中国神经再生研究(英文版) ›› 2023, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (10): 2147-2155.doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.369102
多发性硬化中纤维连接蛋白作用及穿越血脑屏障给药的效果
-
出版日期:2023-10-15发布日期:2023-03-28 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(82001282和81960232);宁夏留学生创新创业项目(2021);宁夏医科大学和宁夏青年人才支持计划项目(XT2019018,TJGC2019081);大学生创新创业培训计划项目(X202210752038)
The role of fibronectin in multiple sclerosis and the effect of drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier
Shuang-Shuang Wei1, Le Chen1, Feng-Yuan Yang1, Si-Qi Wang1, Peng Wang2, *
- 1Ningxia Key Laboratory of Craniocerebral Diseases, School of Clinical Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 2Ningxia Key Laboratory of Craniocerebral Diseases, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2023-10-15Published:2023-03-28 -
Contact:Peng Wang, PhD, pengwang@nxmu.edu.cn or wuyawode_1987@163.com. -
Supported by:This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 82001282 (to PW) and 81960232 (to PW); Overseas Students’ Innovation and Entrepreneurship Individual Project of Ningxia (2021) (to PW); Youth Talents Supporting Program of Ningxia Medical University and Ningxia, Nos. XT2019018 (to PW), TJGC2019081 (to PW); College Students’ Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program, No. X202210752038 (to FYY).
摘要:
髓鞘再生失败是多发性硬化的主要特征,可能与该疾病进展有关。在慢性和进行性多发性硬化病变中,细胞外基质重塑经常失败,这与髓鞘再生失败有关。且慢性多发性硬化病变中,由于纤维连接蛋白持续存在,可形成稳定的纤连蛋白聚合物,并抑制髓鞘再生。尽管在多发性硬化机制和药物的研究方面已取得一些进展,但由于大脑结构和功能的复杂性,特别是血脑屏障的存在使药物很难到达大脑病理组织并发挥作用。因此此次综述总结了多发性硬化中纤连蛋白聚合物组分对髓鞘再生的影响以及不同形式穿越血脑屏障给药治疗多发性硬化的效果。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8594-3766 (Peng Wang)
引用本文
. 多发性硬化中纤维连接蛋白作用及穿越血脑屏障给药的效果[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(10): 2147-2155.
Shuang-Shuang Wei, Le Chen, Feng-Yuan Yang, Si-Qi Wang, Peng Wang. The role of fibronectin in multiple sclerosis and the effect of drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier[J]. Neural Regeneration Research, 2023, 18(10): 2147-2155.
| [1] | . CXC趋化因子受体7增强缺血性脑卒中后的神经可塑性[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(9): 1976-1982. |
| [2] | . 内皮细胞丝裂原活化蛋白激酶磷酸酶1活化能保护改善缺血性脑卒中血脑屏障[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(8): 1743-1749. |
| [3] | . 阿尔茨海默病伴睡眠不足:临床特征、食欲能系统和血脑屏障相关性的横断面研究[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(8): 1757-1762. |
