NRR:青岛大学朱晓岩教授团队揭示动脉粥样硬化相关的lnc_000048可促进M1型巨噬细胞极化
撰写:丁园园,孙雨,张萌,潘旭东,朱晓岩
动脉粥样硬化斑块形成是一种慢性炎症反应[1],是缺血性卒中的主要病理机制[2]。动脉粥样硬化斑块中巨噬细胞的数量和表型影响动脉粥样硬化的进展[3]。抑制促炎症型M1和增强抗炎症型M2已被证明可减轻炎症和动脉粥样硬化[4]。然而,动脉粥样硬化中调控巨噬细胞极化的分子机制尚不清楚。巨噬细胞极化是一个受到严格调控的过程,其中JAK-STAT1/2通路报道与M1型巨噬细胞极化相关[5-6]。长链非编码RNA(LncRNA)作为动脉粥样硬化各阶段的关键调控分子,调控内皮细胞、血管平滑肌细胞和巨噬细胞,从而影响动脉粥样硬化斑块的生长和稳定[7-8]。研究表明,lncRNA通过与RNA结合蛋白(RBPs)直接相互作用而发挥生物学功能[9]。而依赖双链RNA蛋白激 (PKR)也受非编码RNA的调控,并与先天免疫有关[10]。然而,目前lncRNA调控PKR介导的免疫信号通路的研究有限。作者之前的研究表明lnc_000048在大动脉粥样硬化性卒中患者中表达上调,并促进ApoE-/-小鼠的动脉粥样硬化进展[11-12]。然而,关于lnc_000048在M1型巨噬细胞中的作用知之甚少。
青岛大学朱晓岩团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)2024年第11期上发表了研究论文。该研究发现,与动脉粥样硬化相关的lnc_000048可以促进THP-1来源的巨噬细胞向M1型转化。进一步研究发现,lnc_000048和PKR在细胞质中可能形成一个RNA-蛋白复合体,促进STAT1的磷酸化和核易位,激活下游免疫应答基因(TNF-α,IL-6,IL-1β)的转录,从而影响M1型巨噬细胞极化和炎症反应。该文带来的启示:lnc_000048/PKR/STAT1轴可能在动脉粥样硬化斑块内环境重编程中发挥重要作用,lnc_000048或PKR可能是减轻卒中动脉粥样硬化的新治疗靶点。丁园园、孙雨为论文共同第一作者,朱晓岩、潘旭东、张萌为论文共同通讯作者。
M1型巨噬细胞在动脉粥样硬化的发展过程中发挥重要作用,抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化或增强M2型巨噬细胞极化已被证明可减轻炎症和动脉粥样硬化[4,13]。因此,实验首先建立THP-1来源的静息状态巨噬细胞(M0)、M1型巨噬细胞和M2型巨噬细胞,并验证lnc_000048 主要在M1 型巨噬细胞中高表达,接着构建了lnc_000048上调或下调的慢病毒细胞系,流式细胞术、western blot和qRT-PCR结果显示,lnc_000048的下调抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化和炎症反应,而lnc_000048的过表达则发挥促进作用。既往研究表明JAK-STAT1/2通路报道与M1型巨噬细胞极化相关[6]。该研究发现lnc_000048增强STAT1通路的激活介导巨噬细胞M1型极化。该研究还利用catRAPID网站预测、RNA-pull down和质谱鉴定筛选了RNA结合蛋白PKR,利用catRAPID和RPIseq预测lnc_000048与PKR的结合能力。接着通过免疫荧光(IF)-RNA荧光原位杂交(FISH)双标记验证lnc_000048和PKR在M1型巨噬细胞胞质中的共定位,并进一步推测lnc_000048可能形成茎环结构特异性结合并诱导PKR磷酸化激活,进而激活STAT1磷酸化,从而增强STAT1途径介导的THP-1巨噬细胞对M1的极化和炎症因子的表达(图1)。这些结果表明动脉粥样硬化相关的lnc_000048激活PKR增强STAT1介导的THP-1巨噬细胞向M1型极化。
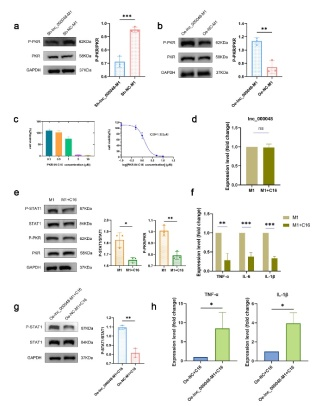
图1. Lnc_000048作用于PKR上游,促进PKR磷酸化和激活,增强STAT1信号通路
综上所述,作者推测lnc_000048和PKR在细胞质中形成一个RNA-蛋白复合体,促进STAT1的磷酸化和转位入核,激活下游免疫应答基因(TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β)的转录,从而影响M1型巨噬细胞极化和炎症反应。lnc_000048/PKR/STAT1轴可能在动脉粥样硬化斑块内环境重编程中发挥重要作用(图2),lnc_000048或PKR可能是减轻卒中动脉粥样硬化的新治疗靶点。然而,该研究有几个局限性:聚焦于lnc_000048的分子机制,仅使用一个细胞系进行实验。虽研究结果与之前探讨THP-1巨噬细胞在动脉粥样硬化中的研究一致,且M1型巨噬细胞是动脉粥样硬化中最主要的炎症免疫细胞。但本研究未检测其他表型如M2a和M2b。然而,该研究结果表明,lnc_000048和M1型巨噬细胞之间的关联是强而可靠的。虽然该研究仅使用了体外实验,但作者使用了多种分子方法,这使他们能够证明lnc_000048靶向PKR调控M1型巨噬细胞极化。因而,接下来,需要进一步在多种细胞系,比如人外周血单核细胞中来验证lnc_000048促进M1型极化,及进一步的动物实验验证其与脑卒中的关系,评估敲减或抑制lnc_000048或PKR作为脑卒中动脉粥样硬化的脑保护疗法的潜力。
