NRR:中国医学科学院医药生物技术研究所刘睿和李卓荣团队揭示GAS5竞争调控miR-23b-3p在阿尔茨海默病的新病理机制
撰写:曾利,赵凯悦,刘江红,刘蜜敏,蔡中頔,孙婷,李卓荣,刘睿
阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer’s
disease, AD)是一种起病隐匿、与年龄高度相关的致死性中枢神经退行性疾病,以记忆力减退、认知功能障碍为主要临床病症,给家庭和社会带来了沉重的负担[1]。不同RNA新颖的串扰机制,即竞争性内源RNA(competing endogenous RNA,ceRNA)假说,具有相同微小RNA(microRNA, miRNA)反应元件结合序列的RNA分子竞争结合miRNA结合域,共调控基因表达水平[2]。ceRNA调控网络立足于复杂疾病多靶点的治疗策略,为阐释阿尔茨海默病的发病机制提供了新见解和新思路。
生长停滞特异性转录本5(GAS5),是一种含有5'-末端寡嘧啶的lncRNA分子,靶向调控多个miRNAs,参与细胞增殖、血管重塑、肿瘤发生、细胞凋亡等多个生理和病理过程[3,4]。然而,GAS5作为ceRNA参与阿尔茨海默病的病理生理功能以及潜在的分子机制尚未见报道。研究表明,GAS5在大脑中广泛分布,调节神经炎症和胰岛素信号通路,参与阿尔茨海默病病理过程[5]。目前的研究表明,GAS5在神经科学领域的生物学作用褒贬不一,GAS5通过调控miR-26a/EGR1信号通路发挥神经损伤功能[6];另一方面,GAS5靶向调控Lhx8,恢复胆碱能损伤大鼠的空间认知能力,发挥神经保护作用[7]。基于此,GAS5在阿尔茨海默病中对认知功能的作用和具体分子机制尚不明确。因此,该研究探索了GAS5在阿尔茨海默病中病理作用,阐释了GAS5靶向调控miR-23b-3p/GSK-3β/PTEN抗阿尔茨海默病的调控网络,为阿尔茨海默病的诊疗提供了新型潜在标志物和药物靶标。
中国医学科学院医药生物技术研究所刘睿和李卓荣研究团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文)》(Neural Regeneration Research)2026年第1期发表的研究发现,GAS5在阿尔茨海默病病理过程中显著上调,参与Aβ聚集、Tau蛋白磷酸化、细胞凋亡等多个病理过程诱导的认知功能障碍。进一步研究证实,GAS5作为竞争性内源RNA分子,以依赖Argonaute 2蛋白诱导的基因沉默的方式调控miR-23b-3p/GSK-3β/PTEN信号通路,参与阿尔茨海默病的发生发展。该文带来的启示,GAS5竞争调控miR-23b-3p参与阿尔茨海默病病理过程,GAS5/miR-23b-3p/GSK-3β/PTEN信号轴线可能是抗阿尔茨海默病潜在的药物靶点。曾利为文章第一作者,刘睿教授和李卓荣教授为文章通讯作者。
1.GAS5在阿尔茨海默病病理进程中显著上调
利用RNA高通量测序对APP/PS1小鼠进行全转录组分析,GAS5具有潜在的诱导神经元损伤的作用。同时,进一步验证GAS5在5×FAD小鼠、APP/PS1小鼠、以及阿尔茨海默病患者血清中显著上调,并表现出良好的临床诊断价值(图1)。
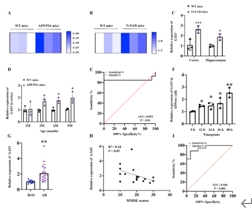
图1 GAS5在阿尔茨海默病病理过程中的表达变化
(图源:Zeng et al., Neural Regen Res, 2026)
2.GAS5的沉默具有神经保护作用
为了明确GAS5在阿尔茨海默病中的病理作用,构建GAS5过表达和敲低阿尔茨海默病体外细胞模型。GAS5过表达显着降低APPswe细胞活力,提高细胞凋亡;GAS5的沉默则表现出相反的作用。与此同时,GAS5表达上调降低抗凋亡和凋亡标志物(Bcl-2/Bax)并激活Caspase-3的活性,GAS5的沉默则显著抑制内源性凋亡信号通路(图2),表明GAS5参与阿尔茨海默病相关的神经元损伤。因此,GAS5的沉默可以提高APPswe细胞的活力,抑制细胞凋亡样退变,发挥神经保护作用。
利用蛋白免疫印迹进一步探究GAS5参与阿尔茨海默病的病理机制。如图2所示,GAS5的过表达显著促进Tau蛋白在AT8,Ser199,Ser396和Ser404位点的磷酸化程度。同时,GAS5的过表达显著促进Aβ1-42的表达水平,并降低非淀粉样途径中阿尔茨海默病AM10蛋白的表达水平;GAS5的沉默则显著促进ADAM10的表达水平,从而降低Aβ1-42的过度生成。上述结果揭示,GAS5参与Aβ生成及Tau蛋白过度磷酸化的病理过程。
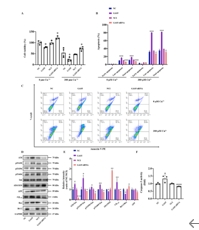
图2 GAS5的过表达和沉默对Aβ1-42的生成、Tau蛋白磷酸化以及凋亡信号通路的作用
(图源:Zeng et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
3.GAS5的沉默改善APP/PS1小鼠的认知功能障碍
