中国神经再生研究(英文版) ›› 2024, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (4): 825-832.doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.381493
线粒体功能障碍与质量控制:蛛网膜下腔出血的核心
Mitochondrial dysfunction and quality control lie at the heart of subarachnoid hemorrhage
Jiatong Zhang1, #, Qi Zhu2, #, Jie Wang2, Zheng Peng1, Zong Zhuang1, 2, Chunhua Hang1, 2, *, Wei Li1, 2, *
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Neurosurgery, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Clinical College of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, Chinahttps://orcid.org/0000-0002-9258-3500
摘要:
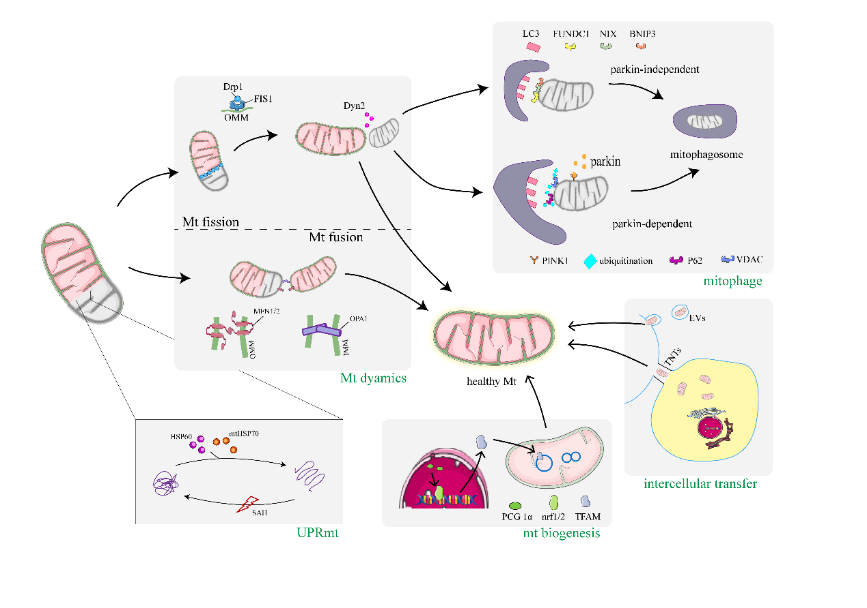
因蛛网膜下腔出血导致的颅内压急剧上升,可造成脑灌注压降低和脑血流减少。线粒体受到缺血缺氧、兴奋性毒性、血红蛋白及其降解产物的毒性等直接因素的影响,从而产生线粒体功能紊乱。功能失调的线粒体释放大量的活性氧、炎症递质和凋亡蛋白,从而激活凋亡通路损伤神经元。为应对这一系列的损伤,细胞已进化出多种受到精密调控的线粒体质量控制机制,如线粒体蛋白质量控制、线粒体动力学、线粒体自噬、线粒体生物生成和细胞间线粒体转移,以在病理条件下维持线粒体稳态。针对线粒体质量控制机制的干预措施已成为蛛网膜下腔出血潜在的治疗策略。文章概述蛛网膜下腔出血后线粒体病理生理过程中有关线粒体质量控制机制的最新研究进展,提出了针对蛛网膜下腔出血中线粒体质量控制机制的潜在治疗策略。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9258-3500 (Wei Li); https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8687-7599 (Chunhua Hang);
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-0277-4486 (Jiatong Zhang); https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8393-9360 (Qi Zhu);
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-2506-2634 (Jie Wang); https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5231-3090 (Zheng Peng);
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2842-4676 (Zong Zhuang)