NRR:上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院杨侃副研究员综述了神经疾病发病机制中线粒体自噬的作用及相互的潜在关系
线粒体作为细胞的能量工厂,在神经元的整个生命活动中扮演者重要角色。线粒体自噬是一个通过自噬机制选择性清除受损或功能失调的线粒体的过程,其功能是维持线粒体的稳态。由于成熟的神经元不能再进行分裂分化和具有高能量需求,其需要高效的线粒体自噬周转来清除受损或功能失调的线粒体[1]。众所周知,在医疗水平发展迅猛的当今时代,神经疾病仍然是一个基础医学领域的巨大难题。虽然越来越多的研究表明线粒体自噬在神经系统疾病的发病机制中发挥着重要作用,但线粒体自噬过程中所涉及到的分子是否能成为潜在的治疗靶点仍需要不断研究探索。
论文概要
近期,上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院环境与儿童健康教育部重点实验室副研究员、中国科学院脑科学与智能技术卓越中心-神经科学国家重点实验室副研究员、湖南工程学院特聘教授杨侃在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“Mitophagy in neurological disease pathogenesis”的综述。该篇文章简要讨论了非选择性自噬和选择性自噬(ERphagy、Aggrephagy和Mitophagy)的过程和特点;介绍了两种线粒体自噬途径(Parkin依赖和非依赖型)的详细机制;总结了线粒体自噬在神经疾病(阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病和肌萎缩侧索硬化)发病机制中的关键作用及治疗靶点,并讨论了线粒体自噬作为抵抗神经系统疾病的潜在治疗靶点的可能性,为神经系统疾病治疗难题提供了一个新的选择。杨侃和云南大学医学院研究生严玉清为论文共同第一作者。杨侃、上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院环境与儿童健康教育部重点实验室副主任张前龙、云南大学医学院副教授吴诗昊和上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院环境与儿童健康教育部重点实验室主任、上海交通大学医学院教授李斐为论文共同通讯作者。
结果分析与阐述
1 非选择性自噬
巨自噬(非选择性自噬)是所有自噬途径中非选择性进行细胞有效降解的主要途径,使细胞能够在饥饿中生存。这种降解途径是通过在细胞质中形成双层囊泡结构包裹细胞器或蛋白质,从而形成自噬体和自噬溶酶体,最终将待降解物降解(图1A)。
2 选择性自噬
除了非选择性自噬,在某些情况下,自噬还通过自噬体特异性识别并降解特定的靶点,这个过程被称为选择性自噬。特定的可溶性蛋白质、超分子复合物、液滴、异常或多余的细胞器以及病原细菌等都会通过选择性自噬降解。在此过程中,受体通过mATG8s蛋白将所选择的底物连接到自噬装置,然后自噬体与溶酶体融合形成自噬溶酶体,使得待降解物被特异性降解。
2.1 内质网自噬
