NRR:中国山西白求恩医院景玮团队概述癫痫的神经回路机制:对结构回路、突触回路和递质回路的深入认识
撰文:杜学青,汪仪,王学峰,田鑫,景玮
癫痫是一种常见的神经系统疾病,容易引起癫痫发作,癫痫发作复发会产生认知、心理和神经生物学后果[1]。癫痫包括发生在分子、细胞和神经回路水平的神经功能障碍[2]。癫痫发作是神经回路功能障碍的常见临床表现,普遍认为这是由兴奋和抑制之间的平衡被破坏引起的,导致神经回路内的不可控的兴奋和“超同步”[3]。近年来,在理解癫痫背后的机制方面取得了重大进展,特别是在细胞和分子水平上[2]。然而,要通过一个离散的基因突变或分子信号通路或特定细胞类型的功能障碍引起癫痫,它必须通过改变回路的功能来实现[4]。这无疑说明从神经回路的角度探讨癫痫的发病机制是一个很好的选择,现有技术的不断改进和新技术的不断涌现也为此提供助力。但是,癫痫在神经回路层面的机制仍缺乏全面且深入的总结。对癫痫神经回路机制进行概述可以为探索癫痫的病理生理机制、提高疾病诊断和临床治疗提供新思路和新视角。
中国山西医科大学第三临床医学院景玮团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“Neural circuit mechanisms of epilepsy: Maintenance of homeostasis at the cellular, synaptic, and neurotransmitter levels”的综述文章,指出癫痫的神经回路机制表现在许多方面。不同结构或者同一结构内部之间存在回路关系,关系的建立与突触和神经递质密不可分,这些神经递质和突触是细胞之间通信所必需的。突触之间存在平衡,神经递质之间也可构建回路,实现兴奋与抑制之间的稳态的维持,调节癫痫表型的发生和发展。提示以神经回路的角度进行癫痫的机制研究,可为探索癫痫的病理生理机制、改进疾病的临床诊治过程带来新的思路。
癫痫是一种常见的神经系统疾病,容易引起癫痫发作,癫痫发作复发会产生认知、心理和神经生物学后果[1]。癫痫包括发生在分子、细胞和神经回路水平的神经元功能障碍[2]。在癫痫发生的发展过程中,许多改变发生在细胞或突触水平,包括神经细胞的损失,胶质细胞的增殖,突触发生,兴奋性和抑制性细胞信号的变化,最终导致异常神经元回路的建立,表现出兴奋性增加[2, 5]。
近年来,在理解癫痫背后的机制方面取得了重大进展,特别是在细胞和分子水平上[2]。然而,要通过一个离散的基因突变或分子信号通路或特定细胞类型的功能障碍引起癫痫,它必须通过改变回路的功能来实现[4]。例如,由最初的诱发性损伤(如长时间的热性惊厥、感染或头部创伤)引起的细胞水平的改变可能改变神经回路,并最终使这些回路自发同步并表现为癫痫[6]。但是癫痫在神经回路层面的机制仍缺乏全面且深入的总结。基于此,景玮等综述了以往关于癫痫神经回路机制的研究和发现,讨论了结构回路、突触回路和递质回路,并对进一步的探索内容进行展望。
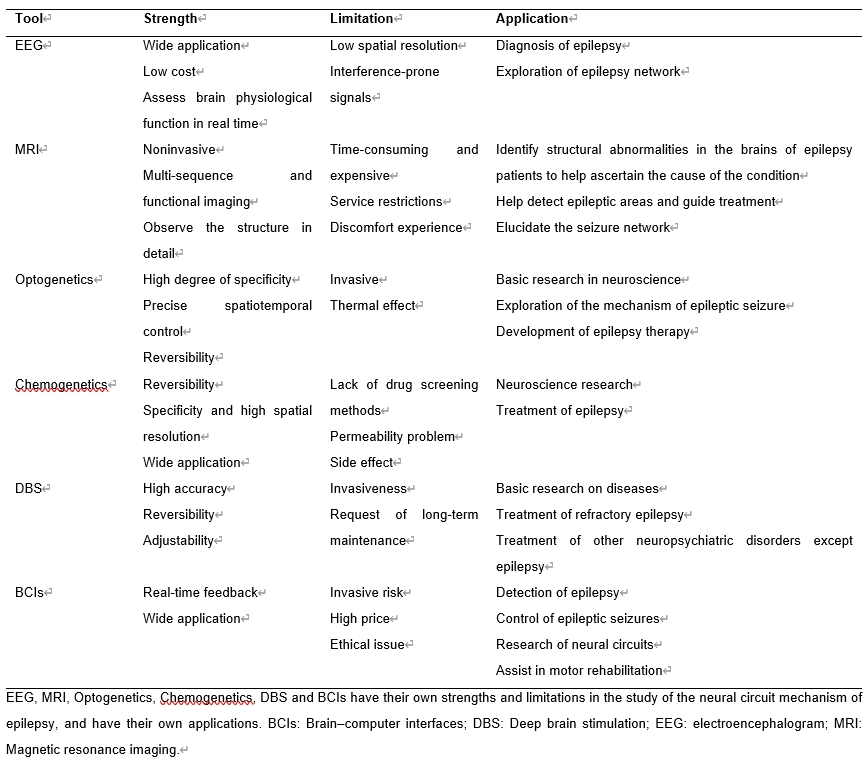
新技术的不断涌现和现有技术的飞速进展,实现了技术的进步。技术的进步促进了癫痫神经回路机制在各水平层面的发现,为许多新的癫痫治疗策略的出现奠定了基础,并为指导抗癫痫药物更准确地靶向受影响回路提供了便利[2]。在研究过程中,脑电图、磁共振成像、光遗传学、脑深部刺激等技术发挥着不同的作用(图1),各有优缺点(表1)。它们并不是孤立的,而是可以互补和整合的。通过合理地单独或联合使用这些技术,已经在基础或临床层面发现了一些研究成果,显示了癫痫神经回路机制研究的广阔前景。
此外,在癫痫的临床诊断和治疗过程中,癫痫的各种并发症也引起了大家的关注。其中,在癫痫发作过程中,在诊断和治疗之前,认知功能障碍和情绪障碍是常见的[7]。癫痫猝死是发生在癫痫患者中的一种被低估的严重并发症[8]。这提示研究人员,当癫痫的神经回路机制研究全面展开时,癫痫相关并发症的神经回路机制研究也可以提上日程。
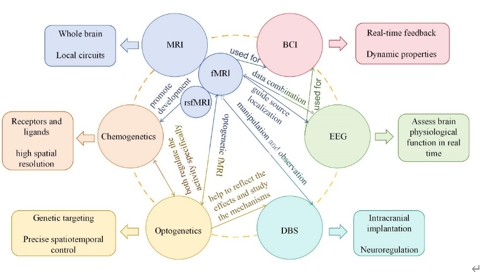
图1癫痫神经回路机制部分研究工具(图源:Du et al., Neural Regen Res, 2026)
表1几种癫痫神经回路机制研究工具的比较分析(表源:Du et al., Neural Regen Res, 2026)
在回顾和总结以往的研究结果后,景玮等认为癫痫的神经回路机制可以从“相对宏观”的结构水平回路和“相对微观”的突触和递质水平回路两方面进行大致的总结。在结构水平回路的概述中,提及了皮质和皮质下区域中的一些结构,包括内嗅皮质、海马旁回、扣带回、齿状回、下托、中缝核和丘脑等,并且提及了这些结构之间的部分信息投射关系(图2)。