| [4] | . 鞘氨醇-1-磷酸受体1 可调节癫痫小鼠血脑屏障的通透性[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(8): 1763-1769. |
| [5] | . 大黄素减轻实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的炎症和脱髓鞘反应[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(7): 1535-1541. |
| [6] | . 抑制磷酸酶肌动蛋白调节因子1表达对创伤性脑损伤的神经保护[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(7): 1578-1583. |
| [7] | . 运动训练联合骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体减少神经元凋亡和轴突重塑具有协同作用[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(6): 1293-1299. |
| [8] | . 脊髓损伤后肠道菌群变化与代谢物谱相关[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(5): 1076-1083. |
| [9] | . 多聚鸟氨酸可阻断纤连蛋白对少突胶质细胞分化的抑制而促进髓鞘修复 [J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(4): 832-839. |
| [10] | . 来源于骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体的miR-23b可减轻脑出血后氧化应激和细胞焦亡[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(3): 560-567. |
| [11] | . 脱细胞神经基质支架抑横断周围损伤神经残端中神经瘤的形成[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(3): 664-670. |
| [12] | . 敲除沉默信息调节因子2基因可减轻创伤性脑损伤[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(2): 350-356. |
| [13] | . M2型巨噬细胞可调控缺血性脑卒中早期纤维瘢痕的形成[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(10): 2208-2218. |
| [14] | . 骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体是治疗缺血性脑卒中的一种潜在方法[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2023, 18(10): 2246-2251. |
| [15] | . 外泌体在帕金森病炎症反应中的作用[J]. 中国神经再生研究(英文版), 2022, 17(9): 1898-1906. |
出版重点
《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》杂志为SCI、PubMed数据库收录的国际唯一一本专注神经再生领域研究的经同行评议的开放获取期刊,出版来自全球神经再生领域专业学者的前沿性基础研究及临床研究及转化医学、循证医学优秀的最新成果。
期刊出版来自于脑损伤与神经再生、脊髓损伤与神经再生、周围神经损伤与神经再生和神经退行性病与神经再生、神经影像与神经再生的相关研究。期刊关注神经损伤与再生过程中的轴突再生、突触生长、神经可塑性、神经修复和替代、神经移植等最新研究成果。尤其关注应用细胞治疗、基因治疗、生物因子治疗、药物治疗、手术治疗、康复治疗、物理疗法、组织工程、生物工程、生物材料、神经假体等干预性方法产生神经再生效果的相关研究。文章应清晰描述抑制神经元损伤、减轻神经元损伤的一系列变化,保护损伤神经元的过程、方法、程度与评价,突出从细胞分子水平以及分子生物学水平解释神经元损伤后以及预后再生的机制。
NRR杂志被国际重要数据库收录
科学引文索引(Science Citation Index Expanded,SCI)
美国国立医学图书馆(PubMed)
美国国立医学图书馆开放获取全文数据库(PubMed Central, PMC)
美国生物学文摘数据库(BIOSIS previews, BP)
美国《化学文摘》(Chemical Abstracts, CA)
Scopus荷兰《医学文摘库/医学文摘》(Excerpta Medica, EM)
波兰《哥伯尼索引》(Index of Copurnicus, IC)
OvidSP平台数据库
中国科学引文数据库(CSCD)
中国科技期刊数据库-统计源期刊(CSTPCD)
编委会
主编Editor-in-Chief