内质网覆盖了整个细胞,有效地增加了细胞内物质运输的膜面积,神经元中的内质网必须定期不断更新和重塑,而内质网自噬则发挥着这个功能。未折叠和错误折叠的蛋白质的积累对内质网膜是有害的,在未折叠蛋白堆积的初始阶段,内质网膜上的应激感应蛋白被激活,与自噬膜上的mATG8连接,启动内质网自噬以降解未折叠和错误折叠的蛋白(图1B)。
2.2 聚集体自噬
生理情况下,泛素-蛋白酶体系统负责清除体内错误折叠或受损的蛋白质,但当错误折叠的蛋白质聚集在一起,聚集体自噬则开始发挥作用。聚集体自噬是由几种受体(如p62/SQSTM1,NBR1,TAX1BP1,Tollip和CCT2)介导的。p62作为中间链,通过其LIR基序募集其他发挥作用的受体,然后通过其泛素结合结构域募集到待降解物中[2]。接下来,p62用多肽上结合的泛素将mATG8连接到自噬膜上,以促进降解(图1C)。
2.3 线粒体自噬
当线粒体受损时,其表面被泛素化,然后产生相关受体,募集一些核心自噬相关蛋白,如OPTN,TAX18P1,NDP52。当这些蛋白质与mATG8连接时,线粒体周围会产生一层膜,逐渐形成自噬囊泡,最终被溶酶体吸收降解(图1D)。
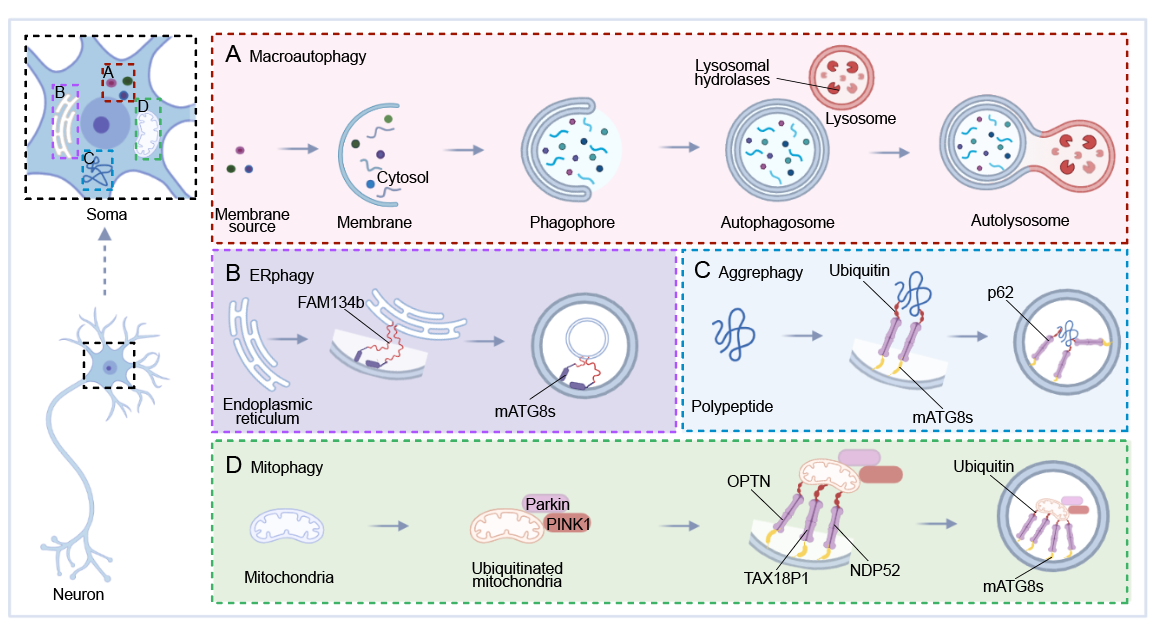
图1:神经元自噬的空间组织表征。(图源:)
3 泛素依赖型线粒体自噬
3.1 Parkin依赖型线粒体自噬
根据线粒体自噬的启动方式,线粒体自噬分为Parkin依赖和非依赖型。泛素依赖性线粒体自噬主要是通过两个蛋白发挥作用: E3泛素蛋白连接酶Parkin和其活化激酶PTEN诱导的假定激酶1(PINK1)。在这个过程中,线粒体损伤传感器(PINK1)、信号放大器(Parkin)和信号效应器(泛素链)组成了泛素链组装途径[3]。
当线粒体受损时,线粒体膜电位的降低导致PINK1在线粒体外膜上的积累,并且活化的PINK1磷酸化与线粒体外膜蛋白连接泛素蛋白,导致Parkin在线粒体外膜上的富集和线粒体外膜蛋白的积累。泛素通过与不同的蛋白结合参与这一过程,指定其降解,并导致氨基酸的释放。泛素连接酶将多个泛素分子添加到靶降解蛋白中,形成聚集的泛素蛋白链,然后被蛋白酶体吸收。受损的线粒体被一组泛素结合的线粒体自噬受体(如TBKI,OPTN,NDP52,p62,NBR1和TAX1BP1)识别,最终降解。泛素偶联的线粒体自噬受体和自噬体膜蛋白LC3B的相互作用,促进受损线粒体的清除(图2A)。
3.2 Parkin不依赖型线粒体自噬
然而,活细胞成像显示在没有ATG8系统的条件下,自噬体闭合和溶酶体融合的内膜破裂延迟,表明存在非经典的自噬途径。与经典线粒体自噬相比,这种非经典线粒体自吞噬途径的功能效率较低,不需要Parkin和PINK1的其他形式的线粒体自噬通常涉及线粒体外膜上LC3家族成员的受体分子的募集。在这种情况下,受损线粒体上的Parkin不会被激活,取而代之的是其与LC3B结合,由其他特征成分介导。这种途径为Parkin依赖型线粒体自噬提供了互补途径,使线粒体自噬能够更有效地维持体内线粒体稳态。#br#
以下是4种受体介导的线粒体自噬机制:
(1)HIF-1和LC3B作为连接体连接线粒体上的FUNDC1(线粒体外膜上的一种线粒体自噬受体)(图2B1)。
(2)线粒体膜上的FUNDC1和NIX/BNIP3L通过与LC3B结合,产生自噬膜。FUNDC1-LC3相互作用和线粒体自噬由LIR结构域的磷酸化或去磷酸化调节(图2B2)。
