NRR: 佛山科学技术学院李欣然团队揭示P7C3-A20在创伤性脑损伤中的作用机制
撰写:杨芷清,王振超,邓晓琪,祝领鑫,宋昭猛,曹嫦妤,李欣然
创伤性脑损伤(Traumatic brain injury, TBI)对人类和动物健康问题危害严重。TBI主要是由机械外力引起的,造成的主要原因有打架、撞击、坠落等。TBI降低了患者的生活质量,甚至导致严重残疾或死亡,预后不佳。TBI发生后,自噬通量受损,小鼠自噬标志物增加[1-2],而过度自噬往往促进细胞凋亡[3]。虽然人们已经意识到TBI的危害,但目前对治疗TBI的特效药物研究仍处于起步阶段,缺乏有效的治疗药物去治疗由TBI引起的各种损伤,如不及时治疗,会造成不可逆的损伤,是一项迫切需要解决的公共卫生和医疗问题。所以需要持续探索对TBI有修复作用的药物,以进一步改善TBI的预后。
3,6-二溴-beta-氟-N-(3-甲氧基苯基)-9H-咔唑-9-丙胺(P7C3-A20)是P7C3的衍生物,能透过血脑屏障,稳定细胞能量水平,具有治疗TBI的潜力[4-5]。一项研究证明了P7C3-A20对缺血性脑卒中有神经保护作用[6]。它还对灵长类动物的海马神经元发挥保护作用[7]。虽然P7C3-A20已被证实在缺血性脑卒中和神经退行性疾病等各种疾病中发挥神经保护作用,但是尚不清楚P7C3-A20是否能通过调控自噬和凋亡对大鼠TBI有治疗作用,及其可能的分子机制。
近期,佛山科学技术学院李欣然团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“P7C3-A20 treats traumatic brain injury in rats by inhibiting excessive autophagy and apoptosis”的研究论文。通过研究,作者发现,P7C3-A20治疗可显著改善TBI引起的动物行为学表现异常,减少细胞损伤,抑制过度自噬和凋亡,从而减轻TBI所致的损伤。该研究带来的启示:P7C3-A20在TBI中的神经保护作用提供了一种新的机制,并提示P7C3-A20可能是治疗TBI的一种有吸引力的策略。杨芷清为论文共同第一作者,李欣然为论文通讯作者。
TBI会导致残疾和死亡。研究表明,TBI后的细胞和生理紊乱会导致神经细胞死亡,神经系统受损及认知和运动功能障碍[8]。TBI的病理机制复杂,包括自噬调节的失控和细胞凋亡的增加[9]。TBI发生后,自噬会显著激活[10],自噬通量受损,导致更多的自噬小体积累,并与更多的神经细胞死亡相关[11]。同时有研究表明,细胞凋亡在创伤性脑损伤后的继发性脑损伤中起着关键作用,神经元和胶质细胞的凋亡是促成TBI病理学的因素[12-13]。所以抑制TBI后神经元的自噬和凋亡可能是一种有效的治疗[14-15]。位置保持试验、尾部悬吊试验、平衡功能试验、行走功能试验和水迷宫这些行为学试验,可通过动物的行为,方便实验者直观地观察到各组大鼠TBI后的情况。在行为学实验中发现,TBI后大鼠表现出神经、平衡和行走功能缺损,学习记忆障碍。有研究表明,P7C3-A20化合物具有神经保护作用,促进海马神经生成,并改善实验性创伤后的功能结果。相似的是,在本试验中,TBI后的大鼠经P7C3-A20治疗后,运动功能和学习记忆能力有所恢复。这些结果表明,P7C3-A20可以治疗TBI后大鼠的运动和记忆功能(图1)。通过HE染色观察到组织的损伤情况。大脑皮质在控制躯体的运动方面发挥着重要作用。海马体是与大鼠和人类学习记忆相关的重要结构,在学习和记忆中起着重要的作用。因此,TBI引起的皮质区损伤是运动和神经功能障碍的病理基础,而海马区损伤会导致学习记忆功能下降。在本研究中,HE染色皮质组织切片和海马组织切片显示TBI大鼠神经元受损,其中包括:出血、坏死与水肿。我们的研究显示P7C3-A20的治疗可以减轻TBI所引发的神经元损伤,这些组织损伤的减少转化为皮质依赖性运动行为和海马依赖性学习和记忆能力的改善(图2)。TBI会导致自噬功能失调,表现为溶酶体功能障碍,自噬小体清除受损,自噬细胞死亡增加。自噬小体是细胞内受损的细胞器被细胞自身的膜包裹而形成的,由双层膜围成的结构。当自噬小体与初级溶酶体融合,就会形成自噬性溶酶体,它们由单层膜包裹,里面含有尚未分解的内质网、线粒体、高尔基复合体、脂类和糖原等。自噬依赖于溶酶体途径来降解受损的细胞质蛋白和老化的细胞器,过度激活的自噬甚至可以诱导自噬凋亡和死亡,抑制自噬可以减少细胞死亡。在本研究中,用电镜观察TBI组的组织发现了自噬溶酶体,而P7C3-A20的治疗可以缓解自噬的情况。LC3是自噬过程中上调的关键自噬成分,LC3-I特异性地将磷脂酰乙醇胺结合到囊泡膜表面,从而形成LC3-Ⅱ。LC3-I到LC3-Ⅱ的转换可以评估自噬水平。p62可与LC3和泛素化的底物连接, 当自噬激活时,p62会被整合到自噬体中,随后自噬体与溶酶体融合,p62蛋白便在自噬溶酶体中被降解,使p62蛋白表达水平降低。自噬活性越强,储存在胞浆内的p62蛋白就越少。p62的水平与自噬程度是成反比的。因此, 可检测LC3-Ⅱ和p62蛋白的表达水平, 来说明自噬的变化。本试验结果显示,P7C3-A20的治疗可以抑制LC3-Ⅱ蛋白的表达,并阻止p62蛋白的降解。过度的自噬已被报道会诱导神经元的凋亡、坏死。因此,P7C3-A20对TBI的功能改善其中的一个重要机制可能是对自噬的抑制(图3)。可以通过TUNEL染色观察到组织的凋亡情况。TUNEL检测结果显示在TBI大鼠中皮质和海马体凋亡的细胞增加,P7C3-A20的治疗后,细胞的凋亡率降低。