增加齿状回区细胞增值(图2B)。SOX2是一种神经干细胞的标志物,BrdU与荧光共标后发现这些增殖的细胞来源于神经干细胞(图2C)。双皮质素(doublecortin,DCX)常被用作迁移的神经母细胞和早期分化但未成熟的神经元的标记。BrdU进一步与DCX共标表明小鼠脑内过表达ET-1增加脑缺血后神经干细胞向神经元的分化(图2D)。

图2.小鼠脑内星形胶质细胞过表达ET-1对细胞增值与分化的作用。
(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
进而利用神经元核蛋白(neuronal nuclei antigen,NeuN)和神经胶质纤维酸性蛋白(glial fibrillary acidic protein,GFAP)与BrdU荧光共标探索这些分化的细胞最终是否转变为神经元或者星形胶质细胞。结果可见,对比WT小鼠,GET-1小鼠脑缺血后神经元的产生减少(图3A和3C),而星形胶质细胞的产生并没有显著增加(图3B和3D),表明小鼠脑内星形胶质细胞过表达ET-1对可抑制脑缺血后神经发生。

图3.小鼠脑内星形胶质细胞过表达ET-1对脑缺血后神经元和星形胶质细胞产生的影响。
(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
然后利用蛋白组学分别检测WT小鼠和GET-1小鼠在脑缺血再灌注后7天和28天的脑组织中差异表达的蛋白质。结果表明,在脑缺血再灌注7天后有223种不同的蛋白质(153中蛋白质上调,70中蛋白质下调);在脑缺血再灌注28天后有243种不同的蛋白质(166中蛋白质上调,77中蛋白质下调)。许多差异表达的蛋白质同时出现在脑缺血再灌注的7和28天的脑组织中,例如GFAP,Prdx6,Vim,Apoe,Lgals1等。

图4.WT小鼠和GET-1小鼠在脑缺血再灌注7和28天后差异表达的蛋白质。
(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
随后采用KEGG分析这些差异表达的蛋白质主要富集在哪些生物学过程。发现这些差异表达的蛋白质主要与神经发生的负调控以及脂质代谢途径相关,侧面印证了荧光共染色的结果(图5A和5B)。同时蛋白质免疫印记法检测GFAP和Prdx6在WT小鼠和GET-1小鼠脑内表达程度,结果表明GET-1小鼠脑组织中GFAP和Prdx6的表达水平均高于WT小鼠,也证实了蛋白质组学结果的可行度(图5C)。

