NRR:南通大学周松林课题组联合海军军医大学上海长征医院赵剑课题组总结CD36在中枢神经系统疾病中的作用
近期,中国南通大学周松林课题组联合海军军医大学上海长征医院赵剑课题组发现,CD36在脊髓胶质瘢痕细胞成分之一的成纤维细胞中表达,因此CD36或可作为治疗脊柱瘢痕的靶点[1]。该团队认为CD36在中枢神经系统疾病具有重要作用,因此综述了CD36在中枢神经系统中的作用以及CD36抑制剂的应用。使用CD36抑制剂靶向抑制CD36的表达,可减轻氧化应激、内皮功能障碍、神经炎症等病理生理过程,从而对帕金森病、阿尔茨海默病、脊髓损伤等中枢神经系统疾病有着良好的治疗效果。
CD36属于B类清道夫受体家族,是一种高度糖基化的跨膜糖蛋白。在神经系统中,CD36已被发现在小胶质细胞、血管内皮细胞、脑周细胞、星形胶质细胞和病理情况下脑中的血源性巨噬细胞上表达[2-5]。近年来研究发现,CD36失调与帕金森病、脑卒中[6]、阿尔茨海默病[7]等神经系统疾病相关。CD36参与介导线粒体功能障碍、神经炎症等,会加速神经退行性变过程和认知能力下降[8]。而通过CD36抑制剂靶向抑制CD36表达,可改善神经功能,从而对治疗多种神经系统疾病有很好的效果。
丹酚酸B对CD36具有靶向作用,通过表面等离子体共振分析显示丹酚酸B可直接结合CD36,降低氧化低密度脂蛋白诱导CD36基因表达[9]。磺基琥珀酰亚胺油酸酯也证明是一种CD36的拮抗剂,其靶点位于CD36上的赖氨酸164[10, 11]。除此之外,CD36的配体Hexarelin和EP 80317同样可干扰CD36的表达[12]。在CD36靶向抑制剂的挖掘中,还发现姜黄素、SS31、载脂蛋白AI模拟肽、微小RNA、α生育酚以及一些降脂药物(如二甲双胍),都具有调节CD36的能力,并在中枢神经系统疾病治疗中显示出良好的效益。
因此,该团队梳理了CD36在中枢神经系统疾病中的作用,这为CD36在中枢神经系统疾病中的研究提供了理论基础(图1);进而总结了CD36靶向抑制剂的种类及其与CD36的靶向结合位点(图2),为开发新型抑制剂提供了理论支持。
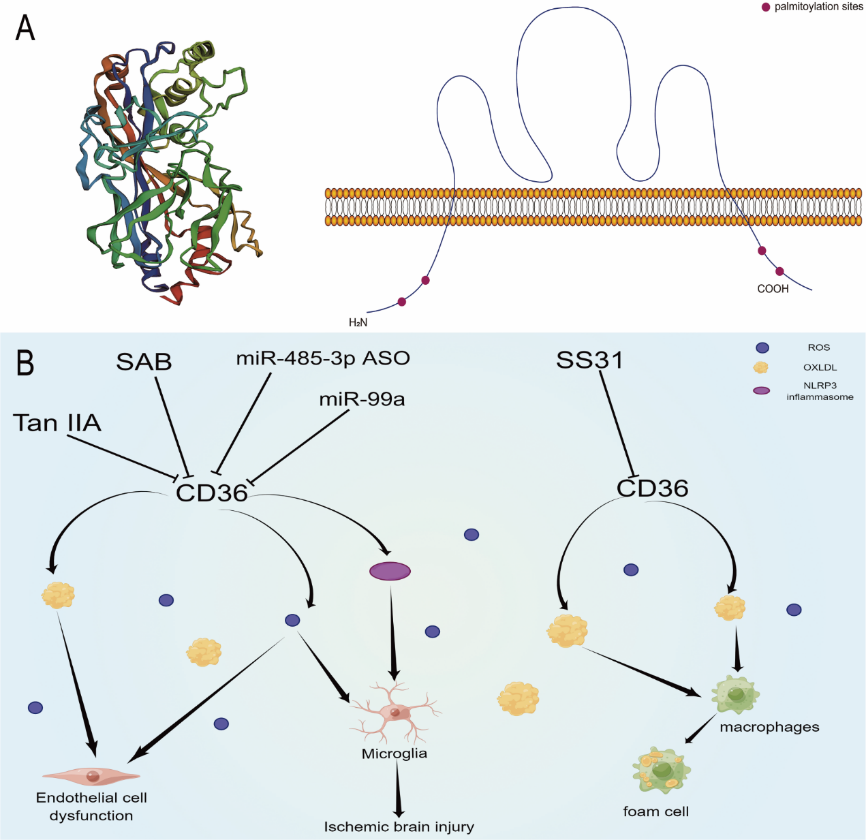
图1 CD36的结构及其在中枢神经系统疾病中的作用(图源:Feng et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
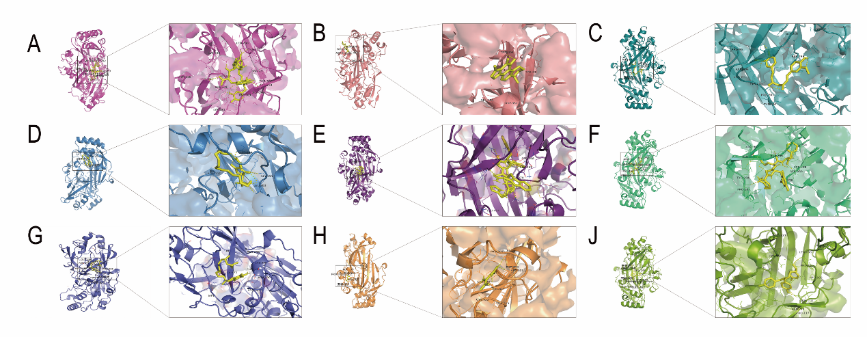
图2由Phyre2网站预测的结合点的三维结构。(图源:Feng et al., Neural Regen Res, 2024)
然而纳入的研究多关注动物模型,较少涉及临床试验,因此仍需大量临床研究来对CD36在中枢神经系统疾病中的作用进行分析。总之,该综述为寻找和开发有效的靶向抑制剂来抑制CD36的表达,从而治疗多种中枢神经系统疾病及相关疾病带来了新的策略,也为CD36拮抗剂的类型和给药时机提供了理论参考。该文章发表在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)2024年第4期。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.380821
参考文献
[1] Gong L, Gu Y, Han X, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of the molecular expression pattern and intercellular interactions in the glial scar response to spinal cord injury. Neurosci Bull. 2023;39(2):213-244.
