NRR:上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院陈晟团队开发一种肌萎缩侧索硬化中的血液蛋白组学标志物
撰文:何璐,周勤明,陈晟
肌萎缩侧索硬化是一种严重的神经退行性疾病,随病情发展可导致严重残疾并最终因呼吸衰竭而致命[1],患者平均生存期较短(中位生存期为2-5年)[2],严重危害健康。尽管肌萎缩侧索硬化在1869年首次描述,但目前其诊断仍主要依赖于进行性肌无力病史和体格检查[2],肌电图对于肌萎缩侧索硬化的鉴别诊断至关重要[3]。然而,在出现典型临床症状和电生理变化后,肌萎缩侧索硬化通常已进展到神经退行改变的中期,大量运动神经元早已丢失[3],因此,这限制了多数疾病潜在疗法的疗效。此外,肌萎缩侧索硬化疾病进展和治疗效果的评估也存在难点,目前主要应用基于临床症状的评估指标,如ALSFRS-R评分;然而,由于其低敏感性,其评估结果仍然存在争议。生化指标的变化在神经元丢失的早期阶段即可出现,因此,探索合适的神经生化标志物不但有助于早期诊断肌萎缩侧索硬化,同时也有助于了解肌萎缩侧索硬化潜在的病理生理学机制,并为疾病修饰药物的研发提供新的思路。
近年来,蛋白质组学越来越广泛地应用于鉴定生物标志物并有助于更好地理解疾病机制,基于其高通量、客观和定量的优点,可以增进对多因素病理生理过程的理解,并帮助探索潜在靶点,从而促进有效治疗干预方法的开发。一些研究已经利用高通量蛋白质组学方法探索新的肌萎缩侧索硬化生物标志物[4, 5]。然而,由于方法学差异、验证样本量较小等因素,上述研究的可重复性受到限制。此外,多数肌萎缩侧索硬化生物标志物的研究重点仍集中在特定通路或特定类型的功能蛋白上,限制了对疾病全貌的理解和描述,其对疾病的表征能力有限。
来自上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院陈晟主任团队基于蛋白组学对肌萎缩侧索硬化患者的异常通路变化及诊断标志物进行了研究,相关结果以“Circulating proteomic biomarkers for diagnosing sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a cross-sectional study”为题在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表。研究发现,抗菌肽相关的溶菌素相关蛋白(CAMP)(AUC:0.713,P < 0.0001)对于散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化和健康对照血清具有最显著的区分度;由血红蛋白β(HBB)、CAMP、肌钙蛋白1(TLN1)、zyxin(ZYX)和转化控制肿瘤蛋白(TPT1)组成的多蛋白联合鉴别算法(AUC = 0.811,P < 0.0001)可进一步提高诊断效能。由TLN1和TPT1组成的双蛋白组合则有助于区分早期散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化患者和健康对照(AUC = 0.766,P < 0.0001)。此外,随着疾病临床评分进展,FKBP1A、CAMP和HBA1三种蛋白的表达上调。该研究开发的蛋白质组学标志物显示了在早期诊断和监测散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化疾病进展方面的潜力,这将为目前基于临床评分诊断和评估预后的现状提供了一定程度的补充。
陈晟等通过使用无标记定量蛋白质组学分析肌萎缩侧索硬化患者及正常对照血清样本,检测到1682种蛋白质,其中387种为与散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化相关的差异表达蛋白。其中,259种蛋白在肌萎缩侧索硬化患者中上调,另128种蛋白下调。主成分分析(PCA)显示差异表达蛋白能够将散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化患者与对照组区分开。对差异表达蛋白整体表达趋势进行热图分析,也提示散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化患者与对照组具有不同的蛋白表达特征。根据GO分析,差异表达蛋白的分子功能主要与抗氧化剂、蛋白质二硫键还原酶、碳氧裂解酶、水解酶和过氧化酶活性相关。这些结果表明抗氧化应激在肌萎缩侧索硬化发病机制中起着重要作用,与已报道的肌萎缩侧索硬化病因学结果相符。根据细胞功能组分的GO分析,差异表达蛋白主要位于皮层细胞骨架和细胞质区域(图1A)。KEGG通路分析显示,差异表达蛋白主要富集在血小板活化、能量代谢(糖酵解、三羧酸循环、碳代谢、氨基酸生物合成)和过氧化物酶体等通路(图1B)。对前50种差异表达蛋白进行相互作用分析绘制蛋白质相互作用网络以进一步筛选潜在的代表性标志物(图1C)。