BNIP3是一种促凋亡蛋白,以二聚体形式存在于线粒体的外膜,通过线粒体与BAX相互作用,同时可调控细胞的自噬与坏死。Bax是一种促凋亡因子,是BNIP3介导的细胞死亡的下游效应蛋白。促凋亡家族成员触发细胞因子释放到细胞质中,会导致caspase激活,从而导致细胞凋亡。在本研究中,用Western blot检测BNIP3和Bax的蛋白表达水平。结果显示,TBI后BNIP3和Bax表达上调,但P7C3-A20逆转了这些变化。一项研究通过激活的caspase-3染色显示出P7C3对脊髓损伤引起的神经元凋亡具有保护作用。基于先前的研究,减轻细胞凋亡的药物可能减少临床并发症,改善脑损伤的预后。提示P7C3-A20可能通过抑制TBI诱导的神经细胞凋亡和降低TBI后凋亡相关因子的蛋白表达水平来治疗创伤性脑损伤(图4)。综上所述,该研究表明,P7C3-A20通过抑制大鼠TBI后过度的自噬与凋亡反应,发挥对大脑神经保护作用。
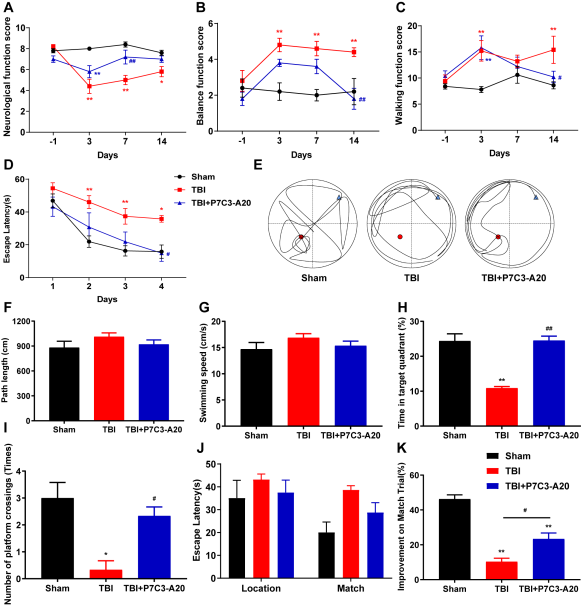
图1 P7C3-A20对TBI大鼠有神经保护作用(图源:Yang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
 #br#
#br#
图2 P7C3-A20可减轻TBI后的细胞损伤(图源:Yang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
 #br#
#br#
图3 P7C3-A20减轻了TBI后的自噬情况(图源:Yang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
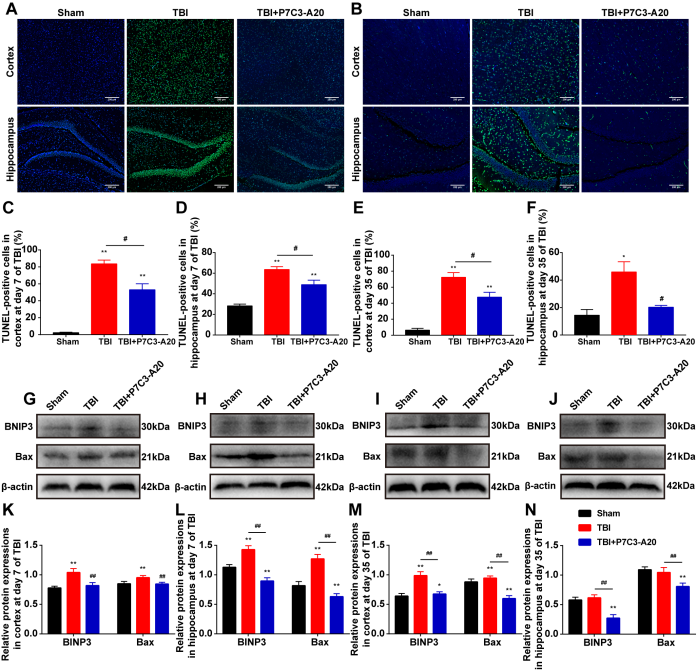
图4 P7C3-A20降低了TBI后的凋亡情况(图源:Yang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
总之,P7C3-A20通过抑制大鼠TBI后过度的自噬与凋亡反应,发挥对大脑神经保护作用。作者的研究表明,P7C3-A20治疗可显著改善TBI引起的动物行为学表现异常,减少细胞损伤,抑制过度自噬和凋亡,从而减轻TBI所致的损伤。该研究表明,P7C3-A20通过抑制大鼠TBI后过度的自噬与凋亡反应,发挥对大脑神经保护作用。该研究结果为P7C3-A20在TBI中的神经保护作用提供了一种新的机制,并提示P7C3-A20可能是治疗TBI的一种有吸引力的策略。#br#
当然该研究也存在一定性局限性。首先,该研究主要关注雄性大鼠在第7天和第35天时间点的数据。为了有更多的临床意义,未来的研究应该考虑使用雌性大鼠,以及更长远的时间点。此外,由于研究资金和时间的限制,没有把更多的关注点放在P7C3-A20对神经发生作用的研究上。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.380910
参考文献
[1] Anderson EN, Gochenaur L, Singh A, et al. Traumatic injury induces stress granule formation and enhances motor dysfunctions in ALS/FTD models. Hum Mol Genet. 2018;27:1366-1381.
[2] Sarkar C, Zhao Z, Aungst S, et al. Impaired autophagy flux is associated with neuronal cell death after traumatic brain injury. Autophagy. 2014;10:2208-2222
[3] Yang G, Yang Y, Tang H, et al. Loss of the clock gene Per1 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression via the AKT/mTOR pathway. Cancer Sci. 2020;111:1542-1554
[4] Vázquez-Rosa E, Shin MK, Dhar M,et al. P7C3-A20 treatment one year after TBI in mice repairs the blood-brain barrier, arrests chronic neurodegeneration, and restores cognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117:27667-27675.
[5] Bai J, Zeng S, Zhu J, et al. The small molecule P7C3-A20 exerts neuroprotective effects in a hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy model via activation of PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling. Neuroscience. 2020;441:197-208