苏国辉院士(Kwok-fai So, Chair Professor and Head, Jessie Ho Professor in Neuroscience, Department of Anatomy, The University of Hong Kong)。
徐晓明教授(Xiao-ming Xu, Professor and Mari Hulman George Chair of Neurological Surgery, Scientific Director of Spinal Cord and Brain Injury Research Group, Indiana University School of Medicine)
联系方式:Email: szb@nrren.org 电话:+86 138 0499 8773
编委会成员
期刊编委队伍由国际神经再生领域著名学者、中国科学院院士、香港大学苏国辉教授和美国印第安纳大学徐晓明教授领导的由100多位国际神经再生优秀专家组成。共同致力于创办一本发表神经再生领域专业学术研究经同行严格评审的优秀学术期刊。
在线投稿平台
作者可以通过www.nrronline.org在线投稿。
所有的稿件都将通过该系统提交至NRR杂志电子投稿出版管理系统。
作者有不明确的问题,请访问szb@nrren.org或咨询+86 138 0499 8773。
投稿后,当论文已处于审稿或等待审稿状态时,2个月内请勿将稿件再投至他刊。
初次投稿:
投稿信:
应说明文章未一稿多投,全部作者是否对所投稿件内容知情同意,推荐2-3位小同行审稿人。
作者协议:
投稿时请注意作者协议,如同意后可继续完成投稿, 投稿成功后作者已与杂志签定了文章的相关版权。
投稿后的同行评议
期刊投稿平台应用国际最大的投稿平台Editorial Manager,投到本刊的每篇稿件都要经过3-4位小同行审稿人评审,审稿方法为国际学科小同行组成双盲审稿。所有发表在杂志的文章都将经过严格的双盲同行层层评议,审稿中注重科学性、伦理学和文章真实性的严格审查。期刊将在投稿后4周内通知作者评审意见。
根据评审意见,编辑部决定稿件返修,再审,被接受或退稿。 稿件被接受后,作者可经投稿平台以通讯作者账号随时查询稿件的出版进程。
出版时间
一般稿件被采用后3-4个月出版,优秀文章可在被采用后1-2个月内发表,有临床试验注册号的优秀临床试验文章可申请加急发表。
出版后传播
文章出版后将在EurekAlert!和EurekAlert!中文新闻平台以中英文双语形式向全世界同仁传播。EurekAlert!和EurekAlert!中文新闻平台是美国科学促进会(AAAS)主办的一项全球的科学新闻服务。美国科学促进会为世界最大的科学协会,并且是《科学》杂志的出版机构。您的文章将以最快时间推送给经严格验证的来自全球的新闻记者8000余人,包括来自国际的纽约时报、华盛顿邮报和路透社等,来自中国的中国日报、新华社、人民日报等国际主流媒体,为科学家们提供了与国际科学记者和国际学术平台直接沟通的一个快速有效的桥梁。我们将随后为您提供您新闻的网站点击情况和媒体报告情况的具体数据。
出版后的新闻传播将极大提高文章的影响力,统计同时表明发布学术新闻的文章将提高其被引率70%以上。
杂志的读者群Audience
来自全球从事神经再生、神经科学、神经解剖、神经病理、神经外科、神经内科、神经生物、神经影像、神经放射、神经康复等领域的学科专家。
对特邀综述稿件的要求:
(1)需提前向编委会提交写作大纲,通过选题后, 文章需在2个月内完成。
(2)全文不超过6000个单词,包括摘要,不包括参考文献,图和表格 ,出版后8-10个版面。
(3)文章写作结构:
文题:不超过 90个字母,20个单词。
摘要:非结构式, 250单词。
引言:
主体内容:
总结:
作者贡献:
利益冲突:
参考文献:采用 Journal of Neuroscience格式。
特邀述评类文章:观点、点评 、研究亮点、给编辑的信等。
特邀观点栏目文章要求:
(1)观点文章为作者对神经再生领域某一热点问题 的评论,有作者鲜明的观点和作者本人
对此科研过程的认识 和总结。
(2)需提前向编委会提交写作大纲,通过选题后, 文章需在2个月内完成。
(3)全文2000- 3000单词,包括参考文献,不需要图和表格,不需要摘要,出 版后2个版面。
(4)文章写作结构:
文题:不超过 90个字母,20个单词。
主体内容:
参考文献:不超过 5条,采用Journal of Neuroscience格式。
特邀点评与研究亮点栏目文章 要求:
(1)点评文章为点评在本刊发表的文章,研究亮点 文章为点评国际优秀杂志近期或在线提前发表的前沿性的优秀文章。
(2)需提前向编委会提交写作大纲,通过选题后, 文章需在2个月内完成。
(3)全文2000- 3000单词,包括参考文献,不需要图和表格,不需要摘要,出 版后2个版面。
(4)文章写作结构:
文题:不超过 90个字母,20个单词。
主体内容:
利益冲突:
参考文献:不超过 5条,采用Journal of Neuroscience格式。
给编辑的信栏目文章要求:
(1)给编辑的信文章为读者对本刊已发表文章的来 信反馈。
(2)全文1000- 2000单词,不包括参考文献,文章不需要摘要、图和表格,出 版后1个版面。
(4)文章写作结构:
文题:不超过 90个字母,20个单词。
主体内容:
利益冲突:
参考文献:不超过 5条,采用Journal of Neuroscience格式。
如果您需要向SCI收录期刊投稿,我们可以为您提供如下服务--