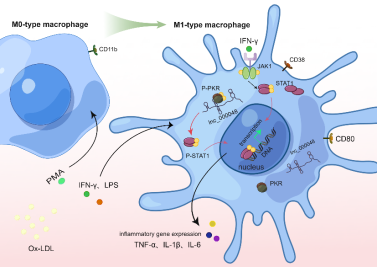
图2.动脉粥样硬化相关的lnc_000048通过lnc_000048/PKR/STAT1轴在M1型巨噬细胞极化中发挥关键作用
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01355
参考文献
[1] Wolf D, Ley K. Immunity and Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2019;124:315-327.
[2] Banerjee C, Chimowitz MI. Stroke Caused by Atherosclerosis of the Major Intracranial Arteries. Circ Res. 2017;120:502-513.
[3] Moore KJ, Sheedy FJ, Fisher EA. Macrophages in atherosclerosis: a dynamic balance. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:709-721.
[4] van Ingen E, Foks AC, Woudenberg T, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-494-3p activates Wnt signaling and reduces proinflammatory macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids . 2021;26:1228-1239.
[5] Li C, Xu MM, Wang K, et al. Macrophage polarization and meta-inflammation. Transl Res. 2018; 191:29-44.
[6] Hu J, Zhang L, Liechty C, et al. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 regulates macrophage polarization and diabetic wound healing. J Invest Dermatol. 2020; 140:1629-1638.
[7] Josefs T, Boon RA. The long non-coding road to atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2020;22:55.
[8] Ding Y, Yin R, Zhang S, et al. The combined regulation of long non-coding RNA and RNA-binding proteins in atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:731958.
[9] Ferrè F, Colantoni A, Helmer-Citterich M. Revealing protein-lncRNA interaction. Brief Bioinform. 2016;17:106-116.
[10] Liu CX, Li X, Nan F, et al. Structure and Degradation of Circular RNAs Regulate PKR Activation in Innate Immunity. Cell. 2019;177:865-880.e21.
[11] Zhang S, Wang X, Yin R, et al. Circulating exosomal lncRNAs as predictors of risk and unfavorable prognosis for large artery atherosclerotic stroke. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11:e555.
[12] Zhang S, Sun Y, Xiao Q, et al. Lnc_000048 promotes histone H3K4 methylation of MAP2K2 to reduce plaque stability by recruiting KDM1A in carotid atherosclerosis. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60:2572-2586.
[13] Barrett TJ. Macrophages in atherosclerosis regression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020;40:20-33
朱晓岩,主任医师,博士生导师,青岛大学附属医院重症医学科,主要从事脑血管病、脓毒血症及大数据研究。