(3) ATG32为线粒体外膜上的线粒体自噬受体,与ATG11结合后再通过LC3B形成自噬膜(图2B3)。
(4) BCL2L13( ATG32的功能性哺乳动物同源物),结合LC3B介导线粒体清除(图2B4)。
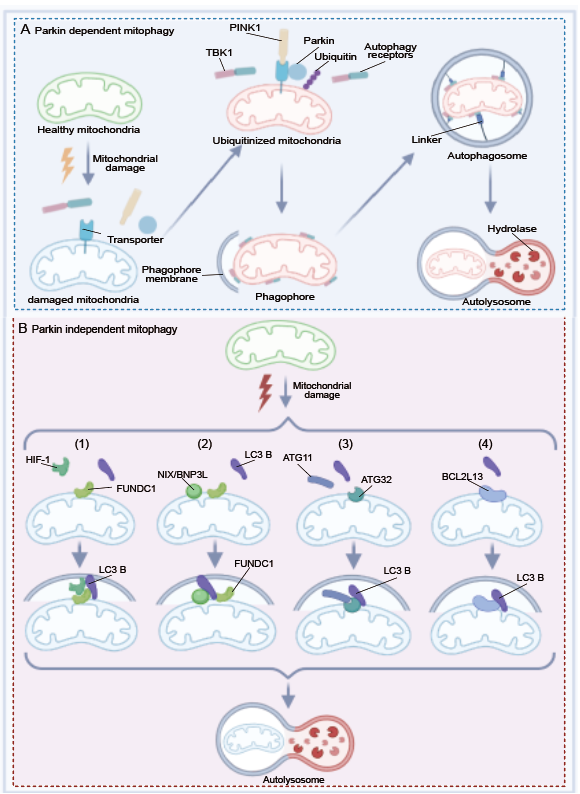
图2:神经元线粒体自噬的Parkin依赖型通路和Parkin非依赖型通路示意图。(图源:)
4 介导线粒体自噬的蛋白质受体和磷脂
线粒体膜上存在线粒体自噬受体,包括BNIP3,Nix,Bcl2-L-13,FUND1和PHB2。这些蛋白质受体都含LIR结构域,通过该结构域促进LC3/GABARAP家族成员与线粒体的直接相互作用。磷脂作为线粒体膜的一种成分,也在介导线粒体自噬中也发挥着不可替代的作用[4]。
5 线粒体自噬与神经疾病
线粒体稳态在其产生、功能障碍或过量的降解之间维持着动态平衡。当线粒体自噬功能失调时,线粒体和神经元的生理稳态就会破坏,从而导致神经系统疾病的发生(图3A)。
5.1 阿尔茨海默病
AD是世界上最常见的神经系统疾病,主要病理表现为神经纤维缠结、Tau蛋白过度磷酸化和Aβ聚集。异常的线粒体自噬阻止受损线粒体被正常清除,增加了与AD相关的病理蛋白的积累、神经元凋亡和能量代谢受阻。根据先前的研究,AD患者大脑中的线粒体自噬功能受损。线粒体蛋白和线粒体DNA(mitDNA)/核DNA的比例都发生了显著变化。在AD患者的海马体中,PINK1在Braak II-III期增加、Parkin在Braak VI期增加,并且检测到线粒体标记物在AD的早期和晚期显著增加,这表明线粒体自噬功能障碍可能与PINK1/Parkin的启动缺陷有关。此外,由于FOXO3a的增加,AD患者的大脑中也出现了其他蛋白质变化,如Bcl-1,ATG12,BNIP3和p-S65-Ub的减少,以及LC3-II/I和p62比率的增加(图3B)。另外,在测量AD患者的外周血后发现血清中存在ATG5和Parkin减少的情况,在外周血中也观察到Parkin,PINK1和LC3的减少。
AD靶向线粒体自噬的各种体外模型表明,AD的发生与线粒体自噬功能障碍有关。据报道,AD秀丽隐杆线虫模型的神经元线粒体自噬减少;相反,PARK2(编码Parkin的基因)的增强补偿了AD中发现的线粒体自噬改变以及泛素化蛋白积累的减少[5]。AD的相关病理表型也反过来影响线粒体自噬,例如,Tau蛋白积累通过增加线粒体膜电位和减少线粒体Parkin来损害线粒体自噬。因此,通过激活线粒体自噬来预防AD的发展是值得思考和探索的。
AD线粒体自噬靶点的治疗策略包括基因编辑技术、药物开发和其他线粒体保护方法。通过在AD成纤维细胞中过表达带有慢病毒递送的Parkin增强了线粒体功能。用尿锂蛋白A治疗小鼠模型,最终挽救线粒体结构并改善认知功能。此外,体育锻炼和热量限制通过SIRT1/PINK1/Parkin信号通路也在AD病理治疗中发挥作用。
5.2 帕金森病
PD是一种慢性神经退行性疾病,其特征是由于黑质多巴胺能神经元的逐渐丧失而导致的运动功能障碍。越来越多的证据表明线粒体自噬功能障碍发生在帕金森病患者的大脑中(图3C)。例如,在常染色体隐性遗传的青少年帕金森病患者中发现了Parkin和PINK1的突变、帕金森病小鼠模型中的线粒体增大和肿胀、帕金森病患者黑质和杏仁核中的线粒体自噬受损,最终导致多巴胺能神经元死亡。反之,线粒体DNA丢失和线粒体损伤影响帕金森病患者的个体多巴胺能神经元。