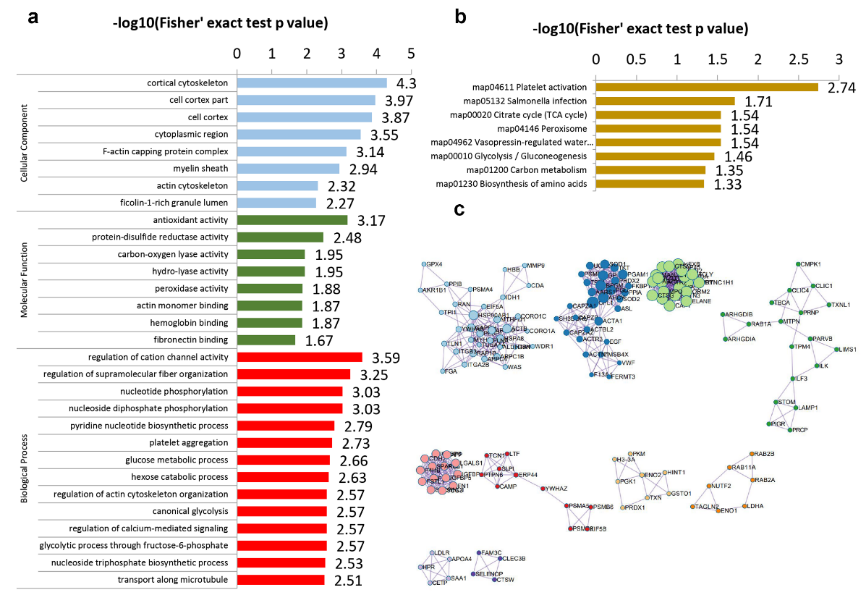
图1肌萎缩侧索硬化患者差异表达蛋白GO分析、KEGG通路分析及相互作用分析(图源:He et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
陈晟等着眼于5倍及以上FDR(伪发现率)筛选出上调的差异表达蛋白成员,鉴定出42种蛋白质。对这42种蛋白质进行相互作用分析。基于蛋白差异程度、对通路的代表性和在中枢神经系统中的表达情况,我们最终筛选了8种差异表达蛋白(FKBP1A、CD84、CAMP、ZYX、HBA1、HBB、TLN1和TPT1)作为候选生物标志物。进一步地招募了110例散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化患者和105名健康对照组成的队列,以验证潜在的诊断生物标志物的性能。验证队列中8种差异表达蛋白的表达在散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化患者中均显著高于对照组(图2A),与发现队列的结果一致。进一步行受试者工作特征(ROC)分析以评估每种生物标志物在区分散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化和对照组方面的敏感性和特异性。其中,CAMP蛋白在区分散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化和对照组方面表现最好(AUC:0.713,P < 0.0001)(图2B和C)。
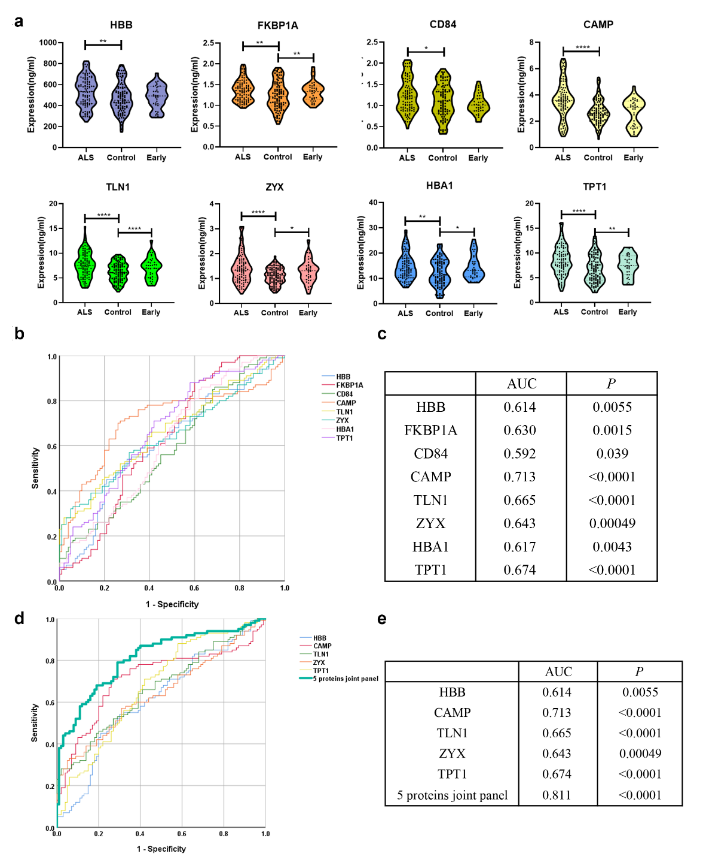
图2 验证候选生物标志物、各标志物诊断效能分析及多蛋白联合算法的建立(图源:He et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
为进一步提高诊断效能,采用logestic回归模型构建了多蛋白组合,最终发现,基于5种蛋白标志物(HBB、CAMP、TLN1、ZYX和TPT1)的蛋白组合,具有较高的诊断效能(AUC:0.811,P < 0.0001)。对于将样本诊断为散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化的概率分数,根据每个蛋白标志物的值定义如下:Logit(P) = 0.002HBB + 0.572CAMP + 0.196TLN1 + 0.900ZYX + 0.201TPT1 - 6.981。
在散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化组中,该概率分数显著高于对照组,当截断值取0.426时,诊断散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化的敏感性和特异性得分分别为79%和71%,AUC为0.811(图2D和E)。在早期散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化中,5种蛋白质(FKBP1A、TLN1、ZYX、HBA1和TPT1)的表达显著高于对照组(图2A)。对于早期散发性肌萎缩侧索硬化患者,基于2种蛋白质(TLN1和TPT1)的诊断模型,AUC为0.766。此外,3种蛋白质(FKBP1A、CAMP和HBA1)在不同ALSFRS-R水平(低、中、高)的患者中表达差异显著,蛋白质表达水平与ALSFRS-R评分相关联,提示具有预测预后的潜力。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.389357