NRR:宁医大王鹏团队探索多发性硬化跨血脑屏障的给药方法
撰文:魏爽爽、陈乐、杨奉源、王思齐、王鹏
多发性硬化(Multiple sclerosis, MS)是一种自身免疫系统介导的中枢神经脱髓鞘疾病,常出现视力障碍、肢体无力、感觉异常以及共济失调等较为复杂的症状和体征[1]。其在高发病地区发病率超过3/100 000,甚至达到1/10 000或万分之几的水平[2]。初步研究认为,多发性硬化进展与髓鞘再生失败有关,而髓鞘再生受细胞外基质蛋白调控[3]。纤连蛋白聚合物(Fibronectin aggregates, aFn)具有抑制髓鞘再生,促进多发性硬化进展的作用[4]。
目前尚未发现可有效降解纤连蛋白聚合物,阻碍其抑制髓鞘再生的方法。纤连蛋白聚合物各组分功能也并未被详细介绍,因此探索纤连蛋白聚合物各组分功能,对于寻求挽救髓鞘再生的方法具有重要意义。尽管在多发性硬化机制和药物的研究方面已取得一些进展,但由于大脑结构和功能的复杂性,特别是血脑屏障的存在使药物很难到达大脑病理组织并发挥作用。
近期,来自中国宁夏医科大学王鹏团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“The role of fibronectin in multiple sclerosis and the effect of drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier”的综述,介绍了多发性硬化进展与髓鞘再生失败有关。脱髓鞘后,纤维连接蛋白(Fibronectin, Fn)在细胞基质中立即产生。慢性多发性硬化病变中, 纤维连接蛋白持续存在,并形成稳定的纤连蛋白聚合物,以抑制髓鞘再生。综述进一步总结了纤连蛋白聚合物组分对髓鞘再生的影响,并提出了几种有希望挽救髓鞘再生的因子,以及为实现跨血脑屏障给药。文章还讨论了经侧脑室给药、经鼻给药以及纳米系统载药的效果。
多发性硬化是一种中枢神经系统慢性自身免疫性疾病,其发病机制尚不清楚,但自身免疫反应、病毒感染、环境因素和遗传易感性等都与其发生发展有关。此外,维生素D缺乏、缺乏阳光和吸烟也可能诱发这种疾病[5]。考虑到不同的受影响区域,多发性硬化的临床表现是复杂多样的。视神经炎、脊髓炎、脑干或小脑疾病可能是其最常见的初始临床特征,表现为视觉障碍、肢体无力、活动障碍和共济失调[6]。基于多发性硬化的病程,患者可分为四大类:复发-缓解型、继发-进行型、原发-进行型和进行-复发型多发性硬化。一般来说,缓解与复发总是交替进行,随着时间的推移,随后往往出现进行性神经恶化[6]。在多发性硬化晚期,残疾和畸形会迫使患者失去劳动力。
多发性硬化的病理特征是脱髓鞘,髓鞘再生失败导致疾病进展[3]。在多发性硬化中,脱髓鞘与活动性病灶中星形胶质细胞的活化和非活动性病灶中胶质瘢痕的形成有关。由于少突胶质祖细胞的募集和分化,多发性硬化病变可在一定程度上出现髓鞘再生,从而促进神经 结构和轴突传导特性的恢复。有趣的是,髓鞘再生失败是多发性硬化的主要特征之一,并可能与该病的持续进展有关[3]。在清楚髓鞘再生具体机制和髓鞘再生失败的原因后,采取相关措施进行干预,将有可能延缓多发性硬化进展。
少突胶质前体细胞(oligodendrocyte precursor cells, OPCs)作为新生髓鞘形成细胞的主要来源,广泛分布于成人中枢神经系统。鉴于其自我更新和产生某些神经元的能力,少突胶质前体细胞可以合理地被视为一种成人神经干细胞[7]。髓鞘再生可分为募集和分化两个阶段。可能是因为少突胶质前体细胞供应不足或缺乏分化成少突胶质细胞的少突胶质前体细胞,最终导致髓鞘再生失败[8]。
细胞外基质(extracellular matrix, ECM)位于神经元和神经胶质细胞之间,占大脑总体积的10-20%。作为由大分子蛋白质组成的网络,细胞外基质发挥着调节细胞生长、极性、形状、迁移和代谢的作用,并能形成复杂和动态的微环境[9]。除为神经元和神经胶质细胞提供物理支持,细胞外基质还充当信号分子的储库,间接影响细胞行为。虽然不同的器官或组织具有不同的细胞外基质成分,但几乎所有细胞类型都可以产生和分泌细胞外基质分子,主要的细胞外基质成分大致相同[10]。细胞外基质由多种大分子组成,大致可分为5类:胶原蛋白、非胶原蛋白、弹性蛋白、蛋白聚糖和糖胺聚糖。细胞外基质的整体生物学特性取决于其组成和结构,其影响着信号传递和细胞反应。动态和复杂的细胞外基质微环境通过细胞外基质分子、各种膜受体分子和可溶性信号以及细胞外基质重塑之间的相互作用来调节中枢神经系统的发育、功能区域化和应激。细胞外基质蛋白的装配缺陷、产量减少和过度积累与多发性硬化病理相关,细胞外基质成分发生明显改变[11]。细胞外基质重塑包括受基质降解酶调节的细胞外基质蛋白的短暂变化,发挥调节作用,促进受损病变恢复,尽管其在健康和病理情况下都会发生,但在正常成人中枢神经系统中是很有限的[10]。慢性和进行性多发性硬化病变中,细胞外基质重塑经常失败,这与髓鞘再生失败有关[12]。