图2癫痫神经回路机制的部分结构水平回路(图源:Du et al., Neural Regen Res, 2026)
癫痫相关神经结构的形成离不开各种细胞的支持,神经结构之间的信息传递也离不开中枢神经系统细胞间的相互作用。中枢神经系统细胞通过旁分泌信号、细胞外囊泡、神经递质和突触介导远距离通信,维持中枢神经系统的稳态[9]。这也表明,事实上,“相对较大”的结构回路的形成离不开无数“相对较小”的突触和传递回路的支持。
随着科学研究的不断深入,人们认为兴奋性和抑制性突触之间的平衡可能在神经回路的异常电信号中起着至关重要的作用,而癫痫的机制也与这种平衡的破坏有关,在颞叶癫痫中,小胶质细胞可以通过特异性地修剪抑制性突触来改变海马的神经元回路,从而改变兴奋性和抑制性突触的数量,最终导致这种平衡失衡,形成癫痫[10]。在齿状回中,已经证明颗粒细胞通过兴奋性突触投射到伽马氨基丁酸(GABA)能的中间神经元和苔藓细胞,而中间神经元通过GABA能突触抑制颗粒细胞和苔藓细胞,而苔藓细胞对颗粒细胞和中间神经元进行兴奋性投射[11],从而实现了这些突触连接之间的平衡回路。这些发现提示突触水平的平衡对神经回路至关重要,并可能进一步影响癫痫的发展。
此外,自噬的重要性不可忽视。自噬在突触可塑性、神经传递、树突棘形成等丰富的神经元活动中发挥作用,被认为参与癫痫发病机制,自噬失败导致兴奋性和抑制性大脑信号失衡,从而引发癫痫发作,而自噬活性降低使GABAA受体向质膜表面的易位减少,阻碍神经元的抑制性输入[12]。自噬机制与神经网络中的突触和递质密切相关,进一步研究这一机制将有助于更全面地了解癫痫的神经回路机制。
在递质水平上,景玮等主要关注兴奋性和抑制性神经递质的相互作用和平衡。位于大脑不同部位和大脑同一部位的神经递质相互作用,形成错综复杂的关系网络。哺乳动物的海马回路包括两种基本的神经元类型,即兴奋性主细胞,通常是指主要释放谷氨酸作为神经递质的输入和输出神经元,和抑制性中间神经元,通常位于主细胞周围,通过轴突调节主细胞的兴奋性,也被称为GABA能或抑制性中间神经元,因为大多数中间神经元合成和释放GABA,而且兴奋和抑制之间的平衡至关重要[13]。2011年,Werner和Coveñas[14]描述了全面性癫痫中经典神经递质和神经肽的变化,并指出在这种情况下神经元网络的形成。在全面性癫痫中,D2多巴胺能神经元激活谷氨酸能神经元,谷氨酸能神经元通过N-甲基-D-天门冬氨酸(NMDA)受体对5-羟色胺(5-HT)2C 5-HT能神经元施加强烈的突触前抑制,而后者对GABA能神经元的激活较弱,GABA能神经元突触前抑制D2多巴胺能神经元[15]。在这些神经元之间的相互作用中,受体起着重要的作用。四种主要神经递质(多巴胺、5-HT、GABA、谷氨酸)之间存在相互的神经递质平衡,这些神经递质参与到维持平衡的回路当中,如果神经递质变化(如多巴胺过度活跃,5-HT活动不足,GABA能突触前抑制不足或谷氨酸兴奋毒性)是永久性的,神经递质失衡似乎会促进癫痫发作的生成并诱发癫痫发作[15]。除上述神经递质外,还有许多其他递质参与癫痫[16]。
在癫痫的神经回路机制研究中,除了神经元的参与外,还有神经胶质细胞的参与。小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞可介导炎症介质的异常激活和释放,加重癫痫的发生[10]。此外,星形胶质细胞的特殊的细胞结构和数量特征使其在不同的代谢途径中扮演重要角色,有助于维持代谢稳态,其代谢功能障碍已被确定为包括癫痫在内的几种神经系统疾病的主要原因[17]。探索胶质细胞参与的代谢和炎症过程可能有助于研究癫痫的神经回路机制。
癫痫涉及的神经元、神经递质和受体是多种多样的,它们之间的相互作用是复杂而丰富的。在大脑皮质和皮质下区域之间有广泛的相互联系。结构内部或结构之间也存在细胞、突触和递质之间的相互作用,以及它们所构建的网络。不同类型的神经元相互激活或抑制,形成回路。
目前对癫痫神经回路机制的研究比较丰富,涉及基础研究和临床研究。通过单独或联合使用包括脑电图、光遗传学和化学遗传学技术在内的多种技术和建立各种动物模型,专家、临床医生和研究人员正在显微镜下探索与癫痫发作相关的突触、分子、蛋白质、受体、神经元、细胞核、通路和神经回路发生了什么。他们想知道这些变化是如何导致癫痫表型的出现,以及干预这些变化如何阻止癫痫发作。
