NRR:重庆医科大学贺桂琼团队揭示HDAC6抑制剂治疗阿尔茨海默病的新机制
撰写:龙志敏,葛传华
阿尔茨海默病(AD)的主要神经病理学特征包括细胞内神经原纤维缠结,细胞外淀粉样斑块沉积,慢性神经炎症、突触丢失、神经元死亡等。过去人们普遍认为细胞外β淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)沉积形成老年斑是AD的罪魁祸首,然而最近的研究认为自噬溶体酸化异常,诱导神经元中Aβ的自噬积聚,才是产生老年斑的关键[1]。因此逆转溶酶体的功能,并重新平衡AD脑内神经元中溶酶体的酸性,可能是AD治疗新的策略。溶酶体酸化的过程受到多种因素的调节,其中微管乙酰化是该研究团队前期研究揭示的一个关键因素[2]。经典的组蛋白脱乙酰酶 6(HDAC6)对微管脱乙酰化具有抑制作用,尽管已有研究报道采用HDAC6抑制剂治疗AD,但HDAC6抑制剂对溶酶体的确切作用及机制仍不清楚。
重庆医科大学贺桂琼教授团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文)》 (Neural
Regeneration Research)2025年第9期上发表研究论文。这项工作使用HDAC6 shRNA和HDAC6抑制剂丙戊酸钠(VPA),通过调节阿尔茨海默病(AD)中的V-ATP酶组装,确定了一种经典的组蛋白脱乙酰酶 6(HDAC6)对溶酶体酸化的积极作用。这些结果证明了HDAC6抑制剂作为溶酶体活性的有效调节因子,在AD治疗中发挥神经保护作用。龙志敏和葛传华为论文共同第一作者,唐清副教授、董志芳教授、贺桂琼教授为论文并列通讯作者。
溶酶体酸化的调节主要取决于质子泵V-ATP酶以及离子转运蛋白介导的阴离子和阳离子在溶酶体膜中的运动[3]。微管修饰如微管的解聚会影响V-ATP酶活性。在最近的一项研究中,新发现微管脱乙酰酶NDST3通过介导α-微管蛋白乙酰化作用于V-ATP酶的组装过程。V-ATP酶组装的改变随后导致溶酶体酸化的变化[4]。因此,作者假设HDAC6作为α-微管蛋白脱乙酰酶,也可能参与V-ATP酶组装的调节,并有助于溶酶体酸化过程。为了证明这一假设,作者首先用HDAC6 shRNA处理SH-SY5Y细胞(图1),然后评估了V-ATP酶的组装,并测量了溶酶体的pH值,结果发现HDAC6缺失通过增加溶酶体膜上的V-ATP酶组装增强溶酶体酸化(图1)。
#br#
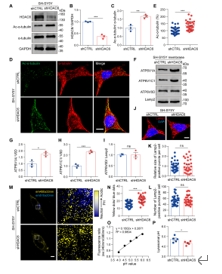
图1 组蛋白脱乙酰酶6(HDAC6)缺失增强了SH-SY5Y细胞中溶酶体酸化(图源:Long et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
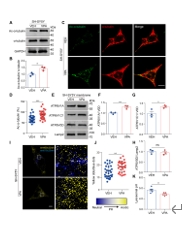
随后,该研究证实VPA是一种HDAC6抑制剂,可阻断微管的脱乙酰化,用VPA处理SH-SY5Y细胞后评估了V-ATP酶的组装,并测量了溶酶体的pH值,结果证实VPA可以促进溶酶体酸化(图2)。这些证据支持HDAC6在调节溶酶体酸化中发挥作用这一假设,促使作者深入研究并探索抑制HDAC6可能恢复AD中溶酶体酸化的可能性,从而为缓解该疾病的相关病理提供了一条潜在的途径。
 #br#
#br#
图2 HDAC6抑制剂丙戊酸钠(VPA)增强了SH-SY5Y细胞中溶酶体酸化(图源:Long et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
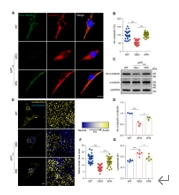
研究发现,AD患者的溶酶体酸化抑制,从而导致自噬障碍,神经元死亡。VPA是一种治疗癫痫和双相情感障碍的常用药物,近年来它作为AD的潜在治疗选择而引起了人们的关注[5,6]。临床前研究表明,它可以降低Aβ,增强突触可塑性,改善认知功能[7]。然而,VPA在AD中的作用机制尚不完全清楚。既然VPA可以通过调节微管乙酰化V-ATP酶组装轴来增强溶酶体酸化,那么VPA是否可以调整AD溶酶体的紊乱呢?于是作者测量了稳定表达APPswe基因的SH-SY5Y细胞(APPswe细胞)在VPA处理后的溶酶体pH。正如预期的那样,VPA增加了APPswe细胞中的Ac-α-微管蛋白水平。LysoSensor探针分析显示,VPA处理的APPswe细胞具有更强的黄色荧光,较弱的蓝色荧光,表明VPA增强了溶酶体酸性。通过对溶酶体pH值测量,观察到VPA处理的APPswe细胞已恢复到接近正常的水平。这意味着VPA恢复了溶酶体的碱化作用(图3)。
 #br#