纤维连接蛋白是脱髓鞘后,作为二聚体瞬时产生的一种细胞外基质成分,其只存在于血管中,而不存在于健康成人中枢神经系统间质细胞外基质中。然而,在溶血卵磷脂诱导的脱髓鞘模型中,纤维连接蛋白在中枢神经系统白质和血管中的表达增加,含量随着髓鞘再生进展而减少[4]。多发性硬化病变中,纤维连接蛋白表达上调是由于血浆穿过血脑屏障渗透和星形胶质细胞合成所致[12, 13]。体外实验中,纤维连接蛋白促进少突胶质前体细胞的迁移和增殖,而纤维连接蛋白涂层干扰少突胶质前体细胞的生长,并阻止髓鞘膜形成[14]。纤维连接蛋白主要位于脱髓鞘区域,并在髓鞘再生过程中被去除[4]。纤维连接蛋白有2种形式:血浆纤连蛋白(plasma fibronectin, pFn)和细胞纤连蛋白(cellular fibronectin, cFn)。血浆纤连蛋白由血浆穿过被破坏的血脑屏障渗透产生,而细胞纤连蛋白主要由星形胶质细胞合成,但也可由小胶质细胞、巨噬细胞和内皮细胞分泌[13]。细胞纤连蛋白可能包含交替剪接的结构域:啮齿动物中的额外的III型重复序列A(extra type III repeat A, EIIIA)、额外的III型重复序列B(extra type III repeat B, EIIIB)和可变区,以及人类中的纤维连接蛋白额外结构域A、纤维连接蛋白额外结构域B和III型连接片段[15]。在细胞纤连蛋白条件性剔除后,为脱髓鞘病灶区募集的少突胶质前体细胞数量显著减少,而血浆纤连蛋白条件性剔除后少突胶质前体细胞数量保持不变。然而,条件性敲除细胞纤连蛋白和血浆纤连蛋白后,髓鞘再生是正常的。细胞纤连蛋白的III型重复序列A和III型重复序列B结构域在脱髓鞘后表达。体外实验表明细胞纤连蛋白的III型重复序列A结构域介导少突胶质前体细胞的增殖,但不介导迁移,虽然其可介导少突胶质前体细胞增殖,但这并不是髓鞘再生成功的必要条件[14]。
慢性多发性硬化病变中纤维连接蛋白持续存在,血浆纤连蛋白和细胞纤连蛋白组装成稳定的纤连蛋白聚合物,其作用类似于二聚体纤维连接蛋白,在单独和联合培养中抑制髓鞘膜的形成和髓鞘再生[16]。此外,在毒素诱导的脱髓鞘病变中,腔内注射纤连蛋白聚合物会阻碍少突胶质前体细胞分化和髓鞘再生,这意味着纤连蛋白聚合物可能导致多发性硬化患者髓鞘再生失败[4]。纤维连接蛋白mRNA很少出现在慢性多发性硬化病变中,且纤连蛋白聚合物在细胞外合成,这表明纤连蛋白聚合物由纤维连接蛋白清除障碍导致,而不是纤维连接蛋白表达上调的结果(图1)[17]。

图1多发性硬化纤维连接蛋白聚集体的形成和功能障碍(图源:宁夏医科大学颅脑重点实验室)
小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞的活化表型决定其功能。经典激活表型由干扰素γ或脂多糖诱导,起促炎作用,而交替激活表型由白细胞介素4或白细胞介素13刺激,具有抗炎作用[18]。值得注意的是,小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞的经典激活表型是髓鞘再生初始阶段所必需的,而后续需转化为交替激活表型,来促进后期髓鞘再生[19]。脱髓鞘后,纤维连接蛋白瞬时表达,诱导经典激活表型,促进髓鞘再生[16]。然而,研究表明,持续存在的纤连蛋白聚合物刺激巨噬细胞,可能还有小胶质细胞,表现为经典-交替激活表型,可能会阻碍髓鞘再生[16]。一般来讲,除了阻碍少突胶质前体细胞分化,小胶质细胞或巨噬细胞不能表达正常的活化表型可能是纤连蛋白聚合物诱导的髓鞘再生失败的潜在机制。对纤连蛋白聚合物进行降解可以被认为是挽救髓鞘再生的有效靶点。
在毒素诱导的损伤中,原位杂交共定位研究表明,星形胶质细胞、小胶质细胞、巨噬细胞和内皮细胞可能产生纤维连接蛋白[4]。然而,尚不清楚这些细胞是否在体内也分泌和沉积纤维连接蛋白。体外实验表明,纤维连接蛋白主要由星形胶质细胞产生,观察到只有星形胶质细胞能够活跃地合成和沉积纤维连接蛋白,而血浆中的纤维连接蛋白在没有星形胶质细胞的情况下不会聚集。蛋白质组学分析显示,大鼠星形胶质细胞衍生的纤连蛋白聚合物中存在18种预测的分泌蛋白[16](表1)。

HtrA丝氨酸肽酶(HtrA serine peptidase, HTRA),是一种具有热休克蛋白特性的膜蛋白,在低温时作为分子伴侣,在高温下作为丝胶蛋白,降解细胞内折叠错误的蛋白。HTRA1是一种非糖基化的丝氨酸蛋白酶,可降解多种底物,如细胞外基质。半胱氨酸丰富血管生成诱导因子61(cysteine-rich 61, CYR61)是一种具有广泛生物学特性的细胞外基质分子,调节细胞增殖、粘附、迁移和凋亡,促进血管生成和细胞外基质形成。凝血栓蛋白为抑制血管生成的糖蛋白家族,其中凝血栓蛋白1 (Thrombospondin 1,TSP1)由星形胶质细胞分泌,支持新鲜突触的生长并保护神经元。此外,凝血栓蛋白1促进CG4少突胶质前体细胞的粘附和迁移,可能影响髓鞘再生[34]。热休克蛋白70保护神经元免受蛋白质聚集、毒性、细胞凋亡和炎症的影响,在抗原呈递中起辅助作用,并参与自身免疫反应。在多发性硬化中,由于免疫反应下调,它可能产生积极影响,但由于病变内的额外抗原靶位出现并募集使免疫反应范围扩大[26]。在不与整合素结合的情况下,纤连蛋白聚合物诱导骨髓来源的巨噬细胞和小胶质细胞释放一氧化氮,可能是由于作为纤连蛋白聚合物支架的其他蛋白质(如热休克蛋白70)的积累。热休克蛋白70和热休克蛋白90β与多发性硬化的病理相关,热休克蛋白47作为多发性硬化病变中胶原纤维形成的受体,但这些热休克蛋白在纤连蛋白聚合物中的作用仍有待确定。在健康中枢神经系统中,腱生蛋白C(tenascin C, Tn-C)主要由星形胶质细胞产生,并限于白质内;而在急性和亚急性病变中,腱生蛋白C的表达下调,甚至超出密布巨噬细胞的斑块边缘,延伸到表面上健康的脑白质[35]。腱生蛋白C在发育中的大脑中大量表达,当身体成熟时消失,对髓鞘碱性蛋白的表达和髓鞘形成产生负面影响[23]。
