NRR:四川大学周良学和仝爱平团队揭示TUG-891减轻脑室出血后神经元焦亡机制
撰文:王昊翔
脑室内出血是一种常见的临床危重症,可分为原发性和继发性脑室出血[1-3]。脑室出血具有高死亡率、高致残率和不良预后等特点[4]。然而,上述灾难性预后的原因是十分复杂的,尚未完全了解。最近,作为神经病变的一个重要因素,非凋亡性炎性细胞死亡在创伤性脑损伤和出血性脑卒中中引起了越来越多的关注。研究表明,以核苷酸结合寡聚结构域、富含亮氨酸重复序列和含吡啶结构域的蛋白3(nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine-rich repeat, and pyrin domain–containing protein 3, NLRP3)炎性小体为特征的经典焦亡通路在出血性脑卒中的发生、发展和预后中起着重要的作用[5]。多项研究已证明细胞焦亡在神经系统损伤机制中的重要性[6-10]。据报道,NLRP3炎症小体的激活与错误折叠的蛋白质聚集有关[11]。而内质网应激有可能诱导NLRP3激活,并促进细胞焦亡的发生[12]。然而,尚未有研究报道关于脑室出血内质网应激与焦亡的联系。
来自中国四川大学华西医院的周良学团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“TUG-891 inhibits neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and pyroptosis activation and protects neurons in a mouse model of intraventricular hemorrhage”的文章,作者发现GRP120受体激动剂TUG-891可显著抑制脑室出血后神经元焦亡,减少神经炎症,从而发挥神经保护作用,且这一作用是通过抑制神经元内质网应激来实现的。
脑室出血后3d内小鼠体质量明显下降,海马和侧脑室中存活神经元减少,脑室扩大,脉络丛受损,侧脑室区室管膜纤毛受损,细胞胞体萎缩,海马核边缘聚集。进一步观察可见,脑室出血后海马神经元焦亡蛋白表达上调。由于以往研究已发现,TUG-891具有抑制内质网应激通路激活的作用,此次结果与既往研究相符[13-15],且还发现其也可抑制细胞焦亡。表明TUG-891对脑室出血的神经保护作用与抑制内质网应激和减轻焦亡的激活有关(图1)。
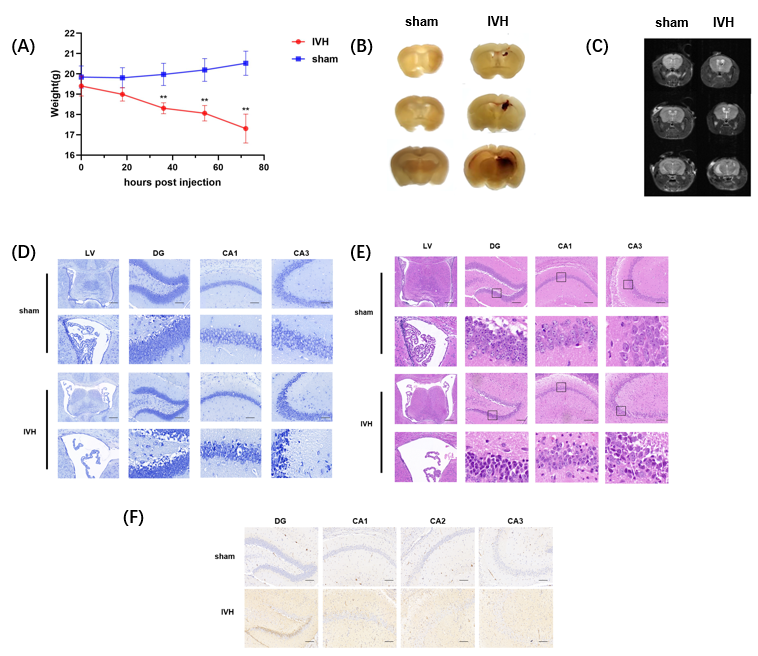 #br#
#br#
图1脑室出血诱导一般效应观察 (图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2023)
总之,GPR120激动剂TUG-891可通过减少内质网应激和神经元焦亡来减少炎症介质的释放,从而在脑室出血后发挥神经保护作用,其机制是脑室出血后,内质网应激-NLRP3-焦亡信号通路被激活,从而导致脑损伤,而TUG-891可逆转其作用(图2)。此项研究为出血性脑卒中的药物研究提供了新的方向。
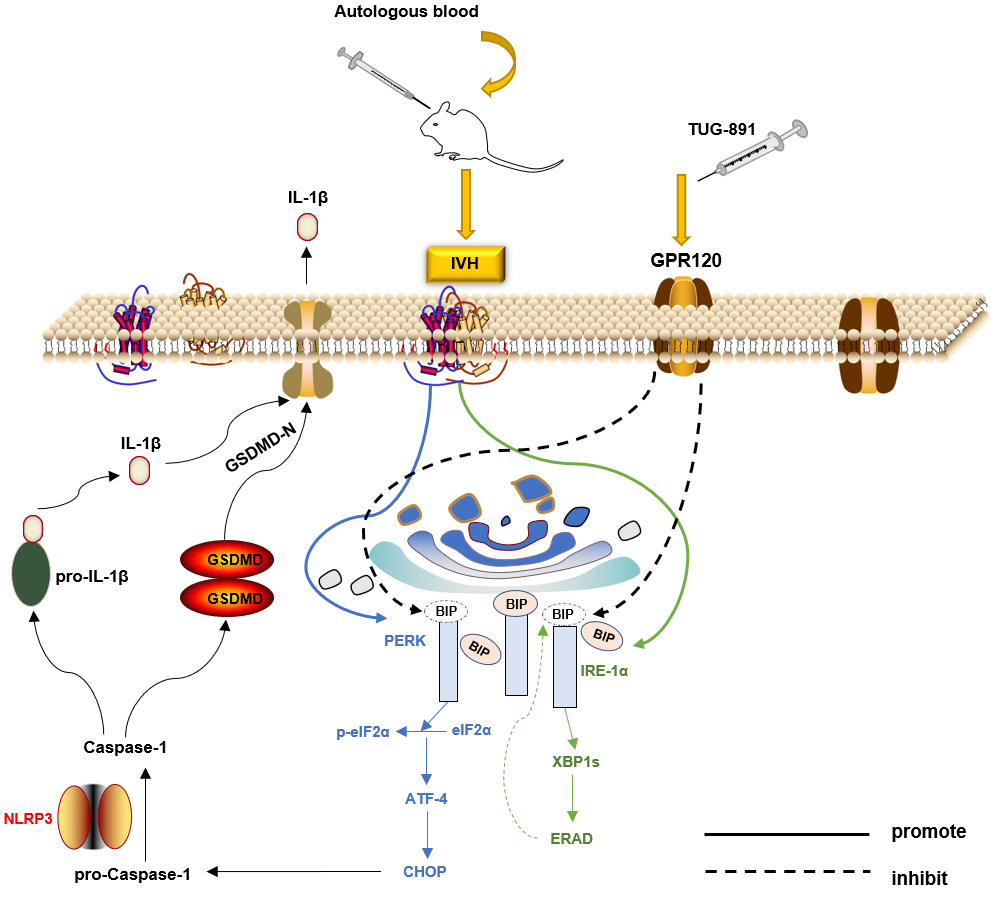 #br#
#br#
图2 TUG-891能抑制内质网应激-NLRP3-焦亡信号通路,从而减轻脑损伤(图源:Wang et al., Neural Regen Res, 2023)
当然,这项研究只关注了脑室出血急性期的神经损伤和恢复功能,没有观察脑室出血后长期变化;其次研究结果,尚未在基因敲除小鼠(如GSDMD-/-或NLRP3-/-)中得到证实。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.369116
参考文献
[1] Bernales S, Papa FR, Walter P. Intracellular signaling by the unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:487-508.
[2] Ron D, Walter P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(7):519-529.
[3] Hanley DF. Intraventricular hemorrhage: severity factor and treatment target in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2009;40(4):1533-1538.
