NRR:首都医科大学宣武医院宋伟宏团队认为神经元介导炎症反应可能是特异阿尔茨海默病的致病机制
撰文:姚静,王喆,宋伟宏
阿尔茨海默病是一种在老年人中十分常见的神经退行性疾病,其发病人群极大,但病因不明,无法治疗,无法预防,是当代医学研究中的热点和难点。阿尔茨海默病的标志性特征是脑内β淀粉样蛋白(amyloid-β,Aβ)在细胞外聚集而成的不溶性老年斑块,以及神经元内高度磷酸化的tau蛋白在细胞内聚集而成的神经纤维缠结。老年斑块是阿尔茨海默病最为特征性的神经病理,而神经纤维缠结或过度磷酸化的tau蛋白可见于多种神经退行性疾病。至少在家族遗传性的阿尔茨海默病中,老年斑块的形成要早于包括神经纤维缠结及神经炎症在内的其它病理变化。NLRP3是炎症小体的核心成分之一,对于固有免疫细胞的防御功能具有重要作用。然而,当脑内的固有免疫细胞—-小胶质细胞过度活化或发生表型转换时,NLRP3也同样过度活化,可导致神经炎症反应。有研究报道,NLRP3炎症小体可介导Aβ的毒性[1],同时又促进Tau的磷酸化[2],因此NLRP3有可能参与老年斑块和神经纤维缠结的之间的相互作用。然而,小胶质细胞中的NLRP3如何促进神经元中tau的磷酸化仍不明确。神经元中的NLRP3是否存在,是否可调节神经元主导的炎症反应,是否可更直接地参与tau磷酸化,以及其表达的调节机制都是值得探讨的问题。
中国首都医科大学宣武医院的宋伟宏团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“FUBP3 mediates the amyloid-β-induced neuronal NLRP3 expression”的研究。其在神经元中发现了NLRP3的表达。尽管NLRP3表达量明显低于小胶质细胞中NLRP3水平,但是在阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠的神经元中抑制NLRP3后,可显著降低tau蛋白的磷酸化。用生化和细胞生物学方法发现,转录因子FUBP3可在神经元中调节NLRP3的表达及功能。FUBP3在阿尔茨海默病小鼠中及老年这一阿尔茨海默病危险因素下,在神经元内显著上升。更为有趣的是,FUBP3仅在Aβ存在的情况下调节NLRP3。且在Aβ存在的情况下,FUBP3还可调节其它炎症小体基因的表达,如NLRP6。这些发现提示,神经元介导的炎症反应可能是更为特异的阿尔茨海默病致病机制。
阿尔茨海默病是一种主要影响老年人的神经退行性疾病,其特征是细胞外神经突触斑块和胞内神经原纤维缠结。神经突触斑块主要由来源于淀粉样前体蛋白(APP)的Aβ组成,而神经原纤维主要是由MAPT基因编码的磷酸化过度的tau蛋白聚集而成。除了这2个特征外,阿尔茨海默病还与神经炎症和神经细胞死亡有关。在阿尔茨海默病病理发展过程中,神经突触斑块是最早的病变,而神经原纤维发生得较晚,也在其他疾病中发现。因此,神经突触斑块的积累可能有助于神经原纤维的形成。
