NRR:长征医院尹又团队提出基于生物材料抗炎治疗阿尔茨海默病的靶向神经炎症策略
撰文:储坚坚,尹又
阿尔茨海默病的病因复杂,其主要病理变化为β淀粉样蛋白沉积、Tau蛋白异常磷酸化以及神经元丢失和突触改变,且发病机制尚未完全确定,可能由多种致病因素、多种通路和分子机制的相互参与引起。目前主流的阿尔茨海默病致病机制假说包括β淀粉样蛋白假说、Tau蛋白假说、衰老假说、线粒体级联假说、血脑屏障功能障碍及脑肠轴的概念等[1-5]。有趣的是,神经炎症可将阿尔茨海默病各个假说相互联系。现有研究已证实,神经炎症与认知障碍密切相关,且贯穿阿尔茨海默病的整个衍变进程,同时炎症会加重阿尔茨海默病的病理负担,从而加速疾病进展[1, 6]。当前治疗阿尔茨海默病的两大类药物胆碱酯酶抑制剂和N-甲基-D-天门冬氨酸受体拮抗剂,均能在一定程度上改善患者的临床表现,但却不能终止或者逆转疾病进程。一直以来,研究者专注于通过减轻或逆转阿尔茨海默病的病理变化来达到疾病修饰治疗的目的。Aducanumab和Lecanemab是仅有的2种美国食品药品监督管理局批准的β淀粉样蛋白单抗类药物,但是其安全性和有效性仍未得到一致认可。
来自中国长征医院尹又团队在《中国神经再生研究(英文版)》(Neural Regeneration Research)上发表了题为“Biomaterials-based anti-inflammatory treatment strategies for Alzheimer’s disease”的综述,回顾了炎症与各种阿尔茨海默病致病假说的关系,认为神经炎症贯穿阿尔茨海默病的整个疾病衍变进程,且炎症会加重阿尔茨海默病的病理负担从而加速疾病进展(图1),同时回顾了小分子药物(非甾体类抗炎药、神经类固醇、植物提取物等)到大分子药物(多肽/蛋白、基因药物)改善神经炎症后进而对阿尔茨海默病的有益影响,并介绍了基于纳米载体的抗炎治疗如何进一步提升阿尔茨海默病的治疗效果,展望了基于纳米载体的抗炎策略在阿尔茨海默病治疗的未来发展。这一综述认为,对抗神经炎症是阿尔茨海默病治疗的非常有潜力的手段,纳米载体对提升阿尔茨海默病的抗炎治疗起到关键的作用。
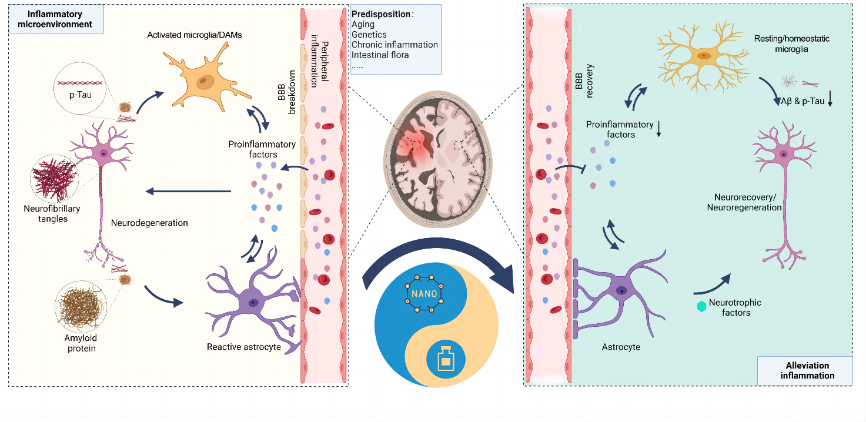
图1基于纳米载体的抗炎治疗可改善阿尔茨海默病患者的炎症微环境(图源:Chu et al., Neural Regen Res, 2023)
当前并无能阻止或逆转阿尔茨海默病的方法。最近几十年,炎症在阿尔茨海默病的发病机制中受到越来越多的关注,多种抗炎治疗药物也在实验中证实了改善阿尔茨海默病的潜力。当前阿尔茨海默病的抗炎治疗主要集中在小分子药物如非甾体类抗炎药、天然植物提取物、神经类固醇和调节肠道菌群等,而大分子治疗药物如单克隆抗体和基因类药物则是最新的研究热点。然而,鉴于阿尔茨海默病炎症机制的复杂程度,尚无单一的抗炎药物能完全改善阿尔茨海默病所有的炎性变化。在充分揭示阿尔茨海默病炎症机制的基础上,并对比不同药物的优势与不足,可从靶向不同炎症通路的药物的联合使用或者开发出具有多种抗炎机制的药物中寻找新的方向,同时植物提取物以及联合用药可能是很有潜力的方法。此外,抗炎治疗的介入时机也十分重要。许多证据表明,早期急性炎症对于阿尔茨海默病是有益的。因此认为,阿尔茨海默病病情的进展可被视为尝试恢复组织稳态的急性炎症的清除功能的失败和疾病触发因素持续存在的结果。因此对于确诊阿尔茨海默病的患者来说,及时的抗炎治疗或许是合适的。未来可在阿尔茨海默病病情评估进一步精确的前提下,能更合理地选择抗炎的介入时机。