#br#
图3 VPA增强了AD模型细胞中溶酶体酸化(图源:Long et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
为了研究VPA对AD模型中自噬流的影响,作者用含有mRFP-GFP-LC3表达的腺病毒感染APPswe细胞,通过用EBSS诱导自噬或用巴伐洛霉素A1抑制自噬,APPswe细胞中的黄点显著增加,而VPA处理的APPswe细胞中黄色斑点减少,红色斑点增加,说明自噬体和酸化程度较低的自噬溶酶体增加,完全酸化自噬溶酶体减少(图4)。随后作者通过免疫印迹检测LC3 I向LC3 II的转化和自噬选择性底物P62的水平进一步证实了VPA处理后,LC3 II表达增加,而P62表达减少,然而,溶酶体标记物Lamp2的水平没有显著变化。这些结果表明,VPA具有增强AD模型细胞自噬流的作用。
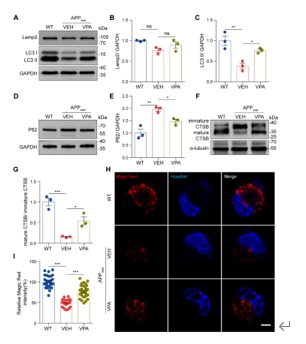
蛋白酶的水解酶活性存在于溶酶体中,如组织蛋白酶B(CTSB),受pH环境的高度控制[8]。CTSB的前体形式通常是无活性的,除非它在最佳酸性pH环境下进行蛋白水解处理和糖基化以形成成熟蛋白[9]。有趣的是,在VPA处理的APPswe细胞中,作者通过蛋白质印迹观察到成熟CTSB与前CTSB的比率显著增加),并使用Magic Red 分析观察到CTSB的活性增强(图5)。基于这些结果,作者提出VPA促进溶酶体水解酶的成熟。
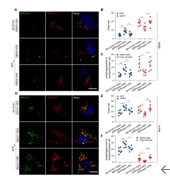
图4 SHAPE \* MERGEFORMAT(图源:Long et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
 #br#
#br#
图5 VPA促进了AD模型细胞中的自噬流并促进溶酶体水解酶的成熟(图源:Long et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
作者进一步通过腹腔注射将VPA注入APP/PS1转基因AD小鼠模型体内一个月,然后免疫印迹法检测发现VPA治疗提高了LC3 II水平,降低了P62表达。VPA处理的APP/PS1小鼠大脑中成熟CTSB的表达增加,而Lamp2的水平保持不变。这些数据表明VPA在APP/PS1小鼠中促进了自噬流。此外,由于自噬途径对Aβ聚集体的降解至关重要,作者进一步采用蛋白质印迹分析来检测发现用VPA处理的AD鼠大脑中Aβ水平显著降低,但APP水平不变。免疫荧光测定显示,VPA组Aβ聚集形成的老年斑少于对照组(图6)。这些数据表明,VPA可能通过增强APP/PS1小鼠的自噬来减少Aβ的沉积。
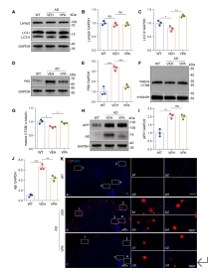
图6 VPA促进了APP/PS1
AD模型小鼠的自噬并减轻Aβ产生和沉积(图源:Long et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
作者还研究了VPA是否会影响APP/PS1小鼠的认知功能。通过Morris水迷宫实验,VPA已被证明可以改善AD模型小鼠的学习和记忆[6]。在该研究中,作者用Barnes-Maze用于评估VPA对APP/PS1小鼠的空间记忆的影响。在训练阶段的第4天、第5天和第6天,作者观察到,VPA处理的小鼠到达逃生孔的时间显著减少,第7天,VPA处理的小鼠发现目标孔的潜伏期更短,并且访问孔的次数增加(图7)。这些结果表明,VPA治疗的APP/PS1小鼠的认知功能显著改善。
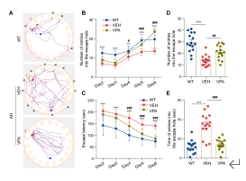
图7 VPA改善了APP/PS1
AD模型小鼠的认知功能(图源:Long et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
总之,该研究已确定HDAC6是自噬-溶酶体途径的强大调节因子,通过影响V-ATP酶组装的微管依赖性机制调节溶酶体酸化和降解能力。常用药物VPA已被发现是HDAC6的抑制剂,可降低α-微管蛋白的脱乙酰化作用。而微管高度乙酰化增加了溶酶体上V-ATP酶的组装(图8)。因此,VPA作为溶酶体活性的有效调节因子,在AD模型中发挥神经保护作用。这项研究的发现为HDAC6抑制剂VPA如何对AD产生神经保护作用提供了一个合理的解释。
然而,该研究存在一些值得注意的局限性。由于VPA是一种广泛的HDAC抑制剂,后续研究将寻找并使用专门针对微管乙酰化和溶酶体酸化的特异HDAC6抑制剂进行干预。此外,未来的研究可采用更多动物模型包括HDAC6敲除小鼠进行进一步的验证。
