中国神经再生研究(英文版) ›› 2025, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (10): 2807-2822.doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00641
中枢-外周-靶器官水平的多层次分析:有助于周围神经损伤后更好的功能恢复
Multilevel analysis of the central–peripheral– target organ pathway: contributing to recovery after peripheral nerve injury
Xizi Song1, 2, Ruixin Li1, 2, Xiaolei Chu3 , Qi Li3 , Ruihua Li4 , Qingwen Li5 , Kai-Yu Tong6, *, Xiaosong Gu1, 2, Dong Ming1, 2, *
- 1 Academy of Medical Engineering and Translational Medicine, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China; 2 Haihe Laboratory of Brain-Machine Interface and HumanMachine Fusion, Tianjin, China; 3 Department of Rehabilitation, Tianjin University Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin, China; 4 Department of Hand Microsurgery, Tianjin University Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin, China; 5 School of Exercise and Health, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin, China; 6 Department of Biomedical Engineering, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, China
摘要:
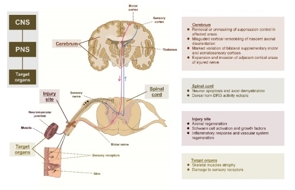
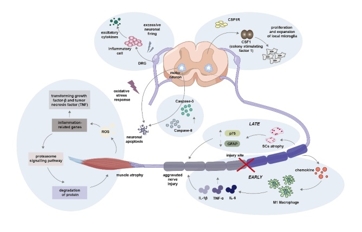
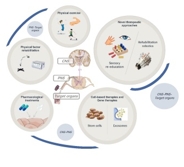
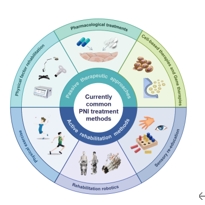
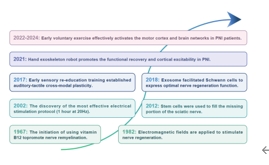
周围神经损伤是临床上常见的神经系统疾病,常导致严重的功能障碍和残疾。以往对周围神经损伤发病机制的研究主要集中在单个损伤部位的病理变化,而忽视了涉及整个神经系统和靶器官的多层次病理分析,这导致了目前治疗方法的局限性。文章首先从整体角度总结了周围神经损伤的潜在机制,涵盖了中枢神经系统、周围神经系统和靶器官三个方面。周围神经损伤发生后,大脑皮质的可塑性会因周围神经的损伤和再生而改变,脊髓会发生神经元凋亡和轴突脱髓鞘等变化。神经会在损伤部位发生轴突再生、许旺细胞活化、炎症反应和血管系统再生。靶器官也会发生相应的损伤,包括骨骼肌萎缩和感觉受体破坏。接下来简要回顾神经损伤治疗方法的研究进展。目前的主要治疗方法是被动治疗,包括物理因素康复、药物治疗、细胞疗法和体育锻炼。然而,大多数治疗方法只能解决部分问题,无法完成整个中枢神经系统-中枢神经系统-靶器官通路的系统恢复。这些表明,应进一步探索效果好、疗效长的多层次治疗方案,或许需要被动(传统)和主动(新型)相结合的治疗方法,刺激患者中枢-周围-靶器官各层次的康复,以实现更好的功能恢复
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4375-653X (Kai-Yu Tong); https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8192-2538 (Dong Ming)