XBP1是一种通过核酸酶ERN1/IREα进行非常规剪接后被内质网应激激活的转录因子,XBP1和PINK1之间的功能相互作用可能影响帕金森病的线粒体自噬[6]。除此之外,右美托咪定通过激活AMPK增强MPTP诱导的帕金森病小鼠模型中PINK1/Parkin介导的线粒体自噬。近年来,有很多药物专注于帕金森病治疗的线粒体自噬。ROCK(线粒体自噬的关键调节因子)抑制剂通过促进HK2(Parkin的正调节因子)向线粒体的募集,以增强线粒体向溶酶体的靶向性。青蒿素叶提取物通过促进线粒体自噬来保护神经元免受毒性。雷公藤红素通过减少MPP(+)诱导的多巴胺能神经元死亡来增强线粒体自噬[7]。总之,帕金森病的分子药物主要基于线粒体自噬的关键蛋白。
5.3 肌萎缩侧索硬化
ALS,也称为运动神经元疾病,其特征是神经元细胞质中被称为包涵体的异常蛋白质聚集,导致恶性循环并加剧氧化损伤(图3D),这些病理变化最终导致进行性肌肉无力和死亡。ALS的发病机制目前有铜锌超氧化物歧化酶基因突变理论、兴奋性氨基酸毒性理论、自身免疫理论和神经营养因子等。尽管有治疗这种复杂的多因素疾病的药物和治疗方法,但疗效有限。幸运的是针对ALS的线粒体自噬领域正在进行深入研究。ALS的发生与线粒体自噬缺陷之间存在一定的联系。OPTN作为ALS发生的原因,在Parkin介导的线粒体自噬途径中发挥着重要作用。其次,有近百种不同的TBK1突变与OPTN相关。此外,受损线粒体的周转缓慢和聚集也可能导致ALS的发生。反过来,ALS相关基因通过破坏线粒体膜电位也可干扰线粒体的稳态。在ALS的患者和动物模型中,都会出现线粒体自噬功能障碍。例如在一项对过表达重组超氧化物歧化酶1(SOD1)小鼠模型的研究中,线粒体功能缺陷以及线粒体的转运被破坏。ALS小鼠的转运蛋白(TSPO)水平显著增加,与ATG12的表达减少有关。相反,过表达TDP-43(一种与ALS相关的蛋白质)会导致线粒体自噬增强。
在小鼠的ALS细胞模型中,人胰岛素样生长因子-1(IGF-1)、维生素E、利美尼定以及烟酰胺核糖(NR)和紫檀芪(PT)的组合能有效保护线粒体免受凋亡,并上调线粒体自噬。此外,基于线粒体保护的药物——苯丁酸钠和牛磺酸二酚,与线粒体自噬的调节密切相关。

图3:线粒体自噬在神经疾病发病机制中的示意图。(图源:)
6 线粒体自噬作为一个有效的治疗靶点
线粒体自噬对疾病发病机制有着重要贡献,一些药理学药物和天然化合物已经在涉及线粒体自噬的研究中进行了实验,然而,目前为止大多数相关研究仅限于体外或临床前试验。例如SIRT1激活剂,如白藜芦醇和虎杖甙;褪黑激素通过激活Parkin/SIRT3/FOXO3a途径以及促进动脉粥样硬化小鼠模型中的线粒体自噬[2]。二甲双胍能有效激活线粒体自噬,被用于神经胶质瘤的治疗。此外,在原代培养的皮层神经元中,PINK1被氯硝柳胺及其类似物AM85激活,导致Parkin依赖的线粒体自噬途径的激活[8]。作者总结了近年来针对线粒体自噬的药物和天然化合物作为治疗方。作者认为,将这些药物重新用于线粒体自噬发挥关键作用的神经系统疾病具有重要前景,并有希望在未来的临床应用中发挥重要作用。
