神经损伤与修复
-
Figure 2|Histochemical staining techniques in central and peripheral nervous systems.
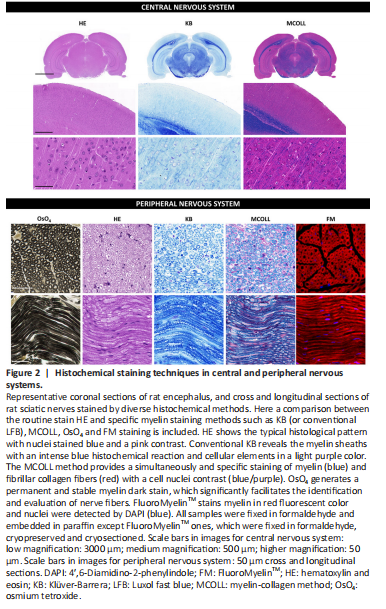
The OsO4 staining, which frequently involves a post-fixation procedure and consequent staining, confers myelin stabilization, and provides a permanent black positive reaction for myelin as well as other lipids present in the tissue. OsO4 penetrates tissues slowly and, a strong oxidizing agent reacts with organic compounds and it is itself reduced into OsO2. This last molecule adheres to structures that have been in contact with OsO4. This reaction prevents myelin sheath swelling and its deposition imparts a dark color at light microscopy and electron opacity at transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (Kiernan, 2007). As a result, myelin is stained black, and the nodes of Ranvier are clearly visible (Figure 2). Schmidt-Lanterman incisures are paler V-shaped formations within the myelin, visible only within well-processed material at high magnifications being clearly visible in TEM analysis. In addition, other staining methods, such as Picrosirius or Masson’s trichome, can be combined with OsO4 staining to identify other important structures in nervous tissue (García-García et al., 2023). OsO4 technique can be applied to cryosections, but it is especially useful for paraffin or resin sections.
The solvent dyes, such as Sudan (III, IV and black) and Oil red O, are able to interact with the hydrophobic domains of lipids including myelin. These dyes are prepared in polar organic solvents and when they are in contact with lipids, they diffuse from their solution to the hydrophobic domains of the lipids present in the tissue. Dyes diffusion occurs because they are much more soluble in lipids than in the solvent used, for these reasons they are commonly known as solvent dyes or lysochromes (Kiernan, 2008). From all the “Sudan” dyes, the Sudan black B is a good option for myelin staining as it is the less hydrophobic Sudan dyes and stains most lipids. Indeed, Sudan Black B dye can interact better with the phosphor and sphingolipids of normal myelin resulting in a dark gray or blue-black myelin staining (Kiernan, 2007). These methods work in paraffin sections, but better results can be obtained in cryosections, especially when the samples were chemically fixed and cryoprotected (Sánchez-Porras et al., 2023).
The myelin-collagen (MCOLL) technique is a trichromatic, histochemical-based method designed to simultaneously stain myelin, collagen fibers and cell nuclei allowing to perform an integrated histological analysis (Carriel et al., 2011; Figure 2). This method combines the classical Luxol fast blue (LFB) myelin staining technique with picrosirius histochemical method for fibrillar collagens and Harris hematoxylin as nuclear contrast (Carriel et al., 2014a). LFB has largely been used for myelin detection since its introduction by Kluver and Barrera (1953) in fact this method is also know as KB technique (Figure 2). It was assumed that LFB stains specifically lipid domains, however, it is currently believed that LFB does not have any histochemical interaction with lipids. Indeed, the colored dye anion enters all parts of the tissue, but the basic amino acids of the myelin proteins may retain them in sites that are not easily reached by the differentiating solution staining myelin with a characteristic blue reaction (Kiernan, 2007). Then, after myelin stain, picrosirius is performed which is based on a strong anionic tetrakisazo dye called Sirius red F3B (Carriel et al., 2011). These dye molecules parallelly interact with cationic groups on the surface of the collagen, giving an intense red colorimetric reaction to the fibrillar collagen fibers in light microscopy (Trau et al., 1991). Moreover, picrosirius molecules increase the natural birefringence of these fibers allowing their select evaluation by polarized light microscopy. MCOLL technique can be conducted in cryosections, but it is especially useful in paraffin-embedded material (Chato-Astrain et al., 2023). In addition, there is another modification of the classical LFB technique, where it was combined with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) histochemical method. This LFB-PAS method is especially useful to evaluate the demyelinating processes and also to identify the inflammatory activity. Indeed, the addition of PAS histochemical method allows to identify the cellular debris phagocyted by immunological cells, mainly by the microglia or foam cells, in some pathological conditions such as multiple sclerosis (Kuhlmann et al., 2017; Frosch et al., 2021).
点击此处查看全文