许多因子可以保护髓鞘再生,并有望成为潜在的治疗药物(表2)。外源性神经节苷脂1a通过蛋白激酶A依赖性信号通路阻滞纤连蛋白聚合物对髓鞘再生的抑制作用[36]。血小板衍生生长因子和成纤维细胞生长因子2促进形成髓鞘的少突胶质细胞生成[37]。多发性硬化患者肠道菌群与人外周血单核细胞孵育可在体外诱导促炎反应,说明多发性硬化患者体内菌群缺乏调节自身免疫的有益微生物,而促炎菌过多[38]。一种有吸引力的治疗多发性硬化的方法是恢复体内菌群平衡,或者利用免疫系统和肠道微生物之间的交流来抑制自身免疫反应。乳杆菌益生菌混合物治疗的实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的临床症状和组织病理学表现均得到不同程度的缓解[39],肠道益生菌的这一干预实验可能为多发性硬化的治疗提供新思路。

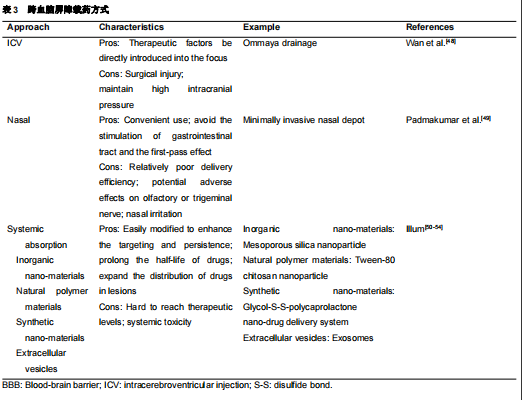
血脑屏障阻止治疗脑部疾病的药物进入大脑,即使是非常小的分子也无法进入[46]。许多研究者已经认识到血脑屏障的阻碍作用,尝试许多新技术跨越血脑屏障,并制定了药物递送策略[46]。有3种常用的血脑屏障给药途径,包括全身吸收、鼻腔给药和脑室给药(图2和表3)。然而总的来说,通过血脑屏障的全身吸收比其他方法更容易。合格的载药系统至少要满足以下条件:将足够的活性成分输送到所需的部位、药物必须以稳定的速率释放。纳米载药系统具有保护药物不被降解、将药物运送到作用靶点、延长血液循环时间、降低对机体毒性的优点,已成为有前途的药物输送方法(图3)。外泌体由于在细胞间信息交换中起重要作用、人体内分布广泛、可以穿过细胞膜且不易引起免疫反应,作为药物载体具有独特优势[47]。然而,其更广泛的临床应用还需进一步研究。外泌体主要纯化方法为超速离心,这种方法效率较低、耗时且相对昂贵,不适合临床应用,凾待优化。

图2三种常见载药方式(图源:宁夏医科大学颅脑重点实验室)

图3无创性纳米载药体系(图源:宁夏医科大学颅脑重点实验室)
由于外泌体的异质性,即使由同一细胞分泌的外泌体也可能具有很大功能差异,从而引发许多工业化问题[55]。载药外泌体的工业化规模、纯度、成本、一致性和标准化是目前面临的主要挑战。对于精确治疗,具有高靶向能力的药物载体是必要的,进一步研究外泌体修饰以提高其靶向性势在必行。外泌体产业目前正呈强劲趋势,我们期待外泌体未来作为新的药物递送载体和治疗手段,为多发性硬化患者带来新的希望。
当然文章存在一定局限性。首先,纤连蛋白聚合物各组分功能讨论中,只提到部分蛋白,尚有其他蛋白功能待探索。大鼠星形胶质细胞来源纤连蛋白聚合物组分是否能代表多发性硬化患者体内纤连蛋白聚合物组分还存在疑问。此外,对挽救髓鞘再生因子的介绍中,仅涉及其对髓鞘再生的积极作用及机制,一些因子的具体作用靶点和通路尚不清楚,需进一步研究总结。正如文章所提到的:体内和体外、小鼠模型和人类患者、多发性硬化的不同阶段都会影响实验结果。作者仅关注了上述1种或2种情况下的实验结果,显示出一种潜在趋势,可能并不代表多发性硬化各期患者体内的结果。除侧脑室给药和鼻腔给药等有创方法外,纳米给药系统为无创治疗提供新思路。而纳米材料目前仍处基础研究阶段,其在大脑的具体分布,机体中的代谢和毒性尚未明确,离临床应用还有很远距离。为提高纳米给药系统靶向性,有一系列表面修饰方法,但文中对此只简要提及,并未详细说明。应充分重视修饰方式的探索,促进其蓬勃发展,以加快纳米载药系统临床应用的步伐。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.369102
参考文献
[1] Feinstein A. The clinical neuropsychiatry of multiple sclerosis. 2007. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
[2] Wallin MT, Culpepper WJ, Campbell JD, et al. The prevalence of MS in the United States: A population-based estimate using health claims data. Neurology. 2019;92(10):e1029-e1040.
[3] Franklin RJ. Why does remyelination fail in multiple sclerosis? Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3(9):705-714.
[4] Stoffels JM, De Jonge JC, Stancic M, et al. Fibronectin aggregation in multiple sclerosis lesions impairs remyelination. Brain. 2013;136(Pt 1):116-131.
[5] Compston A, Coles A. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 2008;372(9648):1502-1517.
[6] Goldenberg MM. Multiple sclerosis review. P T. 2012;37(3):175-184.
