脑损伤
-
Figure 2|P7C3-A20 attenuates cell damage in the brain of rats after TBI.
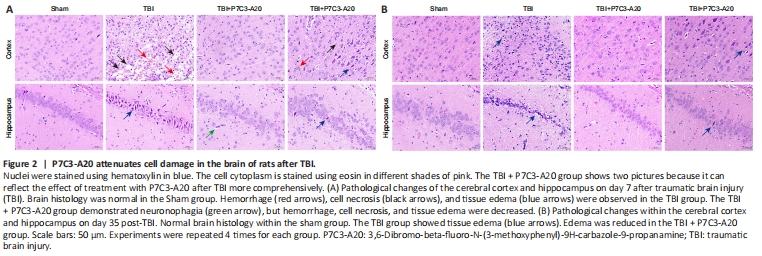
HE staining of the cortex and hippocampus of the rat brain was performed on days 7 and 35 after TBI. On day 7 after TBI, neuronal cells in the Sham group were normal in size and neatly arranged. There was hemorrhage and massive cell necrosis in the cortex of the TBI group, and tissue edema within the hippocampus of the TBI group. Compared with the TBI group, the cortex in the TBI + P7C3-A20 group showed reduced hemorrhage and cell necrosis or tissue edema, with only a small amount of neuronal phagocytosis and tissue edema in the hippocampus (Figure 2A). On day 35 after TBI, a large amount of tissue edema was observed in the cortex and hippocampus of the TBI group compared with the Sham group. A small amount of tissue edema was observed in the cortex and hippocampus of the TBI + P7C3-A20 group (Figure 2B).
Figure 3|P7C3-A20 attenuates autophagy in the brain of rats after TBI.

The cerebral cortex and hippocampus were examined on days 7 and 35 after TBI. Intracellular autophagosomes and autolysosomes were observed by TEM. In tissue obtained on day 7 after TBI, the mitochondria had a closed membrane vesicle structure with two layers of overlapping membranes in the sham group; the two membranes isolated the internal space of the mitochondria from the cytoplasm. Autolysosomes were observed in both the cortex and hippocampus of the TBI group. In contrast, autophagosomes were only observed within the cortex of the TBI + P7C3-A20 group (Figure 3A). Mitochondria were intact in the sham group on day 35 after TBI. Autolysosomes were also present within the TBI group. No abnormalities were observed in the mitochondria and other organelles of the TBI + P7C3-A20 group (Figure 3B).
Autophagy-related proteins (microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3-II [LC3-II] and p62) were examined in the rat cerebral cortex and hippocampus on days 7 and 35 after TBI. P7C3-A20 treatment downregulated LC3-II (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01) and upregulated p62 (P < 0.01) protein expression in TBI rats (Figure 3C–J).
Figure 4|P7C3-A20 attenuates apoptosis in the brain of rats after TBI.
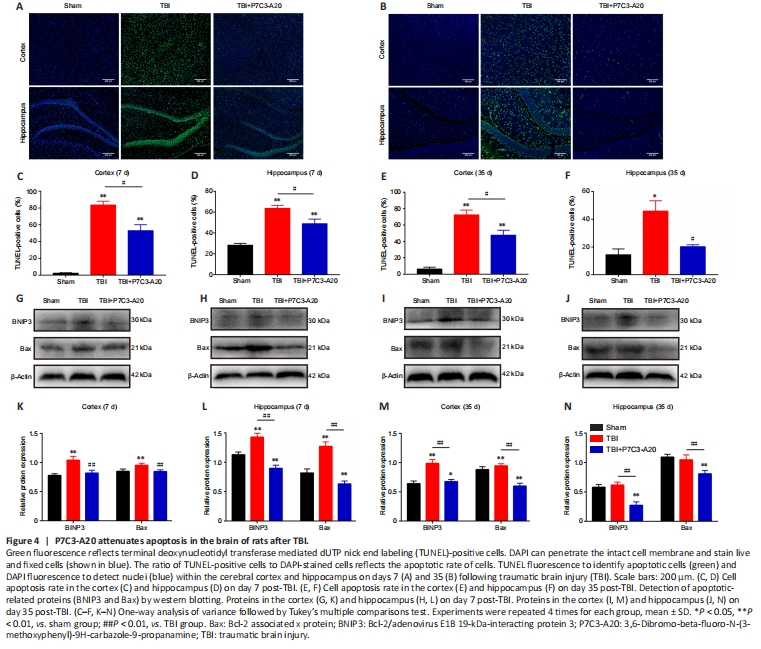
TUNEL staining of the cortex and hippocampus of the rat brain was performed on days 7 and 35 after TBI. On day 7 of TBI, the cortex and hippocampus had more apoptotic cells in the TBI group compared with the Sham group (P < 0.01). Moreover, P7C3-A20 treatment decreased apoptosis in the cortex and hippocampus compared with the TBI group (P < 0.05; Figure 4A, C, and D). Similarly, apoptosis rates were greater in the TBI group than in the Sham group on day 35 of TBI (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). Simultaneously, P7C3-A20 treatment decreased apoptosis in both cortical and hippocampal cells compared with the TBI group (P < 0.05; Figure 4B, E, and F).
Apoptotic-related proteins (BNIP3 and Bax) were examined in the rat cerebral cortex and hippocampus on days 7 and 35 after TBI. P7C3-A20 treatment decreased relative protein expression of BNIP3 and Bax (P < 0.01; Figure 4G–N).