参考文献
[1] Zhou QM, Zhang JJ, Li S, et al. n-butylidenephthalide treatment prolongs life span and attenuates motor neuron loss in SOD1(G93A) mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017;23(5):375-385.
[2] Oskarsson B, Gendron TF, Staff NP. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an update for 2018. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018;93(11):1617-1628.
[3] Brown RH, Al-Chalabi A. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(2):162-172.
[4] Thompson AG, Gray E, Thézénas ML, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid macrophage biomarkers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2018;83(2):258-268.
[5] De Benedetti S, Gianazza E, Banfi C, et al. Serum proteome in a sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis geographical cluster. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2017;11(11-12):1700043.

第一作者:何璐,2020年博士毕业于上海交通大学医学院,上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院住院医师,主要研究方向为神经免疫与变性疾病的临床和发病机制研究。近3年以第一/共一作者发表SCI论文6篇,影响因子40余分;主持国家自然科学基金青年项目1项、瑞金医院“青年培育计划”1项,上海交通大学医学院博士创新基金1项。

并列第一作者:周勤明,上海交通大学医学院神经病学博士,瑞金医院神经内科主治医师,上海市免疫学会神经免疫专委会青年委员,主要从事神经免疫疾病和运动神经元病的临床和科研工作,目前发表SCI论文32篇,其中第一/通讯作者论文17篇,包括Eclinicalmedicine, Annals of Neurology, Journal of Neurology等知名杂志。目前承担国自然科学基金青年项目和上海交通大学医工交叉青年项目各1项,参与《Autophagy:Biology and Diseases》和《肌萎缩侧索硬化症的中西医治疗》等书籍的编写。

通讯作者:陈晟,上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院神经内科副主任,主任医师,教授,中华医学会神经病学分会神经免疫学组委员,中国医师协会神经内科医师分会神经免疫疾病专业委员会委员,上海市医学会神经内科分会青年委员,上海市医学会神经内科分会神经免疫、遗传学组委员,上海市免疫学会神经内科专业委员会副主任委员,第四届中国医师协会杰出青年神经内科医师,柳叶刀主刊审稿人,美国注册医师,以第一作者或通讯作者在Lancet Neurology, JAMA Neurology,Eclinicalmedicine(Lancet子刊),Annals of Neurology, Journal of Neuroinflammation, Autophagy,Neurology,Molecular Neurodegeneration等杂志发表论著、评述或短篇70余篇。影响因子410,他引次数3907; 参加编写各类专著20余部。主持国家自然科学基金3项,入选上海青年拔尖人才,上海市曙光学者,上海东方学者特聘教授。
并列通讯作者:乐卫东教授。