[6] Wang SN, Xu TY, Wang X, et al. Neuroprotective efficacy of an aminopropyl carbazole derivative P7C3-A20 in ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016;22:782-788
[7] Bauman MD, Schumann CM, Carlson EL, et al. Neuroprotective efficacy of P7C3 compounds in primate hippocampus. Transl Psychiatry. 2018;8:202.
[8] Luo CL, Chen XP, Yang R, et al. Cathepsin B contributes to traumatic brain injury-induced cell death through a mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathway. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88:2847-2858.
[9] Wu F, Xu K, Xu K, et al. Dl‐3n‐butylphthalide improves traumatic brain injury recovery via inhibiting autophagy‐induced blood‐brain barrier disruption and cell apoptosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24:1220-1232
[10] Shen M, Wang S, Wen X, et al. Dexmedetomidine exerts neuroprotective effect via the activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in rats with traumatic brain injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;95:885-893.
[11]Zhang JY, Lee JH, Gu X, et al. Intranasally delivered Wnt3a improves functional recovery after traumatic brain injury by modulating autophagic, apoptotic, and regenerative pathways in the mouse brain. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35:802-813.
[12] Tao L, Zhang L, Gao R, et al. Andrographolide alleviates acute brain injury in a rat model of traumatic brain injury: possible involvement of inflammatory signaling. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:657.
[13] Ismael S, Nasoohi S, Ishrat T. MCC950, the Selective Inhibitor of Nucleotide Oligomerization Domain-Like Receptor Protein-3 Inflammasome, Protects Mice against Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35:1294-1303.
[14] Xu X, Zhi T, Chao H, et al. ERK1/2/mTOR/Stat3 pathway-mediated autophagy alleviates traumatic brain injury-induced acute lung injury. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864(5 Pt A):1663-1674.
[15] Wu L, Ji NN, Wang H, et al. Domino Effect of Interleukin-15 and CD8 T-Cell-Mediated Neuronal Apoptosis in Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2021;38:1450-1463.
第一作者杨芷清2020年就读于佛山科学技术学院,攻读兽医硕士专业学位。通讯作者李欣然2018年毕业于东北农业大学,取得博士学位,主要从事小动物疾病诊疗、创伤性脑损伤、小动物麻醉机理方向研究,发表核心刊物和sci论文20余篇,承担小动物外科学、兽医麻醉学等课程。感谢国家自然科学基金32102745的对本研究提供的资金支持。

(照片提供自:李欣然实验室)
#br#

 #br#
#br#
 #br#
#br#