图5.KEGG分析WT小鼠和GET-1小鼠在脑缺血再灌注7天和28天后差异表达的蛋白质富集的生物途径以及验证蛋白组学结果。
(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
最后采用代谢组学对比分析WT小鼠和GET-1小鼠在经历了脑缺血再灌注损伤28天后脑组织内脂质代谢是否有差异,以及这些差异表达的代谢物富集的主要生物学途径。研究者确定了91种不同的代谢物,火山图显示,与WT组相比,GET-1组在脑缺血后有43个明显上调的差异代谢物以及48个明显下调的差异代谢物(图6B和6C)。这些差异表达的代谢物主要集中在胆碱和甘油磷脂代谢、辅酶A的生物合成等途径(图6D)。
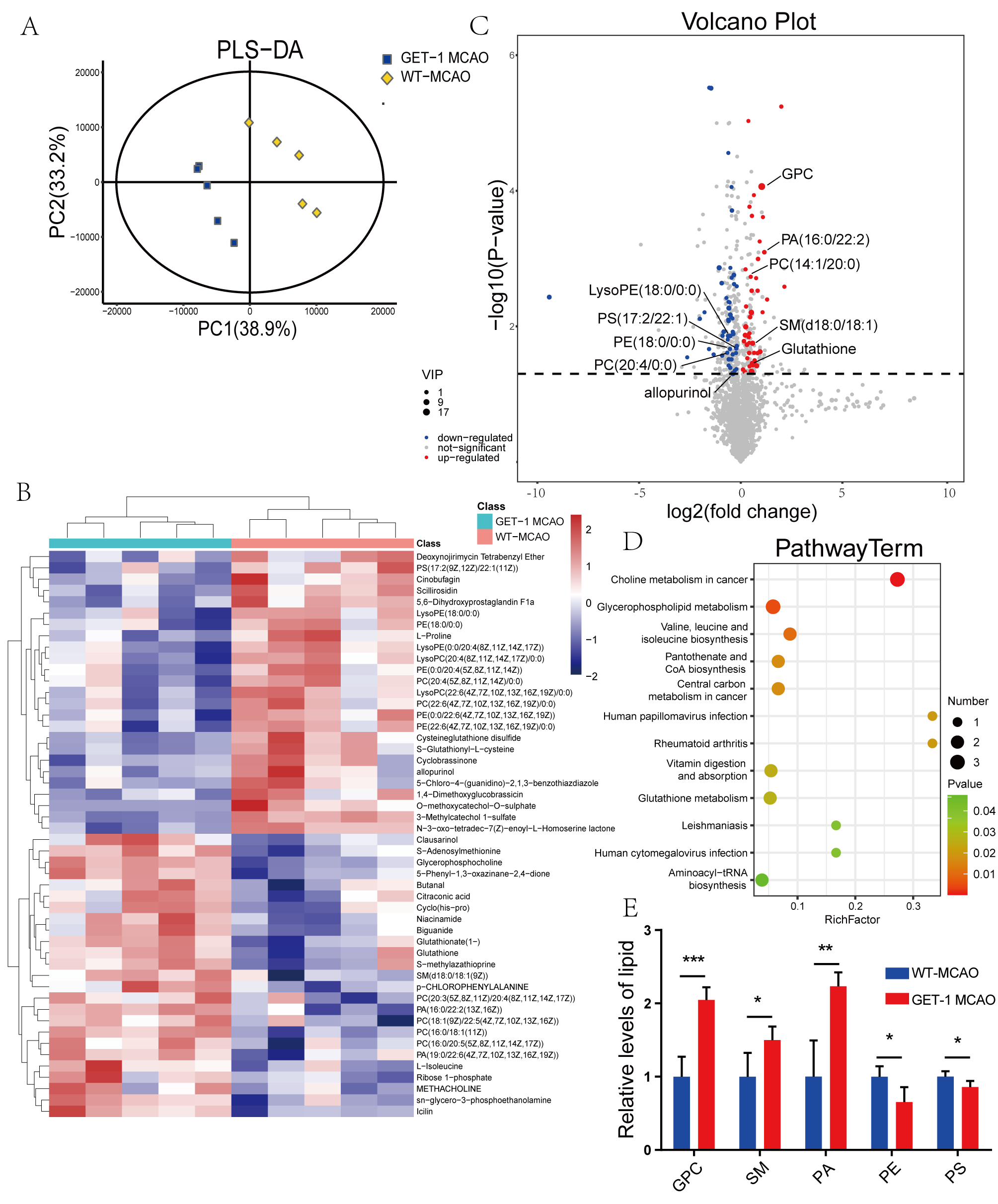
图6.WT小鼠和GET-1小鼠在脑缺血再灌注28天后差异表达的代谢物以及KEGG分析。
(图源:Li et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
综上表明,脑缺血条件下星形胶质细胞中的ET-1过表达能够负向调节海马区的神经发生,改变脑组织的脂质代谢产物,进而损害缺血性脑卒中后空间学习与记忆能力,加剧认知功能障碍影响脑卒中预后。
该研究发现小鼠脑内星形细胞过表达ET-1负向调控了脑缺血损伤后海马的神经发生,其中Prdx6参与了这一过程,但是具体机制尚未研究清楚,下一步需要进一步调控Prdx6,明确其对星形胶质细胞中ET-1参与的脑卒中后认知障碍及脂质代谢的影响及其具体作用通路。同时脑内星形细胞过表达ET-1影响了脑缺血损伤后海马的脂质代谢,这种影响的利弊效应还需要进一步深入探讨,这也是未来研究的方向之一。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.380906
参考文献
[1]Jacquin A, Binquet C, Rouaud O, et al. Post-stroke cognitive impairment: high prevalence and determining factors in a cohort of mild stroke. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;40:1029-1038.
[2]Lampl Y, Fleminger G, Gilad R, et al. Endothelin in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of patients in the early stage of ischemic stroke. Stroke. 1997;28:1951-1955.
[3]Tsang MC, Lo AC, Cheung PT, et al. Perinatal hypoxia-/ischemia-induced endothelin-1 mRNA in astrocyte-like and endothelial cells. Neuroreport. 2001;12:2265-2270.
[4]Zhang X, Yeung PK, McAlonan GM, et al. Transgenic mice over-expressing endothelial endothelin-1 show cognitive deficit with blood-brain barrier breakdown after transient ischemia with long-term reperfusion. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2013;101:46-54.
[5]Hung VK, Yeung PK, Lai AK, et al. Selective astrocytic endothelin-1 overexpression contributes to dementia associated with ischemic stroke by exaggerating astrocyte-derived amyloid secretion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015;35:1687-1696.
[6]Cheng X, Yeung PKK, Zhong K, et al. Astrocytic endothelin-1 overexpression promotes neural progenitor cells proliferation and differentiation into astrocytes via the Jak2/Stat3 pathway after stroke. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16:227.
[7]Anacker C, Hen R. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive flexibility - linking memory and mood. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18:335-346.
 #br#
#br#
通讯作者:程骁,广东省中医院脑病科,主任医师;广州中医药大学第二附属医院中医湿证国家重点实验室与广东省中医急症重点实验室,研究员;作者所在团队主要研究中西医结合防治脑血管病的基础及临床研究,研究内容包括:(1)脑卒中的发病机制及干预;(2)脑卒中的基础到临床转化及分子标志物研究;(3)中医药防治脑卒中的疗效及靶点。
基金支持:国家自然科学基金(81303115,81774042),广东省自然科学基金(2023A1515012174),广州市珠江科技新星计划(201806010025),广州市科技计划项目(202102010268),广东省中医院专科项目(YN2018ZD07)。
第一作者:李杰,广东省中医院二沙岛分院麻醉科主任,主任医师。






 #br#
#br#