通过Morris水迷宫实验评估GAS5对APP/PS1小鼠以及WT野生型对照小鼠空间认知能力的作用。GAS5的敲低改善了APP/PS1小鼠的空间学习能力下降和海马依赖性的记忆障碍,表现出更短的逃逸潜伏期、更多穿越目标平台次数和更长时间的目标象限停留时间。在空间探索实验中,GAS5的沉默使APP/PS1小鼠寻找目标平台表现出相对精确的行进路径(图3);GAS5在APP/PS1小鼠脑内过表达则相反表现出相反的作用。GAS5在WT野生型对照小鼠中过表达与沉默时,认知能力未发生明显变化(图3)。由此可见,GAS5的沉默可以改善APP/PS1小鼠认知障碍,发挥神经保护作用。
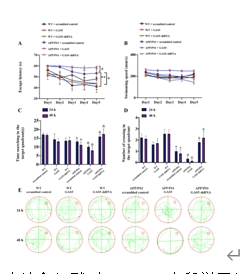
图3 GAS5的过表达和沉默对APP/PS1小鼠学习记忆能力的影响
(图源:Zeng et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
#br#
lncRNA的组织特异性决定了功能特异性,利用RNA荧光原位杂交以及核质分离技术,进一步明确GAS5在阿尔茨海默病中主要作为细胞质lncRNA发挥病理作用。利用生物信息学结合双荧光素酶报告基因系统证明GAS5和miR-23b-3p之间存在直接相互作用。miRNA的转录后调控作用依赖于沉默复合物RISC发挥作用,AGO2是RISC的关键成分,是miRNA功能的关键调节因子。利用RNA结合蛋白免疫共沉淀技术进一步证实了GAS5的靶基因是miR-23b-3p,并且以依赖AGO2的方式特异性负性调节miR-23b-3p的表达水平。
#br#
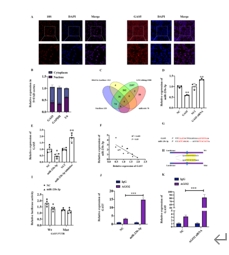
图4 GAS5竞争性调控miR-23b-3p
(图源:Zeng et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
总之,该研究揭示了GAS5/miR-23b-3p/GSK-3β/PTEN信号轴线在阿尔茨海默病中的病理功能,参与Tau磷酸化、Aβ聚集、细胞凋亡诱导的认知功能障碍在内的多种病理过程。作者进一步揭示了GAS5诱导的全新的ceRNA调控机制,即GAS5竞争性结合miR-23b-3p,激活GSK-3β和PTEN参与阿尔茨海默病的发生发展。鉴于这些发现,靶向GAS5/miR-23b-3p/GSK-3β/PTEN通路可能是一种很有潜力的对抗阿尔茨海默病治疗方法。
未来的研究工作拟采用多种阿尔茨海默病动物模型进一步探索GAS5对Tau蛋白磷酸化的作用机制,同时通过多种认知行为检测,更全面、更综合性地证实GAS5对miR-23b-3p/GSK-3β/PTEN信号通路的调控作用。
参考文献
[1] Masters CL, Bateman R, Blennow K, et al.
Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1:15056.
[2] Tay Y, Rinn J,
Pandolfi PP. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition.
Nature. 2014;505:344-352.
[3] Huang W, Shi
Y, Han B, et al. LncRNA GAS5-AS1 inhibits glioma proliferation, migration, and
invasion via miR-106b-5p/TUSC2 axis. Hum Cell 2020;33:416-426.
[4] Wang Y, Shan
K, Yao M, et al. Long noncoding RNA-GAS5: a novel regulator of
hypertension-induced vascular remodeling. Hypertension. 2016;68:736-748.
[5] Patel RS, Lui
A, Hudson C, et al. Small molecule targeting long noncoding RNA GAS5
administered intranasally improves neuronal insulin signaling and decreases
neuroinflammation in an aged mouse model. Sci Rep. 2023;13:317.
[6] Wu Y, Rong W,
Jiang Q, et al. Downregulation of lncRNA GAS5 alleviates hippocampal neuronal
damage in mice with depression-like behaviors via modulation of
microRNA-26a/EGR1 axis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2021;30:105550.
[7] Zhao H, Jin T,
Cheng X, et al. GAS5 which is regulated by Lhx8 promotes the recovery of
learning and memory in rats with cholinergic nerve injury. Life Sci.
2020;260:118388.