讨论
线粒体自噬作为一种有效和可选择性的途径来降解受损的线粒体,在维持神经元的稳态和生理功能方面至关重要。尽管非选择性自噬也靶向线粒体进行降解,但对受损线粒体外膜上的特征蛋白没有特异性识别的能力。因此在一些特定的事件中,非选择性自噬甚至会降解一部分健康的线粒体,如在神经元的早期极性建立和轴突分支事件中。通过抑制非选择性自噬的关键蛋白,甚至可以促进神经元轴突的早期发育。
作者认为非选择性自噬和选择性自噬分别在生理和病理条件下对神经元的贡献不同。神经元刚刚完成最后一次有丝分裂,处于快速发育期,对营养和能量的需求最大。在这时,如何尽快招募任何可用的物质以抵御随时可能面临的危机,对于早期轴突发育等事件很重要。在这种情况下,非选择性自噬利用一种粗略而快速的调节方式来维持线粒体稳态。然而,有效去除受损的线粒体以保持健康线粒体的比例,对于已经成熟多年并不断抵抗环境压力的神经元是至关重要的。这时,选择性线粒体自噬在精细而有效的线粒体调节中发挥着稳定作用。在这种情况下,选择性线粒体自噬作为调节线粒体有效循环的调节方式发挥作用。一旦线粒体自噬发生功能障碍,神经元自我净化系统就会崩溃,从而生物体进入各种病理状态,进一步导致神经系统疾病的发生。因此,通过调节线粒体自噬来治疗神经系统疾病有着很广泛的发展前景。
但是,需要讨论的是,几乎所有的关于Parkin依赖性线粒体自噬的研究都是在非神经元系统中进行的,并且往往存在人工过表达Parkin的实验操控。但是,人工过表达Parkin这种情况不是生理性的,而非神经元系统也可能无法反映神经元线粒体自噬的真实状态。利用非神经元细胞所使用的方法,在神经元系统中几乎无法检测到内源性Parkin向线粒体的募集。对于这种现象,我们认为可能的原因在于神经元具有不同的能量代谢方式,并且神经元在很大程度上依赖于氧化磷酸化来产生ATP。然而,非神经元系统更多地依赖于糖酵解代谢,这可能是神经元募集Parkin的不同反应的根本原因。另一种可能的解释是:神经元通过不同的机制清除功能失调的线粒体,这可能由线粒体损伤的严重程度决定。在这一假设中,Parkin依赖性线粒体自噬可能仅在线粒体损伤严重时被激活,因为神经元中存在的内源性Parkin水平非常低。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.385281
参考文献:
1.Tedesco B, Ferrari V, Cozzi M, et al. The role of autophagy-lysosomal pathway in motor neuron diseases. Biochem Soc Trans . 2022;50:1489-1503.
2.Ma S, Chen J, Feng J, et al. Melatonin Ameliorates the Progression of Atherosclerosis via Mitophagy Activation and NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibition. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:9286458.
