周围神经损伤
-
Figure 1|Administration of a total dose of 9 mg of Y-27632 does not prevent inhibition of axon regeneration induced by anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb.
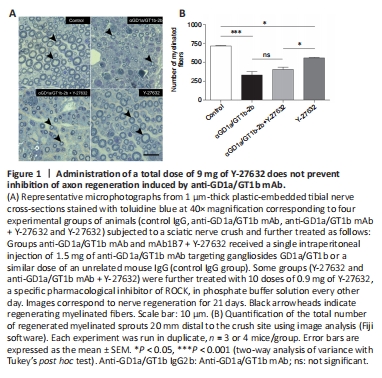
We first analyzed the pro-regenerative effect of the intraperitoneal administration of Y-27632, a specific pharmacological inhibitor of ROCK, in an established animal model of axon regeneration where the potent inhibitory effect of anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb was previously documented (Lehmann et al., 2007). Based on the work published by James et al. (2010), we performed the first experiment with the administration of a total dose of 15 mg of Y-27632 per animal over a period of 21 days. We observed a significant reduction (~60%) in the number of regenerated fibers in the tibial nerves from mice treated with Y-27632 when compared to control vehicle-treated nerves, indicative of a severe toxic effect of this dosage (data not shown). Therefore, we decided to scale down the total dose of Y-27632 to 9 mg. We still observed a significant although diminished reduction in the toxic effect of the treatment on regeneration of myelinated fibers when compared to control nerves receiving only vehicle (Figure 1A). As expected, the administration of a single dose of 1.5 mg of anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb induced a robust inhibition of axon regeneration of myelinated fibers in tibial nerves. However, the combined treatment of Y-27632 (total dose of 9 mg) and anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb did not result in a significant improvement of axon regeneration (Figure 1A and B). In conclusion, the total dosage of 9 mg of Y-27632 exerts a mild toxic effect on axon regeneration of myelinated fibers with no improvement in the regeneration of mice exposed to anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb.
Figure 2|Administration of a total dose of 5 mg of Y-27632 partially prevents inhibition of axon regeneration induced by anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb.
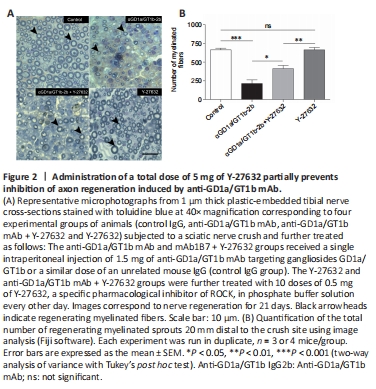
Given the toxicity of high dose Y-27632 (9–15 mg) on myelinated nerve fiber regeneration, we decided to decrease the total dosage to 5 mg to test its efficacy to promote axon regeneration of myelinated nerve fibers. In contrast to the toxic effects of high dose Y-27632, treatment with a dose of 5 mg of Y-27632 did not display toxicity on regenerating myelinated fibers compared to vehicle-treated control group (Figure 2B). Figure 2A depicts representative 1 μm-thick plastic-embedded sections from tibial nerves stained with toluidine blue. The morphometric analysis indicates a pronounced inhibitory effect of anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb on the regeneration of myelinated fibers when compared to control mice receiving irrelevant IgG. Notably, the immunization of anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb in combination with Y-27632 treatment (5 mg total dosage) resulted in significant improvement of axon regeneration compared to anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb treatment alone. However, this anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb-mediated effect was not completely reversed with 5 mg dosage of Y-27632.
Figure 3|Administration of a total dose of 9 mg of Y-27632 completely reverses the inhibitory effect of anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb on the regeneration of sensory unmyelinated fibers.
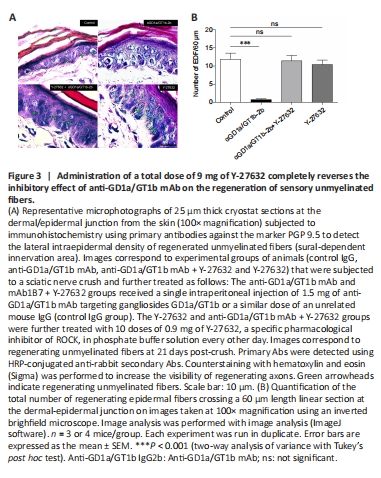
It was previously documented that administration of anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb in an animal model of axon regeneration inhibited regeneration not only of myelinated axons but also unmyelinated fibers (Lehmann et al., 2007). Thus, we decided to study the intraepidermal density of regenerated unmyelinated fibers in areas of hind paw innervated by the sural branch of the sciatic nerve. Figure 3A depicts representative photomicrographs of unmyelinated fibers, at the dermal/epidermal junction, identified by the use of antibodies against the marker PGP 9.5. Morphometric studies indicated absence of toxic effects due to the administration of a total dose of 9 mg/kg of Y-27632 when comparing the number of regenerated fibers to control group receiving vehicle (Figure 3B). Interestingly, while a pronounced inhibitory effect on skin reinnervation was observed in the epidermis from mice exposed to anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb compared to control IgG-treated group, the combinatory treatment of anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb and 9 mg Y-27632 resulted in a complete reversal of the inhibitory effect of anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb. In sum, Y-27632 has no toxic effect on regeneration of unmyelinated sensory fibers and it completely reverses the anti-GD1a/GT1b mAb-mediated inhibition of axon regeneration of unmyelinated fibers.