有研究显示,炎症小体在神经退行性疾病中发挥重要作用。NLRP3(NOD-、LRR-和pyrin结构域含有蛋白3)炎症小体有可能是连接神经突触斑块和神经原纤维的因素之一。NLRP3炎症小体是一个固有免疫防御系统中的蛋白复合物。NLRP3炎症小体由NLRP3、ASC(包含CARD的凋亡相关斑点样蛋白)和caspase-1组成,其中NLRP3是探测病原侵袭的感应蛋白。在将NLRP3炎症小体视为一个可能的直接介导阿尔茨海默病中从神经突触斑块到神经原纤维缠结过渡的候选机制之前,必须回答一个基本问题,即NLRP3是否在神经元中表达。虽然在免疫细胞(如小胶质细胞)中已经确立了NLRP3的表达,但tau的表达和神经原纤维缠结主要是神经元内。如果NLRP3炎症小体直接诱导tau的过度磷酸酸化,它也可能在神经元中表达。但在阿尔茨海默病中神经元中的NLRP3炎症小体尚待考察。
为了检测NLRP3是否也在神经元中表达,本研究发现,在野生小鼠脑组织中,无论是小胶质细胞还是神经元中的NLRP3都几乎检测不到,而在和APP/PS1ΔE9转基因小鼠的脑组织中,NLRP3强烈定位于神经突触斑块附近的小胶质细胞,但仅个别皮质的神经元含有较弱的NLRP3(图1)。双氧水导致的氧化应激使得神经元内NLRP3显著上调。的在野生型原代神经元(PNWT)中,NLRP3在细胞质中仅呈现弥散的背景样分布(图1),而在Swedish突变单转基因的阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠的原代神经元中(PNAPP),NLRP3染色在神经元中富集(图1)。小鼠神经母细胞瘤细胞系Neuro2A中也有NLRP3 mRNA和NLRP3蛋白表达。对PNAPP使用NLRP3抑制剂CY-09(抑制NLRP3的ATP酶活性)和CORM-3(防止依赖糖酵解的NLRP3炎症小体激活)处理后,磷酸化tau(p-tau202/205和p-tau181)显著下降(图1)。综上,该数据证明NLRP3和NLRP3炎症小体复合物在神经元中微弱表达,但可高效地调节tau磷酸化。
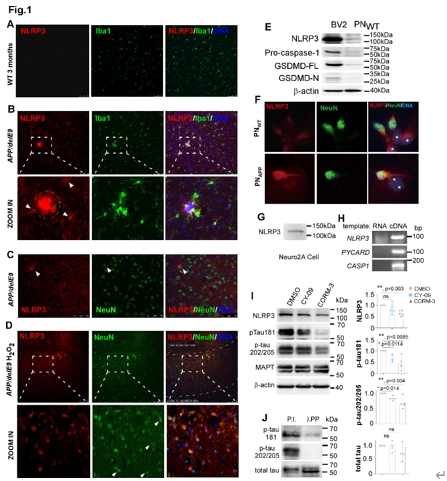
图1 NLRP3在神经元中表达以调控tau的磷酸化(图源:Yao et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
宋伟宏等进一步使用双荧光素酶测定法结合体外的生化实验,发现转录因子FUBP3是一个可能的NLRP3基因的转录因子促进NLRP3的表达(图2)。然而,细胞内的的实验结果发现,FUBP3在Neuro2A细胞系及野生原代神经元中并不能直接调节细胞内源NLRP3的表达,但是在Aβ存在的情况下,FUBP3的存在对于NLRP3的表达变得不可或缺。而在PNAPP(高表达人源Aβ)中,FUBP3可直接调节NLRP3(图3)。