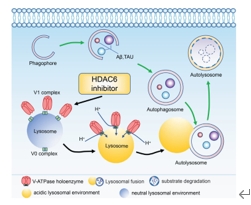
图8 模式图:HDAC6抑制剂VPA通过增强V-ATP酶组装和溶酶体酸化治疗阿尔茨海默病(图源:Long et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01633
参考文献
[1] Lee JH, Yang DS, Goulbourne CN, et al.
Faulty autolysosome acidification in Alzheimer's disease mouse models induces
autophagic build-up of Aβ in neurons, yielding senile plaques. Nat Neurosci. 2022;25:688-701.
[2] Tang Q, Liu M, Liu Y, et al. NDST3 deacetylates
α-tubulin and suppresses V-ATPase assembly and lysosomal acidification. EMBO J.
2021;40:e107204.
[3] Song Q, Meng B, Xu H, et al. The emerging roles of vacuolar-type
ATPase-dependent Lysosomal acidification in neurodegenerative diseases. Transl
Neurodegener. 2020;9:17
[4] Colacurcio DJ, Nixon RA. Disorders of lysosomal acidification-The
emerging role of v-ATPase in aging and neurodegenerative disease. Ageing Res
Rev. 2016;32:75-88.
[5] Long ZM, Zhao L, Jiang R, et al. Valproic
acid modifies synaptic structure and accelerates neurite outgrowth via the
glycogen synthase kinase-3β signaling pathway in an Alzheimer's disease model.
CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015;21:887-897.
[6] Long Z, Zeng Q, Wang K, et al. Gender
difference in valproic acid-induced neuroprotective effects on APP/PS1 double
transgenic mice modeling Alzheimer's disease. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 2016;48:930-938.
[7] Naseh M,
Bayat M, Akbari S, et al. Neuroprotective effects of
sodium valproate on hippocampal cell and volume, and cognitive function in a
rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Physiol Behav. 2022;251:113806.
[8] Johnson DE,
Ostrowski P, Jaumouillé V, et
al. The position of lysosomes within the cell
determines their luminal pH. J Cell Biol 2016;212:677-692.
[9] Hook G, Reinheckel T, Ni J, et al. Cathepsin
B gene knockout improves behavioral deficits and reduces pathology in models of
neurologic disorders. Pharmacol Rev. 2022;74:600-629.
#br#

 #br#
#br#
 #br#
#br#

 #br#
#br#