由于血脑屏障的存在,绝大部分小分子药物和所有的大分子药物均被阻隔在中枢神经系统之外,这严重阻碍了阿尔茨海默病的治疗。为解决这一问题,可采用纳米载体辅助药物递送,尤其是对于植物提取物和大分子药物而言。各类纳米载体均被证实可增加脂溶性药物的循环稳定性,并在一定程度上提高药物在大脑中的浓度。尤其是经过特殊配体修饰后,纳米载体的体内稳定性和组织相容性进一步增加,且血脑屏障的靶向性和穿透能力显著提高。在改善纳米载体血脑屏障穿透性的基础上,通过多重修饰可实现阿尔茨海默病的精准治疗,即通过特定响应性化学键或次级靶向配体使药物在阿尔茨海默病的炎症微环境或病理改变部位定向释放。
即使基于纳米载体的抗炎治疗目前还处于实验室研究阶段,但是已展现出治疗阿尔茨海默病的广阔前景。除作为载体,部分金属纳米载体如金、氧化铈、硒等和纳米凝胶、纳米乳液等也能产生一定的抗炎或结合β淀粉样蛋白等对阿尔茨海默病治疗有益的作用。纳米载体自身的药理作用还需要更多的研究,并与负载药物发挥治疗阿尔茨海默病的协同作用。此外,鉴于阿尔茨海默病人群的的特殊性,在临床上推荐采用口服方式给药以减轻照料者的负担并获得最大化的社会经济效益,然而文章未充分讨论不同种类纳米制剂的最合适的给药方式,还需总结其他的研究。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.374137
参考文献
[1] Garbuz DG, Zatsepina OG, Evgen'ev MB. Beta amyloid, Tau protein, and neuroinflammation: an attempt to integrate different hypotheses of Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2021;55(5):734-747.
[2] Kritsilis M, S VR, Koutsoudaki PN, et al. Ageing, cellular senescence and neurodegenerative disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(10):2937.
[3] Huang Z, Wong LW, Su Y, et al. Blood-brain barrier integrity in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2020;59:100857.
[4] Rutsch A, Kantsjö JB, Ronchi F. The gut-brain axis: how microbiota and host inflammasome influence brain physiology and pathology. Front Immunol. 2020;11:604179.
[5] Swerdlow RH, Khan SM. The Alzheimer's disease mitochondrial cascade hypothesis: an update. Exp Neurol. 2009;218(2):308-315.
[6] De Oliveira J, Kucharska E, Garcez ML, et al. Inflammatory cascade in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis: a review of experimental findings. Cells. 2021;10(10):2581.