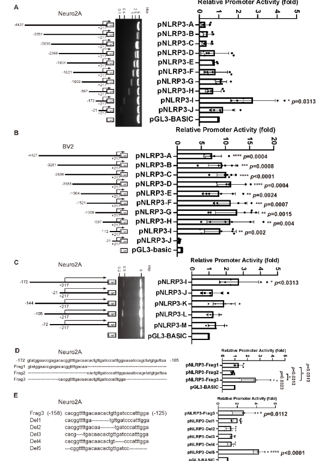
图2 鉴定NLRP3启动子中的最小活性区域(图源:Yao et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
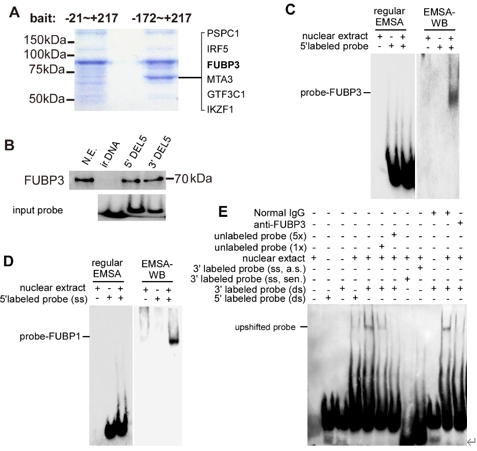
图3 鉴定FUBP3作为神经元中NLRP3最小启动子的结合蛋白(图源:Yao et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
进一步研究发现,在年轻的野生型小鼠(3个月)中,FUBP3的表达很弱(图4)。而在8个月大的APP/PS1ΔE9小鼠的大脑中,几乎所有皮质神经元中的FUBP3都显著上调(图4)。由于衰老是阿尔茨海默病的最重要的风险因素,实验还检测了20个月龄的野生型小鼠的大脑中的FUBP3,在皮质和海马中基本上所有神经元中都检测到强烈的FUBP3表达(图4)。
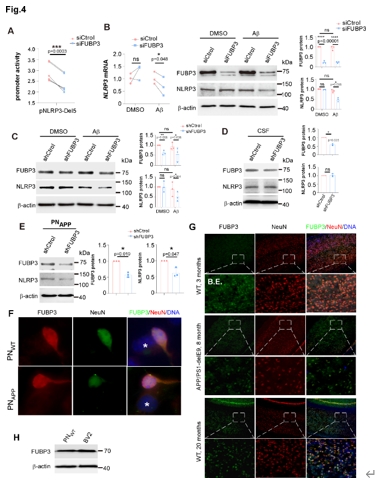
图4 在Aβ存在的情况下,FUBP3对神经元中NLRP3表达是必要的(图源:Yao et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
为检查Aβ是否诱导FUBP3进入细胞核,从而调节NLRP3的转录,宋伟宏等首先用Aβ处理细胞,发现Aβ确可在一定程度上促进FUBP3进入细胞核,但考虑到PNAPP中的FUBP3并不在细胞核内积累,Aβ并非通过促进FUBP3入核来调节NLRP3表达(图5)。因此,Aβ通过FUBP3调节NLRP3表达的机制仍有待检测。
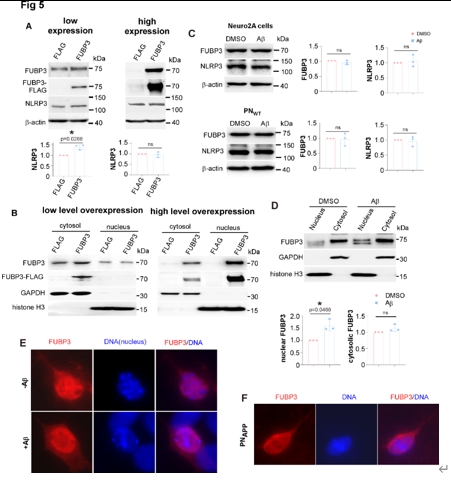
图5 FUBP3在Aβ存在的情况下核富集可能对NLRP3表达不是必需的(图源:Yao et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
由于在Aβ存在时或在PNAPP中,FUBP3对于维持NLRP3蛋白水平是不可或缺的,宋伟宏等进一步检测了在此条件下,FUBP3是否在神经元中调节NLRP3的功能。NLRP3炎症小体对于白细胞介素1β的成熟和分泌具有不可替代的作用。结果显示,在FUBP3下调时,PNAPP的培养基中白细胞介素1β的水平显著下降(图6),说明白细胞介素1β的成熟和/或分泌受到了损害,这可以由NLRP3炎症小体催化。为了证明在Aβ存在的情况下FUBP3抑制是否能通过调节NLRP3减少tau磷酸化,本研究使用表达FUBP3靶向shRNA的AAV感染了PNAPP,发现p-tau181和p-tau202/205均随FUBP3的下调而降低。对tau相关激酶和磷酸酶的分析显示,一些在以往研究中响应NLRP3的缺失并调节tau磷酸化的酶类分子并未受FUBP3的减少而产生明显变化(图6)。
