神经退行性病
-
Figure 1|Modelling the G2019S LRRK2-induced molecular alterations with iPSC technology.
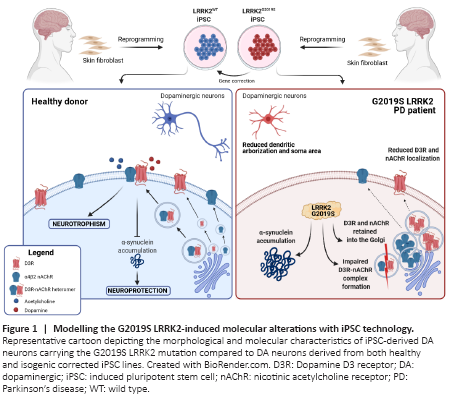
On these bases, we recently investigated the characteristics of DA neurons derived from iPSCs obtained from two PD patients harboring the G2019S LRRK2 mutation (Bono et al., 2021). Mutations in the LRRK2 gene are the most frequent cause of late-onset familial PD and a major risk factor for idiopathic PD, with the G2019S mutation accounting for up to 6–40% of familial cases and up to 2% of all sporadic cases (Ryden and Lewis, 2019). Many different experimental approaches, including iPSC-derived neurons, have been used to clarify the role of the G2019S LRRK2 mutation in DA neuron degeneration. In particular, iPSC-derived DA neurons carrying the G2019S LRRK2 mutation have been described as characterized by reduced neurite outgrowth, increased levels of alpha-synuclein, and alterations in mitochondrial morphology with impaired mitophagy and increased sensitivity to stress (Weykopf et al., 2019). We identified additional neuronal alterations that likely represent pre-degenerative features associated with the mutation in the LRRK2 gene, regardless of age- and environment-related events that might significantly contribute to the selective vulnerability of DA neurons (Bono et al., 2021) (Figure 1).