中国神经再生研究(英文版) ›› 2026, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (1): 195-211.doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00877
基于果蝇模型研究癫痫的相关基因
Investigation of epilepsy-related genes in a Drosophila model
Xiaochong Qu1 , Xiaodan Lai1 , Mingfeng He1 , Jinyuan Zhang2 , Binbin Xiang3 , Chuqiao Liu1 , Ruina Huang1 , Yiwu Shi1 , Jingda Qiao1, *
- 1 Department of Neurology, Institute of Neuroscience, Key Laboratory of Neurogenetics and Channelopathies of Guangdong Province and the Ministry of Education of China, the Second Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China; 2 School of Health Management, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China; 3 The First Clinical Medicine School of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
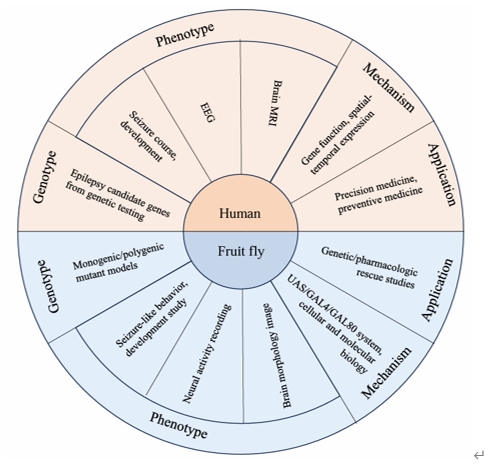
复杂的遗传结构是癫痫异质性的主要原因,其对准确诊断和精确治疗提出了挑战。随着下一代测序技术的广泛应用,临床研究中已鉴定出大量癫痫候选基因。验证这些候选基因正成为一项有价值且具有挑战性的工作。果蝇是一种能够验证癫痫等神经遗传性疾病候选基因的理想动物模型,其具有快速的繁殖率、强大的遗传工具以及有效的行为学和电生理学检测。此次综述系统地总结了基于果蝇模型的优势技术来研究癫痫基因的进展,包括操纵靶基因表达的遗传工具、癫痫样行为分析、电生理技术和神经活动记录的功能成像;然后总结了一些识别癫痫基因的典型方法;还为癫痫与多基因病因的基因相互作用提供了新方案。文章还总结了这些针对癫痫的成熟的精确医学策略,并基于果蝇模型对遗传性癫痫的药物治疗和基因治疗等的策略进行了展望。最后,研究讨论了遗传咨询和辅助生殖技术对预防遗传性癫痫的作用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4693-8390 (Jingda Qiao)