[7] Nunes MC, Roy NS, Keyoung HM, et al. Identification and isolation of multipotential neural progenitor cells from the subcortical white matter of the adult human brain. Nat Med. 2003;9(4):439-447.
[8] Smith KJ, Blakemore WF, Mcdonald WI. Central remyelination restores secure conduction. Nature. 1979;280(5721):395-396.
[9] De Jong JM, Wang P, Oomkens M, et al. Remodeling of the interstitial extracellular matrix in white matter multiple sclerosis lesions: Implications for remyelination (failure). J Neurosci Res. 2020;98(7):1370-1397.
[10] Barthes J, Özçelik H, Hindié M, et al. Cell microenvironment engineering and monitoring for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: the recent advances. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:921905.
[11] Satoh JI, Tabunoki H, Yamamura T. Molecular network of the comprehensive multiple sclerosis brain-lesion proteome. Mult Scler. 2009;15(5):531-541.
[12] Lindner M, Thümmler K, Arthur A, et al. Fibroblast growth factor signalling in multiple sclerosis: inhibition of myelination and induction of pro-inflammatory environment by FGF9. Brain. 2015;138(Pt 7):1875-1893.
[13] Hibbits N, Yoshino J, Le TQ, et al. Astrogliosis during acute and chronic cuprizone demyelination and implications for remyelination. ASN Neuro. 2012;4(6):393-408.
[14] Stoffels JM, Hoekstra D, Franklin RJ, et al. The EIIIA domain from astrocyte-derived fibronectin mediates proliferation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells following CNS demyelination. Glia. 2015;63(2):242-256.
[15] Schwarzbauer JE, Patel RS, Fonda D, et al. Multiple sites of alternative splicing of the rat fibronectin gene transcript. EMBO J. 1987;6(9):2573-2580.
[16] Sikkema AH, Stoffels JMJ, Wang P, et al. Fibronectin aggregates promote features of a classically and alternatively activated phenotype in macrophages. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):218.
[17] Mao Y, Schwarzbauer JE. Fibronectin fibrillogenesis, a cell-mediated matrix assembly process. Matrix Biol. 2005;24(6):389-399.
[18] Liu YC, Zou XB, Chai YF, et al. Macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 2014;10(5):520-529.
[19] Miron VE, Boyd A, Zhao JW, et al. M2 microglia and macrophages drive oligodendrocyte differentiation during CNS remyelination. Nat Neurosci. 2013;16(9):1211-1218.
[20] Oka C, Tsujimoto R, Kajikawa M, et al. HtrA1 serine protease inhibits signaling mediated by Tgfbeta family proteins. Development. 2004;131(5):1041-1053.
[21] Lau LF. CCN1/CYR61: the very model of a modern matricellular protein. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(19):3149-3163.
[22] Yoshida H, Nagaoka A, Kusaka-Kikushima A, et al. KIAA1199, a deafness gene of unknown function, is a new hyaluronan binding protein involved in hyaluronan depolymerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(14):5612-5617.
[23] Czopka T, Von Holst A, Ffrench-Constant C, et al. Regulatory mechanisms that mediate tenascin C-dependent inhibition of oligodendrocyte precursor differentiation. J Neurosci. 2010;30(37):12310-12322.
[24] Stebbins JW, Jaffe H, Fales HM, et al. Determination of a native proteolytic site in myelin-associated glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1997;36(8):2221-2226.
[25] Cid C, Alvarez-Cermeño JC, Camafeita E, et al. Antibodies reactive to heat shock protein 90 induce oligodendrocyte precursor cell death in culture. Implications for demyelination in multiple sclerosis. FASEB J. 2004;18(2):409-411.
[26] Turturici G, Sconzo G, Geraci F. Hsp70 and its molecular role in nervous system diseases. Biochem Res Int. 2011;2011:618127.
[27] Wang H, Liu M. Complement C4, infections, and autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2021;12:694928.
[28] Shimo T, Nakanishi T, Nishida T, et al. Connective tissue growth factor induces the proliferation, migration, and tube formation of vascular endothelial cells in vitro, and angiogenesis in vivo. J Biochem. 1999;126(1):137-145.
[29] Li W, Chen J, Zhao S, et al. High drug-loaded microspheres enabled by controlled in-droplet precipitation promote functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):1262.
[30] Xia C, Fu Z, Battaile KP, et al. Crystal structure of human mitochondrial trifunctional protein, a fatty acid β-oxidation metabolon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(13):6069-6074.
[31] Randell A, Daneshtalab N. Elastin microfibril interface-located protein 1, transforming growth factor beta, and implications on cardiovascular complications. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2017;11(7):437-448.
[32] Ruzha Y, Ni J, Quan Z, et al. Role of Vitronectin and its receptors in neuronal function and neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20):12387.
[33] Tabibian S, Shiravand Y, Shams M, et al. A comprehensive overview of coagulation factor V and congenital factor V deficiency. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2019;45(5):523-543.