[2] Kim E, Febbraio M, Bao Y, et al. CD36 in the periphery and brain synergizes in stroke injury in hyperlipidemia. Ann Neurol. 2012;71(6):753-764.
[3] Bao Y, Qin L, Kim E, et al. CD36 is involved in astrocyte activation and astroglial scar formation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2012;32(8):1567-1577.
[4] Coraci IS, Husemann J, Berman JW, et al. CD36, a class B scavenger receptor, is expressed on microglia in Alzheimer's disease brains and can mediate production of reactive oxygen species in response to beta-amyloid fibrils. Am J Pathol. 2002;160(1):101-112.
[5] Li J, Li M, Ge Y, et al. β-amyloid protein induces mitophagy-dependent ferroptosis through the CD36/PINK/PARKIN pathway leading to blood-brain barrier destruction in Alzheimer's disease. Cell Biosci. 2022;12(1):69.
[6] Balkaya M, Kim ID, Shakil F, et al. CD36 deficiency reduces chronic BBB dysfunction and scar formation and improves activity, hedonic and memory deficits in ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021;41(3):486-501.
[7] Moore KJ, El Khoury J, Medeiros LA, et al. A CD36-initiated signaling cascade mediates inflammatory effects of beta-amyloid. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(49):47373-47379.
[8] Ioghen O, Chițoiu L, Gherghiceanu M, et al. CD36 - A novel molecular target in the neurovascular unit. Eur J Neurosci. 2021;53(8):2500-2510.
[9] Bao Y, Wang L, Xu Y, et al. Salvianolic acid B inhibits macrophage uptake of modified low density lipoprotein (mLDL) in a scavenger receptor CD36-dependent manner. Atherosclerosis. 2012;223(1):152-159.
[10] Harmon CM, Abumrad NA. Binding of sulfosuccinimidyl fatty acids to adipocyte membrane proteins: isolation and amino-terminal sequence of an 88-kD protein implicated in transport of long-chain fatty acids. J Membr Biol. 1993;133(1):43-49.
[11] Kuda O, Pietka TA, Demianova Z, et al. Sulfo-N-succinimidyl oleate (SSO) inhibits fatty acid uptake and signaling for intracellular calcium via binding CD36 lysine 164: SSO also inhibits oxidized low density lipoprotein uptake by macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(22):15547-15555.
[12] Marleau S, Harb D, Bujold K, et al. EP 80317, a ligand of the CD36 scavenger receptor, protects apolipoprotein E-deficient mice from developing atherosclerotic lesions. FASEB J. 2005;19(13):1869-1871.
团队介绍:
第一作者:冯敏、周强
 #br#
#br#
通讯作者:周松林,医学博士,哈佛大学医学院博士后,南通大学神经再生重点实验室副研究员。长期从事中枢及外周神经损伤与修复研究,发现了一系列调控中枢视神经节细胞及外周背根神经节神经元内在再生能力和轴突再生微环境表型调节的非编码RNA和转录因子。主持国自然4项,以第一作者或通讯作者(含共同)多次在Neuron(封面文章)、J Cell Sci、Exp Neurol(封面文章)、Neurosci Bull、Neuroscience(封面文章)等神经科学高水平期刊发表论文。曾获江苏省“青蓝工程”优秀青年教师,“六大高峰”C类人才项目。
 #br#
#br#
通讯作者:赵剑,博士,现任海军军医大学上海长征医院骨科、脊柱外科教授、主任医师。主持与参加多项国家、省部级科研项目,目前合作国家自然科学基金重点项目1项,主持上海市科委项目2项,近年来以第一作者或通讯作者发表SCI收录论文10多篇。学术任职包括中国医药教育协会血液学专业委员会多发性骨髓瘤外科学组副主任委员、中华医学会医学工程分会第八届委员会数字骨科学组委员、中国残疾人康复协会脊髓损伤康复专业委员会委员、国际脊髓学会中国脊髓损伤学会委员等。同时担任《中国临床解剖学杂志》副主编、《脊柱外科杂志》、《中国矫形外科杂志》编委等。


 #br#
#br#
 #br#
#br#