中国神经再生研究(英文版) ›› 2026, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (7): 2836-2848.doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00923
• 原著:脑损伤修复保护与再生 • 上一篇
小胶质细胞Caspase激活和募集结构域19减轻脑卒中后神经炎症
Microglial CARD19 ameliorates post-stroke neuroinflammation by stabilizing mitochondrial cristae
Yujie Hu1, 2, Liwen Zhu1, 3, Chao Zhou1, 2, Qi Li1, 2, Huiya Li1, 2, Shiji Deng1, 2, Shengnan Xia1, 2, Haiyan Yang1, 2, Xinyu Bao1, 2, Pinyi Liu1, 2, *, Yun Xu1, 2, 3, 4, 5, *
- 1 Department of Neurology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China; 2 Department of Neurology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology and Institute of Translational Medicine for Brain Critical Diseases, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China; 3 Department of Neurology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Clinical College of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China; 4 Jiangsu Provincial Key Discipline of Neurology, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China; 5 Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Molecular Medicine, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
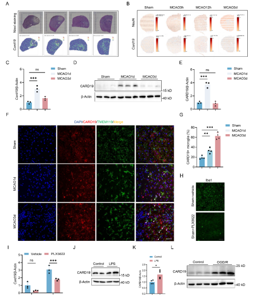
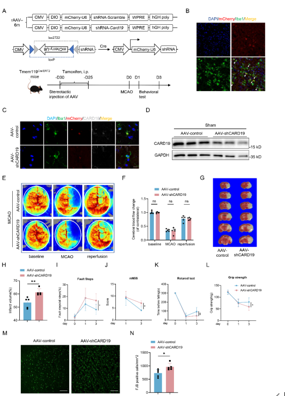
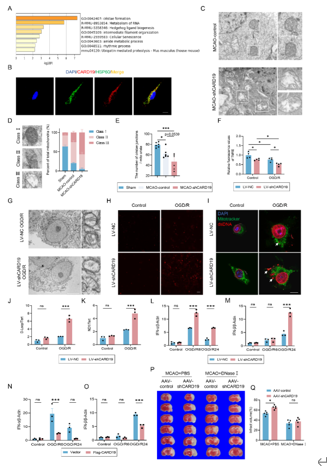
小胶质细胞是缺血性脑卒中后大脑中最初激活的免疫细胞。线粒体功能障碍会加剧小胶质细胞介导的脑卒中后神经炎症。Caspase 激活和招募结构域 19(CARD19)可触发巨噬细胞的先天性免疫信号传导;然而,CARD19 在小胶质细胞生物学和缺血性脑卒中中的功能仍然难以捉摸。实验发现,在缺血性卒中后半暗带区,小胶质细胞CARD19显著升高。在小胶质细胞中条件性敲减CARD19加重了卒中后神经炎症,并恶化了卒中结局。进一步研究发现,CARD19定位于线粒体,促进线粒体膜间桥(MIB)组分的组装,而小胶质细胞CARD19缺失导致线粒体嵴超微结构和功能损伤,加重炎症反应。这些结果表明,通过靶向CARD19维持线粒体嵴结构可能是一种改善缺血性卒中后神经炎症和挽救缺血半暗区的治疗新策略。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7887-5286 (Yun Xu); https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0403-0034 (Pinyi Liu)