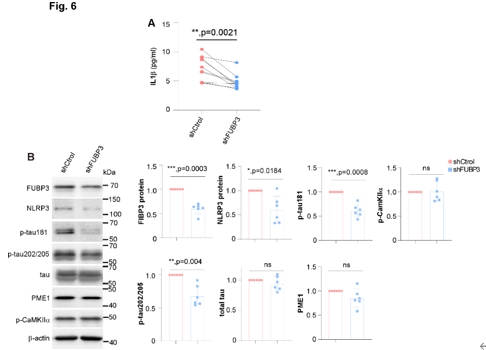
图6 FUBP3在PNAPP中对白细胞介素1β的分泌和tau的磷酸化是必需的(图源:Yao et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
为进一步阐释FUBP3如何调节神经元的功能,宋伟宏等在Neuro2A中敲低FUBP3,在有或没有Aβ的情况下进行了转录组学分析(图7)。结果显示,FUBP3很可能参与了神经类细胞中的免疫反应,除了NLRP3,NLRP6也同样在Aβ存在时相应FUBP3的缺失。而磷酸酶抑制蛋白PPP1R1A的减少,可能解释为何FUBP3的下调会减少tau的磷酸化。除此以外,FUBP3还可能与DNA损伤时的同源重组修复有关,这可能与FUBP3对DNA异常5’端的修剪功能相关。
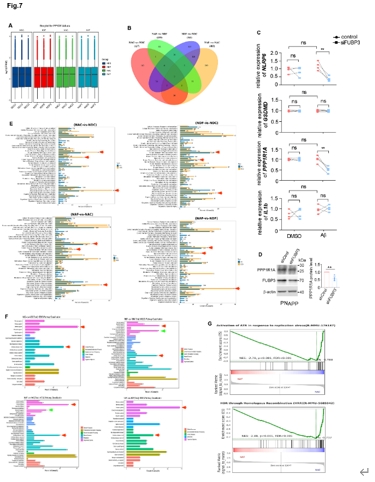
图7 FUBP3参与了Neuro2A细胞中的免疫反应(图源:Yao et al., Neural Regen Res, 2025)
此次实验检测到NLRP3在神经元中表达,并调控tau的磷酸化。转录因子FUBP3在且仅在Aβ存在的情况下对神经元中的NLRP3表达起重要作用。在阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠的原代神经元中,FUBP3对白细胞介素1β的分泌和tau的磷酸化也是必需的。类似于NLRP3炎症小体,FUBP3可能通过其在修剪DNA结合物的5'端方面的潜在活性,参与神经元介导的免疫响应和应激诱导的响应。鉴于仅在老年和阿尔茨海默病大脑中表达高水平的神经元FUBP3,神经元FUBP3可能是预防阿尔茨海默病进展的一个目标,特别是对于大脑中存在神经突触斑块而无NFT的患者。
研究发现NLRP3及其炎症小体也存在于神经元中,以介导白细胞介素1β的分泌和tau的磷酸化,转录因子FUBP3在存在Aβ的情况下对神经元中的NLRP3表达是不可或缺的。NLRP3炎症小体可能与tau病变密切相关,并且NLRP3炎症小体可能是预防神经退行性疾病中tau病理的潜在靶点。这也为NLRP3炎症小体如何参与不同神经退行性疾病提供了另一种解释,NLRP3炎症小体活性较高的神经元可能更容易形成NFT和焦亡,这些神经元释放的促炎细胞因子以及小胶质细胞释放的细胞因子可能促进这种免疫反应的传播。因此,疾病类型可能是由tau高度表达的神经元内在确定的。然而,本研究仍然需更深入的研究,如尚需确定在神经元中NLRP3炎症小体的下游效应,除了促炎细胞因子之外的其他效应因子或蛋白;在活体内获得证据以巩固这项研究的结论,并且需要研究神经元NLRP3在调节tau磷酸化方面的功能以及FUBP3在Aβ依赖功能方面的分子机制。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01799