[34] Li Z, Calzada MJ, Sipes JM, et al. Interactions of thrombospondins with alpha4beta1 integrin and CD47 differentially modulate T cell behavior. J Cell Biol. 2002;157(3):509-519.
[35] Gutowski NJ, Newcombe J, Cuzner ML. Tenascin-R and C in multiple sclerosis lesions: relevance to extracellular matrix remodelling. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1999;25(3):207-214.
[36] Qin J, Sikkema AH, Van Der Bij K, et al. GD1a overcomes inhibition of myelination by fibronectin via activation of protein kinase A: implications for multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci. 2017;37(41):9925-9938.
[37] Murtie JC, Zhou YX, Le TQ, et al. PDGF and FGF2 pathways regulate distinct oligodendrocyte lineage responses in experimental demyelination with spontaneous remyelination. Neurobiol Dis. 2005;19(1-2):171-182.
[38] Cox LM, Maghzi AH, Liu S, et al. Gut microbiome in progressive multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2021;89(6):1195-1211.
[39] Lavasani S, Dzhambazov B, Nouri M, et al. A novel probiotic mixture exerts a therapeutic effect on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mediated by IL-10 producing regulatory T cells. PLoS One. 2010;5(2):e9009.
[40] Kuroda M, Muramatsu R, Maedera N, et al. Peripherally derived FGF21 promotes remyelination in the central nervous system. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(9):3496-3509.
[41] Diniz LP, Matias I, Siqueira M, et al. Astrocytes and the TGF-β1 pathway in the healthy and diseased brain: a double-edged sword. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(7):4653-4679.
[42] Kataria H, Alizadeh A, Shahriary GM, et al. Neuregulin-1 promotes remyelination and fosters a pro-regenerative inflammatory response in focal demyelinating lesions of the spinal cord. Glia. 2018;66(3):538-561.
[43] Muir EM, Adcock KH, Morgenstern DA, et al. Matrix metalloproteases and their inhibitors are produced by overlapping populations of activated astrocytes. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2002;100(1-2):103-117.
[44] Wang P, Gorter RP, De Jonge JC, et al. MMP7 cleaves remyelination-impairing fibronectin aggregates and its expression is reduced in chronic multiple sclerosis lesions. Glia. 2018;66(8):1625-1643.
[45] Zhou B, Yuan Y, Zhang S, et al. Intestinal flora and disease mutually shape the regional immune system in the intestinal tract. Front Immunol. 2020;11:575.
[46] Nair KGS, Ramaiyan V, Sukumaran SK. Enhancement of drug permeability across blood brain barrier using nanoparticles in meningitis. Inflammopharmacology. 2018;26(3):675-684.
[47] Zhang L, Yu D. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and immunity. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019;1871(2):455-468.
[48] Wan Y, Li X, Wang Y, et al. Clinical characteristic of 15 cases of cryptococcal meningitis treated with Ommaya reservoir. Acta Neurol Belg. 2020;120(5):1139-1145.
[49] Padmakumar S, Jones G, Pawar G, et al. Minimally invasive nasal depot (MIND) technique for direct BDNF AntagoNAT delivery to the brain. J Control Release. 2021;331:176-186.
[50] Illum L. Is nose-to-brain transport of drugs in man a reality? J Pharm Pharmacol. 2004;56(1):3-17.
[51] Fateh Basharzad S, Hamidi M, Maleki A, et al. Polysorbate-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as an efficient carrier for improved rivastigmine brain delivery. Brain Res. 2022;1781:147786.
[52] Dragomir M, Chen B, Calin GA. Exosomal lncRNAs as new players in cell-to-cell communication. Transl Cancer Res. 2018;7(Suppl 2):S243-s252.
[53] Goyal K, Konar A, Kumar BSH, et al. Lactoferrin-conjugated pH and redox-sensitive polymersomes based on PEG-S-S-PLA-PCL-OH boost delivery of bacosides to the brain. Nanoscale. 2018;10(37):17781-17798.
[54] Yadav M, Parle M, Sharma N, et al. Brain targeted oral delivery of doxycycline hydrochloride encapsulated Tween 80 coated chitosan nanoparticles against ketamine induced psychosis: behavioral, biochemical, neurochemical and histological alterations in mice. Drug Deliv. 2017;24(1):1429-1440.
[55] Ferguson SW, Nguyen J. Exosomes as therapeutics: the implications of molecular composition and exosomal heterogeneity. J Control Release. 2016;228:179-190.

第一作者:魏爽爽,宁夏医科大学2018级临床医学专业本科在读。

通讯作者:王鹏,理学博士,副教授,硕士生导师。主要研究方向为小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞解除细胞外基质蛋白抑制多发性硬化症髓鞘再生;癫痫发生机制;中医药治疗多发性硬化;种质资源保护。现为国家自然科学基金通讯评审专家。2019年入选宁夏回族自治区第四批“青年科技人才托举工程”。主持国家自然科学基金2项,宁夏自然科学基金1项,厅局级2项,作为第一作者或通讯论文发表SCI论文20余篇,申请专利2项,学术论著1部。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||