3.Okatsu K, Kimura M, Oka T, et al. Unconventional PINK1 localization to the outer membrane of depolarized mitochondria drives Parkin recruitment. J Cell Sci. 2015;128:964-978.
4.Maguire JJ, Tyurina YY, Mohammadyani D, et al. Known unknowns of cardiolipin signaling: The best is yet to come. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017;1862:8-24.
5. Araya J, Tsubouchi K, Sato N, et al. PRKN-regulated mitophagy and cellular senescence during COPD pathogenesis. Autophagy. 2019;15:510-526.
6.Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Mechanisms of Parkinson's disease linked to pathological alpha-synuclein: new targets for drug discovery. Neuron. 2006;52:33-38.
7.Wu LK, Agarwal S, Kuo CH, et al. Artemisia Leaf Extract protects against neuron toxicity by TRPML1 activation and promoting autophagy/mitophagy clearance in both in vitro and in vivo models of MPP+/MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease. Phytomedicine. 2022;104:154250.
8.Barini E, Miccoli A, Tinarelli F, et al. The anthelmintic drug niclosamide and its analogues activate the Parkinson's disease associated protein kinase PINK1. Chembiochem. 2018;19:425-429.
主要贡献者介绍

杨侃:上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院教育部-上海市环境与儿童健康重点实验室副研究员、湖南工程学院特聘教授。2020年至2022年于中国科学院脑科学与智能技术卓越创新中心分别担任助理研究员、副研究员; 2022 年入选中国科学院青年促进会。以第一作者和通讯作者 (含并列)在 Cell Reports、Autophagy、Biological Psychiatry、Neuroscience Bulletin 等国际知名学术杂志上发表了多篇研究论文,工作涉及孤独症的遗传基础和神经机制以及自噬调控下的神经发育与神经系统疾病发生。获得国家自然科学基金委员会青年科学基金项目、中国科学院青年促进会人才专项、神经科学国家重点实验室青年基金项目、“率先行动”中国博士后科学基金会与中国科学院优秀博士后联合资助项目、中国博后基金第六十二批面上项目资助。担任Neural Regeneration Research 等学术期刊审稿人,入选中国神经科学学会、中国细胞生物学会及美国神经科学学会会员。

吴诗昊:云南大学医学院副教授。2021年至2022年于中国科学院昆明动物研究所担任副研究员。主要科研工作是利用非人灵长类动物和AAV病毒从事脑疾病相关的研究,主持国家自然基金青年项目一项,主持云南大学双一流科研项目一项。以第一作者或共同第一作者发表7篇SCI论文,其中5篇为一区文章。申请15项专利,目前已获得4项发明专利及5项实用新型专利的授权,另有6项发明专利已进入实质审查阶段。担任SCI杂志:Frontiers In Behavioral Neuroscience和Neural Regeneration Research审稿人。

张前龙:医学硕士、副主任技师。教育部-上海市环境与儿童健康重点实验室副主任、实验室质谱分析测试平台负责人、上海市医学会卫生专科分会委员、上海市实验室资质认定资深评审员、黄浦区优秀共产党员。长期从事环境污染物检测及男性生殖健康研究,建立了上海男性生殖健康队列,开发了生物样本中多种新型环境污染物(全氟、酚类及重金属等)的LC-MS/MS、ICP-MS检测方法,质谱平台年检测样本量超20000例。曾获上海市疾控系统“优秀人才称号,发表或共作过中英文论文43篇。

李斐:儿科学博士、主任医师、教授、博士生导师。先后获得国家自然基金“优秀青年”基金/“杰出青年”基金上海市“领军”人才,上海市优秀学术带头人上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院附属新华儿童医院副院长,上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院/发育行为儿童保健科主任教育部-上海市儿童环境与健康重点实验室主任,国际自闭症研究学会(INSAR)Senior Mentor (全球 16位)中华医学会儿科分会/发育行为儿科学组副组长,卫生部、共青团中央“青年岗位能手,人民日报“国之名医·青年新锐“。主持国家自然基金重点/国合重点等项目,以第一/通讯(含共同作者发表 60 余篇 SCI论文,包括 Nature Communication、American Journal of Psychiatry 、Molecular Psychiatry JAMA Network Open、Pediatric 等顶级期刊。成果写入国际知名教科书,推动美国儿科和妇产科学会指南政策更新,并受邀为 New England Journal of Medicine 撰写综述。