尽管科学技术的进步取得了重大进展,但许多新的发现仍在不断涌现。这不仅有助于扩展甚至修正研究者们现有的理解,而且有助于建立更广泛的癫痫神经回路或网络,为探索新的治疗策略铺平道路。当前,这项研究仍处于探索阶段,研究人员对不同类型癫痫的精确神经回路机制的了解并不完全清楚。对癫痫神经回路机制的深入研究已逐渐成为癫痫机制研究和药物开发的中心焦点。技术的进步也支持了各种特异回路的发现,从而为癫痫的病理生理机制、临床诊断和治疗提供了新的思路和视角。从神经递质和受体的角度深入了解癫痫神经回路将有助于临床选择合适的抗癫痫药物。同时,对临床抗癫痫药物药理机制的不断探索,将增强研究者对癫痫所涉及的神经回路机制的认识。在未来的研究中,研究人员需要建立各种实验动物模型,并利用光遗传学、化学遗传学、脑机接口等技术来阐明各种类型癫痫发作所涉及的核心靶点,它们如何通过信号通路相互连接,以及它们如何形成病理回路。许多研究工具的应用对于癫痫神经回路的研究是必不可少的,也需要考虑患者是否愿意接受这些工具,以及它们是否会对患者造成伤害。
总之,目前对癫痫的神经回路机制的研究比较丰富。通过建立各种动物模型和使用包括脑电图、磁共振成像、光遗传学在内的各种技术,研究人员已经探索了与癫痫发作相关的神经回路,并在基础研究和临床研究中确定了一些成果。癫痫的神经回路机制内涵丰富,包括不同结构间的信息传递、同一结构内的相互作用以及在细胞、突触、神经递质水平上构建的稳态的维持。作者通过对相关研究的概述,对癫痫神经回路机制做出了大致的框架构建,为下一步对癫痫的神经回路进行纵向地深入理解和横向的广泛扩展奠定了坚实的基础。
当然,该综述也存在一定局限性。文章以“癫痫的神经回路机制”为主题进行综述。选题范围之广就要求全文内容丰富、全面,但在这方面仍存在不足。此外,本文的一个显著局限性是在文献选择过程中对综述文章依赖较多。此外,还应该对同一内容的不同观点进行更多的辩证讨论,这是未来需要注意和并改进的问题。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00537
参考文献
[1] Beghi E. The Epidemiology of Epilepsy. Neuroepidemiology. 2020;54(2):185-191.
[2] Wang Y, Chen Z. An update for epilepsy research and antiepileptic drug development: Toward precise circuit therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;201:77-93.
[3] Rao VR, Lowenstein DH. Epilepsy. Curr Biol. 2015;25(17):R742-746.
[4] Goldberg EM, Coulter DA. Mechanisms of epileptogenesis: a convergence on neural circuit dysfunction. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013;14(5):337-349.
[5] Ono T, Galanopoulou AS. Epilepsy and epileptic syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;724:99-113.
[6] Sutula TP. Mechanisms of epilepsy progression: current theories and perspectives from neuroplasticity in adulthood and development. Epilepsy Res. 2004;60(2-3):161-171.
[7] Pugh R, Vaughan DN, Jackson GD, et al. Cognitive and psychological dysfunction is present after a first seizure, prior to epilepsy diagnosis and treatment at a first seizure clinic. Epilepsia Open. 2024;9(2):717-726.