[4] Hwang BY, Bruce SS, Appelboom G, et al. Evaluation of intraventricular hemorrhage assessment methods for predicting outcome following intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 2012;116(1):185-192.
[5] Mckenzie BA, Dixit VM, Power C. Fiery Cell Death: Pyroptosis in the Central Nervous System. Trends Neurosci. 2020;43(1):55-73.
[6] Chen GY, Nuñez G. Sterile inflammation: sensing and reacting to damage. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(12):826-837.
[7] Franchi L, Muñoz-Planillo R, Núñez G. Sensing and reacting to microbes through the inflammasomes. Nat Immunol. 2012;13(4):325-332.
[8] Kayagaki N, Stowe IB, Lee BL, et al. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling. Nature. 2015;526(7575):666-671.
[9] Lin X, Ye H, Siaw-Debrah F, et al. AC-YVAD-CMK Inhibits Pyroptosis and Improves Functional Outcome after Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:3706047.
[10] Zhao H, Chen Y, Feng H. P2X7 Receptor-Associated Programmed Cell Death in the Pathophysiology of Hemorrhagic Stroke. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(9):1282-1295.
[11] Shi F, Kouadir M, Yang Y. NALP3 inflammasome activation in protein misfolding diseases. Life Sci. 2015;135:9-14.
[12] Westrate LM, Lee JE, Prinz WA, et al. Form follows function: the importance of endoplasmic reticulum shape. Annu Rev Biochem. 2015;84:791-811.
[13] Schilperoort M, Van Dam AD, Hoeke G, et al. The GPR120 agonist TUG-891 promotes metabolic health by stimulating mitochondrial respiration in brown fat. EMBO Mol Med. 2018;10(3):e8047.
[14] Wang X, He S, Gu Y, et al. Fatty acid receptor GPR120 promotes breast cancer chemoresistance by upregulating ABC transporters expression and fatty acid synthesis. EBioMedicine. 2019;40:251-262.
[15] Huang Z, Guo F, Xia Z, et al. Activation of GPR120 by TUG891 ameliorated cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via repressing ER stress and apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;126:110056.
 #br#
#br#
 #br#
#br#