[8] Guo J, Min D, Farrell EK, et al. Enhancing the action of serotonin by three different mechanisms prevents spontaneous seizure-induced mortality in Dravet mice. Epilepsia. 2024;65(6):1791-1800.
[9] Capobianco DL, Simone L, Svelto M, et al. Intercellular crosstalk mediated by tunneling nanotubes between central nervous system cells. What we need to advance. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1214210.
[10] Fan J, Dong X, Tang Y, et al. Preferential pruning of inhibitory synapses by microglia contributes to alteration of the balance between excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the hippocampus in temporal lobe epilepsy. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023;29(10):2884-2900.
[11] Yu Y, Han F, Wang Q. A hippocampal-entorhinal cortex neuronal network for dynamical mechanisms of epileptic seizure. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2023;31:1986-1996.
[12] Sayed N, Ali AE, Elsherbiny DM, et al. Involvement of autophagic machinery in neuropathogenesis: targeting and relevant methods of detection. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. doi: 10.1007/7651_2024_516.
[13] Liu YQ, Yu F, Liu WH, et al. Dysfunction of hippocampal interneurons in epilepsy. Neurosci Bull. 2014;30(6):985-998.
[14] Werner FM, Coveñas R. Classical neurotransmitters and neuropeptides involved in generalized epilepsy: a focus on antiepileptic drugs. Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(32):4933-4948.
[15] Werner FM, Coveñas R. Neural networks in generalized epilepsy and novel antiepileptic drugs. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(4):396-400.
[16] Werner FM, Coveñas R. Classical neurotransmitters and neuropeptides involved in generalized epilepsy in a multi-neurotransmitter system: How to improve the antiepileptic effect? Epilepsy Behav. 2017;71(Pt B):124-129.
[17] Zhang YM, Qi YB, Gao YN, et al. Astrocyte metabolism and signaling pathways in the CNS. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1217451.


